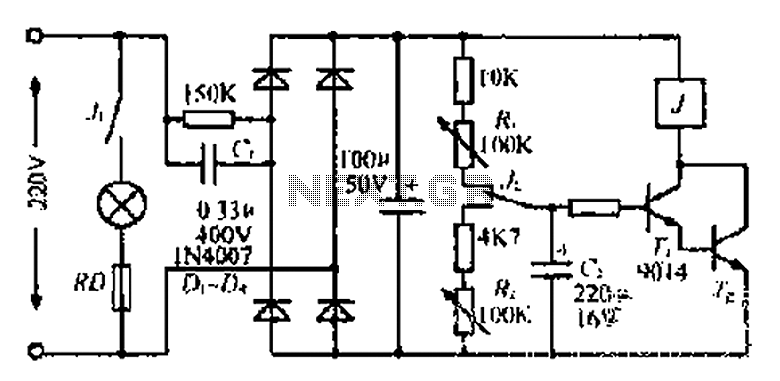
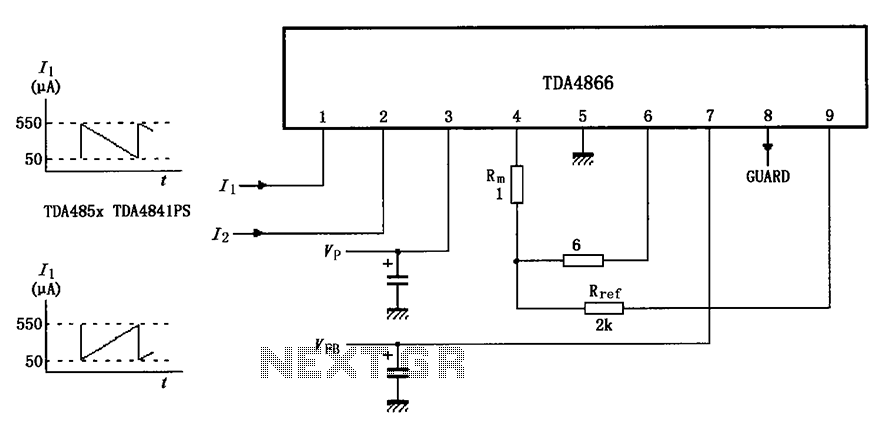
5G169 holiday lights integrated circuit
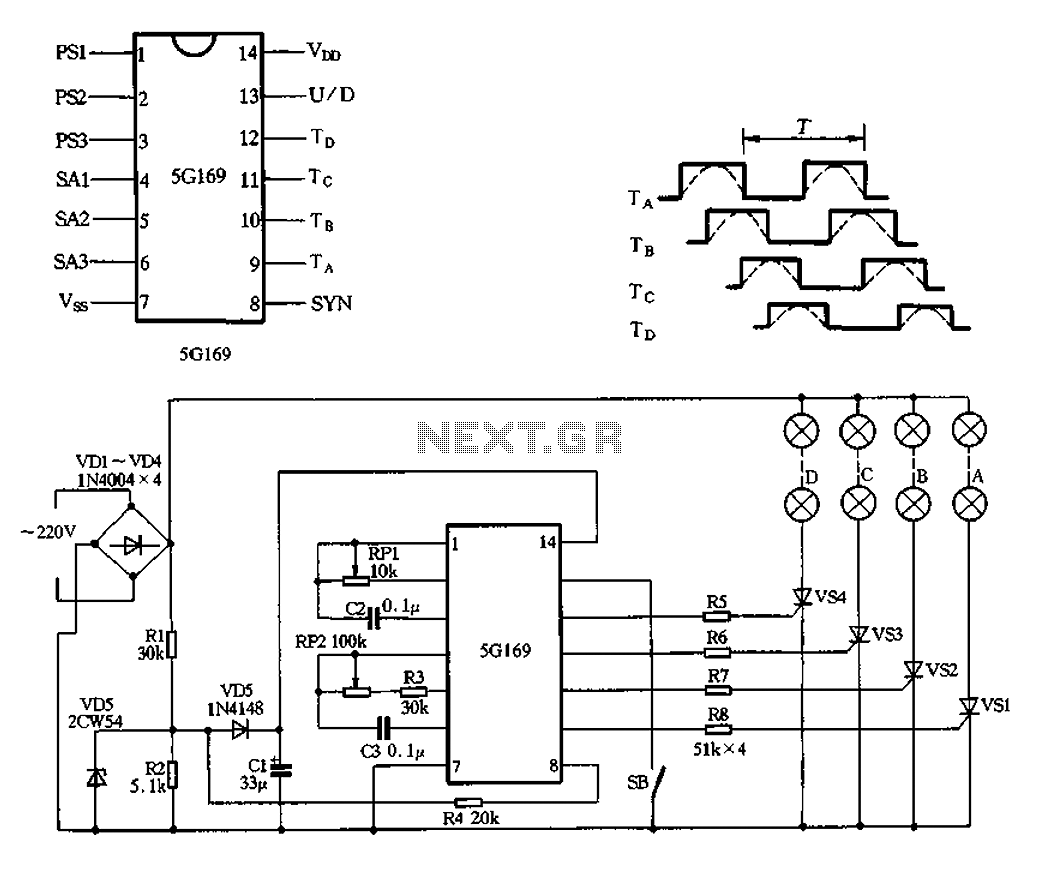
The circuit features an AC input from VDI, which is converted to pulsating DC power using a VD4 full-wave bridge rectifier to power four lights. Resistors R1 and R2, along with diode VD5, form a simple circuit, while VD6 serves as a voltage regulator. Capacitor C1 filters the output to approximately 6V DC. The power supply is designed to manage voltage ripple, which operates at a frequency of 100Hz, twice that of the alternating current input. The signal is synchronized through R4, which injects a synchronization signal into the manifold. Switch SB controls the forward and reverse operation; when open, the circuit operates in positive mode, and when closed, it reverses the circulation. The configuration in Figure 2-102 illustrates the forward loop, with pin outputs 9 to 12. The dashed line denotes the changing arc light levels, which can be adjusted within a range of 100ms to 5s.
The circuit operates by first converting the alternating current (AC) from the VDI source into direct current (DC) using a full-wave bridge rectifier comprised of four diodes, designated as VD4. This rectification process results in a pulsating DC output that is suitable for powering multiple lighting elements. The output voltage is smoothed and regulated by the combination of components R1, R2, VD5, and VD6. Resistors R1 and R2 help in current limiting and voltage division, while VD5 acts as a simple diode to ensure current flows in the correct direction. VD6 is specifically utilized as a voltage regulator, maintaining the output voltage at a stable 6V DC despite variations in the load or input voltage.
Capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in filtering the pulsating DC output, effectively reducing ripple voltage and providing a more stable DC supply. The ripple frequency, which is double the input AC frequency, is noted to be 100Hz. The circuit includes a mechanism for synchronization, achieved through resistor R4, which injects a signal into the power supply manifold to ensure consistent operation across the circuit.
The operation of the circuit can be controlled using switch SB, which toggles between forward and reverse modes. In the forward mode, the switch is open, allowing current to flow in a designated direction. Conversely, closing the switch reverses the current flow, altering the operation of the connected lights. The configuration detailed in Figure 2-102 outlines the forward loop, indicating the pin outputs from 9 to 12, which are integral to the circuit's functionality. The dashed lines in the figure represent the varying arc light levels, which can be adjusted over a period ranging from 100 milliseconds to 5 seconds, providing flexibility in light intensity and timing for the application.AC by VDI ~ VD4 full-wave bridge rectifier output pulsating DC power for four lights. Rl, R2, VD5 simple composition and VD6 regulator circuit, Cl filtered output by about 6V D C power supply manifold. VD6 here isolators, so to get across R2 6V full-wave pulsating direct current voltage ripple frequency of the alternating current to twice that of 100Hz, 100Hz for this signal by R4 injection manifold 8 feet as a synchronization signal. FIG. SB is forward and reverse control switch, SB open cycle is positive; SB closed reverse circulation. Figure 2-102 is the forward loop convolutions 9 to 12-pin output, the dashed line indicates the arc light levels change, period r adjustable range lOOms ~ 5s.
The circuit operates by first converting the alternating current (AC) from the VDI source into direct current (DC) using a full-wave bridge rectifier comprised of four diodes, designated as VD4. This rectification process results in a pulsating DC output that is suitable for powering multiple lighting elements. The output voltage is smoothed and regulated by the combination of components R1, R2, VD5, and VD6. Resistors R1 and R2 help in current limiting and voltage division, while VD5 acts as a simple diode to ensure current flows in the correct direction. VD6 is specifically utilized as a voltage regulator, maintaining the output voltage at a stable 6V DC despite variations in the load or input voltage.
Capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in filtering the pulsating DC output, effectively reducing ripple voltage and providing a more stable DC supply. The ripple frequency, which is double the input AC frequency, is noted to be 100Hz. The circuit includes a mechanism for synchronization, achieved through resistor R4, which injects a signal into the power supply manifold to ensure consistent operation across the circuit.
The operation of the circuit can be controlled using switch SB, which toggles between forward and reverse modes. In the forward mode, the switch is open, allowing current to flow in a designated direction. Conversely, closing the switch reverses the current flow, altering the operation of the connected lights. The configuration detailed in Figure 2-102 outlines the forward loop, indicating the pin outputs from 9 to 12, which are integral to the circuit's functionality. The dashed lines in the figure represent the varying arc light levels, which can be adjusted over a period ranging from 100 milliseconds to 5 seconds, providing flexibility in light intensity and timing for the application.AC by VDI ~ VD4 full-wave bridge rectifier output pulsating DC power for four lights. Rl, R2, VD5 simple composition and VD6 regulator circuit, Cl filtered output by about 6V D C power supply manifold. VD6 here isolators, so to get across R2 6V full-wave pulsating direct current voltage ripple frequency of the alternating current to twice that of 100Hz, 100Hz for this signal by R4 injection manifold 8 feet as a synchronization signal. FIG. SB is forward and reverse control switch, SB open cycle is positive; SB closed reverse circulation. Figure 2-102 is the forward loop convolutions 9 to 12-pin output, the dashed line indicates the arc light levels change, period r adjustable range lOOms ~ 5s.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713