Lantern making use of a relay control circuit
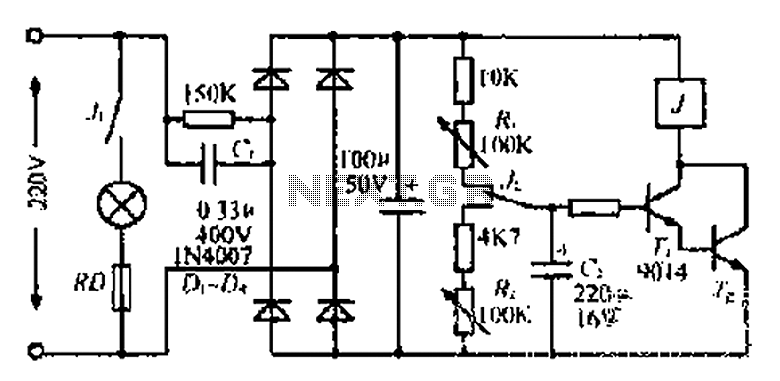
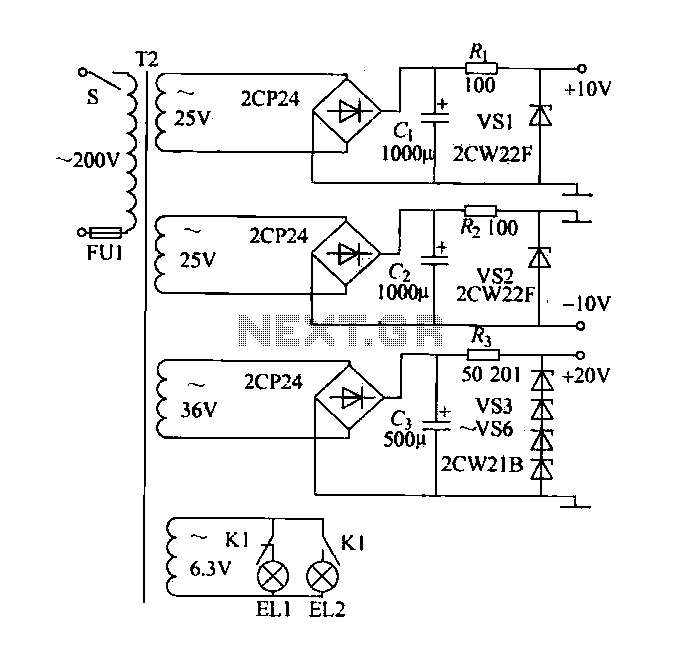
220V mains electricity is sent through a 0.33 µF capacitor (Ci) and a 50 kΩ resistive drop. A bridge rectifier composed of diodes D1 to D4 converts the AC voltage to DC. After passing through a 100 µF capacitor for filtering, the circuit controls a 2V source. When the voltage reaches a certain threshold, the circuit engages various components. If the voltage drops below a certain level, the system disables certain functions, resulting in lights turning off. A 10 kΩ resistor (Ri) is involved in charging a capacitor (C2). The electronic circuit activates at a specific voltage, causing lights to illuminate. At this point, normally closed contacts open, and normally open contacts close, allowing current to flow through a 4.7 kΩ resistor (R) to discharge the capacitor. After a predetermined time, a relay (L2) is deactivated, turning off the lights. A photoelectric sensor (C1) is involved in the operation, which cycles through these processes.
This circuit serves as a power supply and control mechanism for low-voltage lighting systems. The use of a 220V AC mains supply is standard in many regions, and the initial stage of the circuit involves a capacitive dropper to reduce the voltage for safe processing. The 0.33 µF capacitor (Ci) acts as a filtering component, allowing only the AC component to pass through while dropping the voltage to a manageable level.
The bridge rectifier, consisting of four diodes (D1 to D4), converts the incoming AC voltage to DC. This rectification is crucial for powering devices that require a stable DC supply. Following this, the 100 µF capacitor acts as a smoothing capacitor, reducing ripple in the DC output and providing a more stable voltage to the subsequent components.
The control circuit operates at a threshold voltage, which is monitored to ensure proper operation. When the voltage exceeds a certain limit, the circuit engages the lighting system. The 10 kΩ resistor (Ri) plays a role in charging the capacitor (C2), which is essential for the timing and control functions of the system. The operation of the lights is governed by a relay (L2) that is controlled by the state of the contacts, which change based on the voltage levels.
The inclusion of a photoelectric sensor (C1) allows the system to respond to ambient light conditions, potentially enabling automatic on/off functionality based on surrounding light levels. This feature enhances the efficiency of the lighting system, ensuring that lights are only activated when needed.
Overall, this circuit is designed to provide a reliable and efficient means of controlling low-voltage lighting using standard mains electricity, incorporating features such as voltage regulation, timing, and light sensing to optimize performance.220V mains electricity sent through 0.33 u F (Ci). ] 50kn ohmic drop Sui, Di - D4 bridge circuit composed of rectifier. After 100 u F capacitor filter technology,: [born about 2V (iiIU source control circuit skewer beginning Ding ashamed towels, electricity on rG. When the pressure began to ov, save n, Tz off, no suction units, not bright lights In this case the power supply by iOk n electrical resistance, Ri, often just contact charging C2 .Q dagger electronic music rises to a certain extent, the mantle Taiwan, point lights are bright. At this time, normally closed contact off open, normally open contact conduction .c through 4.7k fl resistor, R, discharge and after a predetermined time after .J release L2, lights off .c1 photoelectric again, after a period of time after tI.
a., i died station, colored lights, pocket. such a process may go bite cycle F,
This circuit serves as a power supply and control mechanism for low-voltage lighting systems. The use of a 220V AC mains supply is standard in many regions, and the initial stage of the circuit involves a capacitive dropper to reduce the voltage for safe processing. The 0.33 µF capacitor (Ci) acts as a filtering component, allowing only the AC component to pass through while dropping the voltage to a manageable level.
The bridge rectifier, consisting of four diodes (D1 to D4), converts the incoming AC voltage to DC. This rectification is crucial for powering devices that require a stable DC supply. Following this, the 100 µF capacitor acts as a smoothing capacitor, reducing ripple in the DC output and providing a more stable voltage to the subsequent components.
The control circuit operates at a threshold voltage, which is monitored to ensure proper operation. When the voltage exceeds a certain limit, the circuit engages the lighting system. The 10 kΩ resistor (Ri) plays a role in charging the capacitor (C2), which is essential for the timing and control functions of the system. The operation of the lights is governed by a relay (L2) that is controlled by the state of the contacts, which change based on the voltage levels.
The inclusion of a photoelectric sensor (C1) allows the system to respond to ambient light conditions, potentially enabling automatic on/off functionality based on surrounding light levels. This feature enhances the efficiency of the lighting system, ensuring that lights are only activated when needed.
Overall, this circuit is designed to provide a reliable and efficient means of controlling low-voltage lighting using standard mains electricity, incorporating features such as voltage regulation, timing, and light sensing to optimize performance.220V mains electricity sent through 0.33 u F (Ci). ] 50kn ohmic drop Sui, Di - D4 bridge circuit composed of rectifier. After 100 u F capacitor filter technology,: [born about 2V (iiIU source control circuit skewer beginning Ding ashamed towels, electricity on rG. When the pressure began to ov, save n, Tz off, no suction units, not bright lights In this case the power supply by iOk n electrical resistance, Ri, often just contact charging C2 .Q dagger electronic music rises to a certain extent, the mantle Taiwan, point lights are bright. At this time, normally closed contact off open, normally open contact conduction .c through 4.7k fl resistor, R, discharge and after a predetermined time after .J release L2, lights off .c1 photoelectric again, after a period of time after tI.
a., i died station, colored lights, pocket. such a process may go bite cycle F,