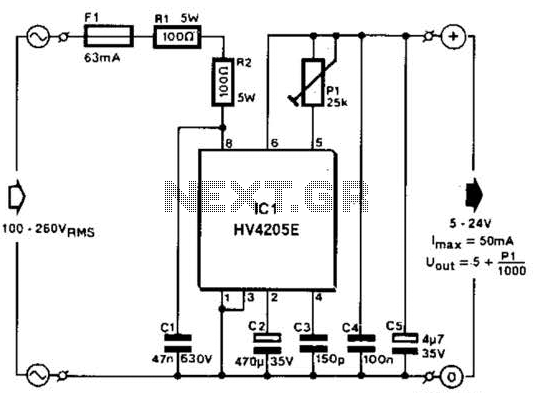
5V Supply High-Side Switcher
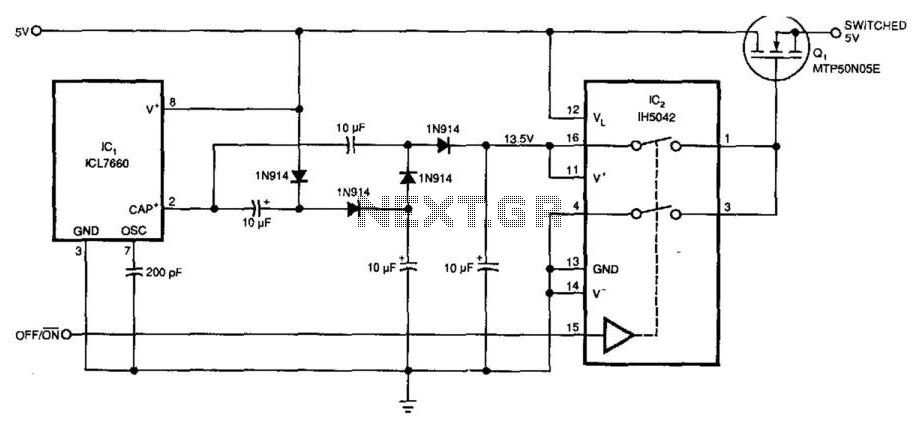
Requiring only 10 µA of quiescent current, the circuit produces an ON-resistance of only 0.1 ohm. IC1 serves as a charge pump voltage converter to generate a 5V level, allowing analog switch IC2 to provide a 10V swing to MOSFET Q1. This configuration utilizes a voltage converter to enable the analog switch to apply a 4.3V swing to the logic level NMOS power transistor Q1, which has a typical ON-resistance of 0.03 ohm. Additional stages in the voltage-multiplying circuit are implemented to achieve a higher gate voltage swing, facilitating the use of a converter for the NMOS switching transistor.
The circuit described operates with a remarkably low quiescent current of 10 µA, making it suitable for applications where power efficiency is critical. The primary component, IC1, functions as a charge pump voltage converter, stepping up the input voltage to a stable 5V. This voltage is essential for the operation of the analog switch IC2, which is responsible for generating a 10V swing necessary for driving the MOSFET Q1.
MOSFET Q1 is a key element in this circuit, acting as a logic level NMOS power transistor. The circuit design allows the analog switch to apply a 4.3V swing to Q1, which is optimized for low ON-resistance, typically around 0.03 ohm. This low resistance is crucial for minimizing power loss during operation, enhancing the efficiency of the overall circuit.
The implementation of additional stages in the voltage-multiplying circuit is a significant feature of this design. These stages increase the gate voltage swing, which is vital for ensuring that the NMOS switching transistor operates effectively. By providing a higher gate voltage, the circuit ensures that the NMOS transistor can switch on and off rapidly, which is essential for high-speed applications.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-engineered design that prioritizes low power consumption and efficient operation, making it suitable for a variety of electronic applications where performance and efficiency are paramount. Requiring only 10uA of quiescent current, the circuit of (Fig. 62-1 (a)) produces only 0.1ohm ON-resis-tance. IC1 is a charge pump voltage converter to produce a 5V level, so analog switch IC2 can provide a 10-V swing to MOSFET Ql. This circuit uses a voltage converter to enable the analog switch to apply a 4.3V swing to logic level NMOS power transistor Q1.
ON resistance is 0.03ohm typical. This circuit uses additional stages in the voltage-multiplying circuit to provide a higher gate voltage swing. This would enable the use of a converter for an NMOS switching transistor. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described operates with a remarkably low quiescent current of 10 µA, making it suitable for applications where power efficiency is critical. The primary component, IC1, functions as a charge pump voltage converter, stepping up the input voltage to a stable 5V. This voltage is essential for the operation of the analog switch IC2, which is responsible for generating a 10V swing necessary for driving the MOSFET Q1.
MOSFET Q1 is a key element in this circuit, acting as a logic level NMOS power transistor. The circuit design allows the analog switch to apply a 4.3V swing to Q1, which is optimized for low ON-resistance, typically around 0.03 ohm. This low resistance is crucial for minimizing power loss during operation, enhancing the efficiency of the overall circuit.
The implementation of additional stages in the voltage-multiplying circuit is a significant feature of this design. These stages increase the gate voltage swing, which is vital for ensuring that the NMOS switching transistor operates effectively. By providing a higher gate voltage, the circuit ensures that the NMOS transistor can switch on and off rapidly, which is essential for high-speed applications.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-engineered design that prioritizes low power consumption and efficient operation, making it suitable for a variety of electronic applications where performance and efficiency are paramount. Requiring only 10uA of quiescent current, the circuit of (Fig. 62-1 (a)) produces only 0.1ohm ON-resis-tance. IC1 is a charge pump voltage converter to produce a 5V level, so analog switch IC2 can provide a 10-V swing to MOSFET Ql. This circuit uses a voltage converter to enable the analog switch to apply a 4.3V swing to logic level NMOS power transistor Q1.
ON resistance is 0.03ohm typical. This circuit uses additional stages in the voltage-multiplying circuit to provide a higher gate voltage swing. This would enable the use of a converter for an NMOS switching transistor. 🔗 External reference