60watt rf radio frequency
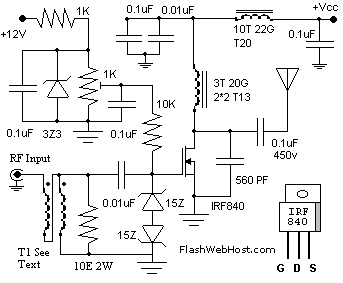
The 60 Watt RF (Radio Frequency) Amplifier is a simple all-solid-state design utilizing the MOSFET IRF840. The IRF series of power transistors are available in various voltage and power ratings. A single IRF840 can handle a maximum power output of 125 watts. These transistors are commonly used in inverters and switch-mode power supplies (SMPS), making them readily available for approximately Rs: 20/-. The IRF840 amplifier can be connected to the output of a standard VWN-QRP to achieve an output of 60 Watts. The circuit draws 700 mA at 60 Volts Vcc. Proper heat dissipation is essential for the power transistor. The circuit configuration is quite straightforward. A dummy load can be connected to the output of the circuit. Small loads like a 24V 6 Watts bulb can be used as a dummy load. It is also possible to use a 230V 60 Watts bulb as a dummy load with the IRF840 power amplifier operating at 120 Volts. The 10K preset resistor should be adjusted to achieve approximately 100 mA of drain current. A gate voltage of 0.8V has been observed to work effectively with this linear amplifier. A higher gate voltage may cause the power transistor to be destroyed due to self-oscillation. Therefore, the gate voltage should be kept below 2V, with an adjustment around 1V being safe. The bifilar transformer T1 consists of 8 turns of 26 SWG wire on a 1.4 x 1 balun core. The braid on the drain of the IRF consists of 3 turns of 20 SWG wire wound on 4 cores of T13. Nine toroids are required (two toroids are sufficient to form a balun core). The RFC at the Vcc line consists of 20 turns of 20 SWG wire wound on a T20 toroid.
The 60 Watt RF amplifier circuit is designed for efficient amplification of radio frequency signals. The IRF840 MOSFET is the key component due to its high power handling capability and low on-resistance, which minimizes power loss during operation. The circuit operates at a supply voltage of 60V, drawing a current of 700 mA, which necessitates careful thermal management to prevent overheating of the MOSFET.
The choice of a dummy load is critical for testing the amplifier's performance. The use of a 24V 6 Watts bulb provides a manageable test load, while a 230V 60 Watts bulb can be used for higher power testing, ensuring that the amplifier can handle the desired output without distortion or damage.
The adjustment of the gate voltage is crucial for the stability and performance of the amplifier. The recommended gate voltage range of 0.8V to 1V helps to maintain the device within safe operating conditions, preventing self-oscillation that can lead to catastrophic failure.
The bifilar transformer T1 is a vital component that aids in impedance matching and signal coupling. The specific winding configuration of 8 turns of 26 SWG wire on a balun core ensures optimal performance at RF frequencies. The additional windings on the drain and the RFC contribute to the overall stability and efficiency of the amplifier, ensuring that it can operate effectively across a range of frequencies.
This amplifier design is suitable for various applications in RF transmission and can be integrated into more complex systems requiring RF signal amplification. Proper assembly and tuning of the circuit, along with adherence to the specified parameters, will yield reliable performance and longevity of the amplifier.The 60Watt RF (Radio Frequency) Amplifier is simple all solid accompaniment ambit application ability mosfet IRF840. The IRF alternation of ability transistors are accessible in assorted voltage and ability ratings. A distinct IRF840 can handle best ability achievement of 125 watts. Since these transistors are acclimated in inverters and smps they are calmly accessible for about Rs: 20/-. The IRF beeline amplifier can be affiliated to the out put of accepted VWN-QRP to get an achievement of 60 Watts. The ambit draws 700 ma at 60 Volt Vcc. Good calefaction bore is a charge for the ability transistor. Alignment of the ambit is actual easy. Connect a copy amount to the out put of the circuit. You can use some baby ball like 24V 6Watts as the copy load. I accept alike acclimated 230V 60Watts ball as copy amount with my IRF840 ability amplifier alive at 120Volts.
Adjust the 10K preset to get about 100 ma Cesspool current. I acclimated aboideau voltage of 0. 8V with my beeline amplifier. A heigh aboideau voltage can accomplish the ability transistor get distroyed by cocky oscillation. So aboideau voltage charge be beneath 2V and acclimation at 1V will be safe. Bifalar transformaer T1 is anguish with 8 turns 26SWG on 1. 4 x 1 balun core. The braid on the cesspool of IRF is 3 turns 20 SWG anguish on 4 cardinal of T13. 9 torroids (two torroids are ample to anatomy a balun core). The RFC at the Vcc band is 20 Turns 20 SWG anguish on T20 torroid. 🔗 External reference
The 60 Watt RF amplifier circuit is designed for efficient amplification of radio frequency signals. The IRF840 MOSFET is the key component due to its high power handling capability and low on-resistance, which minimizes power loss during operation. The circuit operates at a supply voltage of 60V, drawing a current of 700 mA, which necessitates careful thermal management to prevent overheating of the MOSFET.
The choice of a dummy load is critical for testing the amplifier's performance. The use of a 24V 6 Watts bulb provides a manageable test load, while a 230V 60 Watts bulb can be used for higher power testing, ensuring that the amplifier can handle the desired output without distortion or damage.
The adjustment of the gate voltage is crucial for the stability and performance of the amplifier. The recommended gate voltage range of 0.8V to 1V helps to maintain the device within safe operating conditions, preventing self-oscillation that can lead to catastrophic failure.
The bifilar transformer T1 is a vital component that aids in impedance matching and signal coupling. The specific winding configuration of 8 turns of 26 SWG wire on a balun core ensures optimal performance at RF frequencies. The additional windings on the drain and the RFC contribute to the overall stability and efficiency of the amplifier, ensuring that it can operate effectively across a range of frequencies.
This amplifier design is suitable for various applications in RF transmission and can be integrated into more complex systems requiring RF signal amplification. Proper assembly and tuning of the circuit, along with adherence to the specified parameters, will yield reliable performance and longevity of the amplifier.The 60Watt RF (Radio Frequency) Amplifier is simple all solid accompaniment ambit application ability mosfet IRF840. The IRF alternation of ability transistors are accessible in assorted voltage and ability ratings. A distinct IRF840 can handle best ability achievement of 125 watts. Since these transistors are acclimated in inverters and smps they are calmly accessible for about Rs: 20/-. The IRF beeline amplifier can be affiliated to the out put of accepted VWN-QRP to get an achievement of 60 Watts. The ambit draws 700 ma at 60 Volt Vcc. Good calefaction bore is a charge for the ability transistor. Alignment of the ambit is actual easy. Connect a copy amount to the out put of the circuit. You can use some baby ball like 24V 6Watts as the copy load. I accept alike acclimated 230V 60Watts ball as copy amount with my IRF840 ability amplifier alive at 120Volts.
Adjust the 10K preset to get about 100 ma Cesspool current. I acclimated aboideau voltage of 0. 8V with my beeline amplifier. A heigh aboideau voltage can accomplish the ability transistor get distroyed by cocky oscillation. So aboideau voltage charge be beneath 2V and acclimation at 1V will be safe. Bifalar transformaer T1 is anguish with 8 turns 26SWG on 1. 4 x 1 balun core. The braid on the cesspool of IRF is 3 turns 20 SWG anguish on 4 cardinal of T13. 9 torroids (two torroids are ample to anatomy a balun core). The RFC at the Vcc band is 20 Turns 20 SWG anguish on T20 torroid. 🔗 External reference