A circuit diagram of a phase comparator
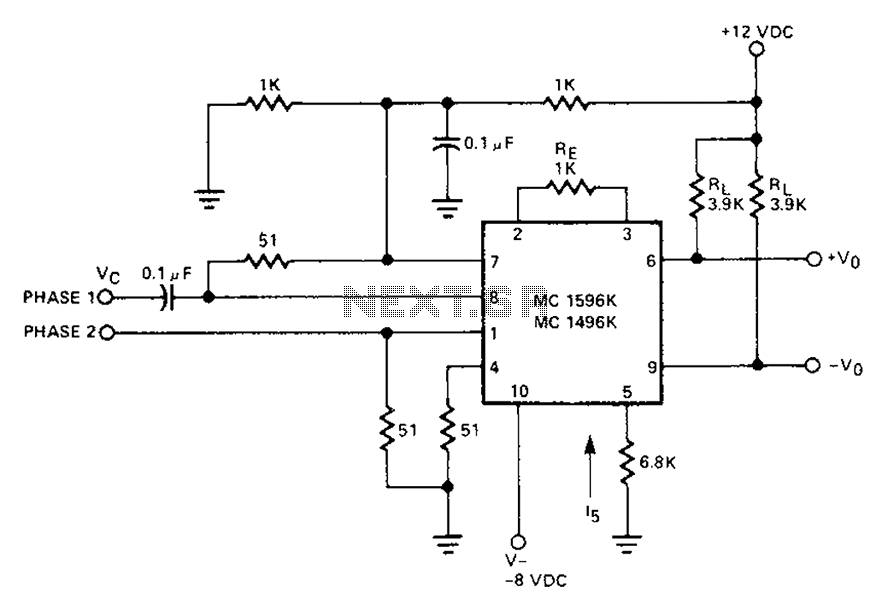
The circuit involves a Signetic balance modem connection utilizing a transistor array as a phase detector. It provides information about the cosine of the phase angle, which corresponds to the frequency of the input signal combined with the integrated circuit (IC), resulting in a total frequency difference. The direct current component derived from this setup becomes a non-essential sum of components linked to the phase angle.
The described circuit employs a Signetic balance modem connection that leverages a transistor array functioning as a phase detector. This arrangement is critical for determining the phase relationship between the input signal and a reference signal. The output of the phase detector is proportional to the cosine of the phase angle, which is indicative of the frequency characteristics of the input signal when processed through the integrated circuit (IC).
In this configuration, the IC generates a total frequency difference, which is the result of the interaction between the input signal and the reference signal. This frequency difference is essential for various applications, including communication systems where phase modulation is utilized. The circuit effectively filters out the direct current (DC) component, which is considered extraneous for the purpose of phase detection. Instead, it focuses on the alternating current (AC) components that are directly related to the phase angle.
The transistor array serves as a crucial element in this circuit, providing the necessary gain and switching capabilities to accurately detect and process the phase information. The arrangement of transistors can be configured to optimize performance, ensuring that the output is a reliable representation of the phase differences present in the input signals.
This phase detector circuit can be integrated into larger communication systems, where precise phase measurements are vital for maintaining signal integrity and synchronization. The ability to extract phase information from the input signals allows for improved modulation schemes and enhances overall system performance. Circuit Description: Signetic balance modem connection transistor array as a phase detector, which contains information about the output of the cosine of the phase angle, equal to the frequency of the input signal plus IC, generating total frequency difference frequency. The difference between the direct current component becomes useless sum of the components associated with the phase angle.
The described circuit employs a Signetic balance modem connection that leverages a transistor array functioning as a phase detector. This arrangement is critical for determining the phase relationship between the input signal and a reference signal. The output of the phase detector is proportional to the cosine of the phase angle, which is indicative of the frequency characteristics of the input signal when processed through the integrated circuit (IC).
In this configuration, the IC generates a total frequency difference, which is the result of the interaction between the input signal and the reference signal. This frequency difference is essential for various applications, including communication systems where phase modulation is utilized. The circuit effectively filters out the direct current (DC) component, which is considered extraneous for the purpose of phase detection. Instead, it focuses on the alternating current (AC) components that are directly related to the phase angle.
The transistor array serves as a crucial element in this circuit, providing the necessary gain and switching capabilities to accurately detect and process the phase information. The arrangement of transistors can be configured to optimize performance, ensuring that the output is a reliable representation of the phase differences present in the input signals.
This phase detector circuit can be integrated into larger communication systems, where precise phase measurements are vital for maintaining signal integrity and synchronization. The ability to extract phase information from the input signals allows for improved modulation schemes and enhances overall system performance. Circuit Description: Signetic balance modem connection transistor array as a phase detector, which contains information about the output of the cosine of the phase angle, equal to the frequency of the input signal plus IC, generating total frequency difference frequency. The difference between the direct current component becomes useless sum of the components associated with the phase angle.