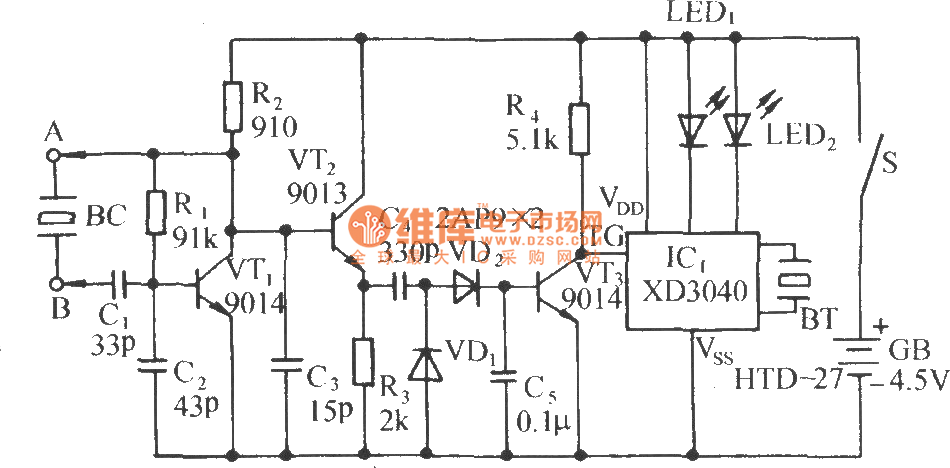
A DC motor reverse brake circuit
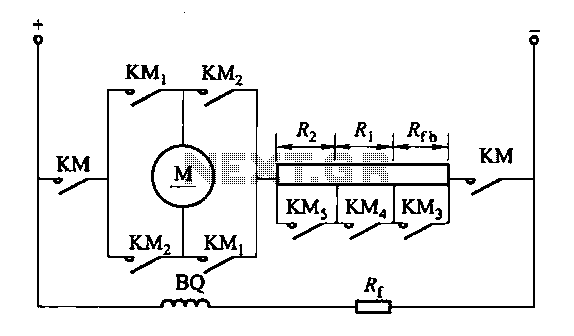
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-200 (a) illustrates the operation of a reverse braking system. When reverse braking is initiated, the forward contacts of contactor KMi open, and the reverse brake contactor KM3 disconnects while the reverse contactor KM2 contacts remain closed. The configuration of the reverse relay KA is shown in Figure 3-200 (h). The reverse relay KA activates when reverse braking begins, connecting the braking resistor Rf to the armature circuit. As the motor speed approaches zero, the reverse braking resistor is shorted. The connection point for the KA relay coil is determined by a resistance value R. This point should equal the total resistance (Rq plus Rf) divided by two. The general pickup voltage setting for the KA relay is typically between 0.4 and 0.45 times the supply voltage (Ue).
The circuit operates by utilizing multiple contactors and relays to manage the reverse braking process efficiently. When the operator engages the reverse braking mechanism, the system ensures that the forward motion is halted by opening the KMi contacts, which prevents any forward current from reaching the motor. Simultaneously, the KM3 contactor is deactivated, effectively isolating the forward drive circuit. The reverse contactor KM2 remains closed, allowing for the necessary current flow to facilitate reverse braking.
The reverse relay KA plays a critical role in this system. It monitors the operational state of the motor and ensures that the braking resistor Rf is introduced into the armature circuit during reverse braking. This resistor serves to dissipate energy generated during the braking process, thus protecting the motor from potential damage due to excessive back EMF. Once the motor speed diminishes to nearly zero, the circuit short-circuits the braking resistor to optimize performance and efficiency, allowing the motor to transition smoothly to a standstill without unnecessary energy loss.
The design stipulates that the resistance value R at the connection point for the KA relay coil should be carefully calculated. This ensures that the total resistance (Rq plus Rf) is halved, providing the correct conditions for the relay to activate reliably. The pickup voltage for the KA relay is set within a range of 0.4 to 0.45 times the supply voltage (Ue), allowing for consistent and dependable operation under varying load conditions. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the relay engages at the appropriate moment during the reverse braking sequence, thereby enhancing the overall safety and effectiveness of the braking system.FIG circuit 3-200 (a) in Fig. When the reverse brake, forward contacts open contacts KMi, reverse brake contactor KM3 contact is disconnected, reverse contactor KM2 contacts ar e closed. Tuning reverse relay KA line shown in Figure 3-200 (h). By reverse relay KA, when the reverse brake open when beginning to reverse braking resistor Rf access armature circuit; and when the brake to the motor speed approaches zero, the reverse braking resistor temple shorted. A connection point KA relay coil by R: resistance value is determined. A point should be the total resistance (Rq ten Rf) at half. KA relay pickup voltage setting in general (0. 4 ~ 0. 45) Ue.
The circuit operates by utilizing multiple contactors and relays to manage the reverse braking process efficiently. When the operator engages the reverse braking mechanism, the system ensures that the forward motion is halted by opening the KMi contacts, which prevents any forward current from reaching the motor. Simultaneously, the KM3 contactor is deactivated, effectively isolating the forward drive circuit. The reverse contactor KM2 remains closed, allowing for the necessary current flow to facilitate reverse braking.
The reverse relay KA plays a critical role in this system. It monitors the operational state of the motor and ensures that the braking resistor Rf is introduced into the armature circuit during reverse braking. This resistor serves to dissipate energy generated during the braking process, thus protecting the motor from potential damage due to excessive back EMF. Once the motor speed diminishes to nearly zero, the circuit short-circuits the braking resistor to optimize performance and efficiency, allowing the motor to transition smoothly to a standstill without unnecessary energy loss.
The design stipulates that the resistance value R at the connection point for the KA relay coil should be carefully calculated. This ensures that the total resistance (Rq plus Rf) is halved, providing the correct conditions for the relay to activate reliably. The pickup voltage for the KA relay is set within a range of 0.4 to 0.45 times the supply voltage (Ue), allowing for consistent and dependable operation under varying load conditions. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the relay engages at the appropriate moment during the reverse braking sequence, thereby enhancing the overall safety and effectiveness of the braking system.FIG circuit 3-200 (a) in Fig. When the reverse brake, forward contacts open contacts KMi, reverse brake contactor KM3 contact is disconnected, reverse contactor KM2 contacts ar e closed. Tuning reverse relay KA line shown in Figure 3-200 (h). By reverse relay KA, when the reverse brake open when beginning to reverse braking resistor Rf access armature circuit; and when the brake to the motor speed approaches zero, the reverse braking resistor temple shorted. A connection point KA relay coil by R: resistance value is determined. A point should be the total resistance (Rq ten Rf) at half. KA relay pickup voltage setting in general (0. 4 ~ 0. 45) Ue.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713