A microcontroller (MCU) is a small computer
A microcontroller (MCU) is a compact computer integrated into a single circuit, comprising a relatively simple CPU along with supporting functions such as crystal oscillators, timers, sensors, and serial and analog input/output (I/O). Microcontrollers are designed for small-scale applications, emphasizing simplicity compared to microprocessors used in personal computers and high-performance tasks. Some microcontrollers can function at clock frequencies as low as 32 kHz, which suffices for certain applications and allows for low power consumption, measured in milliwatts or microwatts. The microcontroller can maintain functionality while waiting for an interrupt, with idle power consumption potentially dropping to nanowatts, making them suitable for applications requiring long-lasting battery life. Microcontrollers are employed in devices with automated and controlled functions, such as automotive engine control systems, remote controls, office machines, electrical equipment, and toys. By minimizing the dimensions and size of the device, costs can be reduced compared to designs utilizing separate microprocessors, memory, and I/O devices, thus making the development of digital devices more economical. The AT89S51 microcontroller belongs to the MCS-51 family and shares the same configuration as the well-known AT89C51. The AT89S51 features In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash Memory, allowing it to be programmed directly within an electronic system without the need for a programmer board. Programming can be performed via an ISP cable connected to a personal computer's parallel port. This feature simplifies the use of the AT89S51 and minimizes the requirement for additional integrated circuits (ICs). The AT89S51 microcontroller has 40 pins and is typically packaged in a Dual Inline Package (DIP). Each pin serves a specific function: Port 0, located on pins 32-39, functions as a versatile I/O port in simple designs, while in more complex designs, it can be multiplexed to the data and address bus for external memory. Port 1, found on pins 1-8, is designated as an I/O port, with specific functions assigned to certain pins, such as P1.5 (motion), P1.6 (MISO), and P1.7 (SCK), which are used for program downloading. Pin 29 serves as an output signal that acts as a control signal, allowing the microcontroller to read programs from external memory. This pin is typically connected to an EPROM. When executing programs from internal ROM or flash memory (Atmel AT89SXX), it remains inactive (high). The ALE output signal on pin 30 functions similarly to the ALE on Intel microprocessors (8085, 8088, or 8086). The ALE signal is demultiplexed for the address and data bus, generating pulses at one-sixth the oscillator frequency, which can be utilized as a general clock. Pin 31 is an input signal that can be at logic low (ground) or logic high (+5 V). A logic high directs the microcontroller to access the program from internal ROM (EPROM/flash memory), whereas a logic low allows access from external memory. The on-chip oscillator is driven by an XTAL connected to pins 18 and 19, requiring a stabilizing capacitor of 30 pF. The XTAL value typically ranges from 3 MHz to 33 MHz. XTAL1 serves as the input for the inverting oscillator amplifier and as the internal clock input for circuit operation.
The AT89S51 microcontroller is a versatile and cost-effective solution for embedded systems, particularly in applications where space and power efficiency are critical. It features a robust architecture that supports a variety of peripheral interfaces, making it suitable for controlling various devices. The ability to program the microcontroller in-system simplifies development and reduces the time required for product iterations.
The pin configuration of the AT89S51 is designed to facilitate easy integration into electronic systems. The dual inline package enhances its compatibility with standard breadboards and circuit boards, promoting ease of prototyping and deployment. The microcontroller's architecture includes built-in timers and serial interfaces, which can be used for communication with other devices, enhancing its functionality in complex applications.
Additionally, the low power consumption characteristics of the AT89S51 make it an ideal choice for battery-operated devices, where longevity is a key requirement. Its capability to operate at low frequencies without sacrificing performance allows it to be utilized in a wide range of applications, from simple control systems to more sophisticated automation tasks.
In summary, the AT89S51 microcontroller represents a powerful, efficient, and flexible component for modern electronic designs, providing essential features that support a broad spectrum of applications while maintaining cost-effectiveness and ease of use.A microcontroller (MCU) is a small computer in a single integrated circuit consisting of a CPU is relatively simple combined with support functions such as crystal oscillators, timers, sensors, serial and analog I / O etc. Microcontroller designed for small applications. Thus, in contrast to microprocessors used in personal computers and high perf ormance applications, simplicity is emphasized. Some microcontrollers can operate at clock frequencies as low as 32KHz, because it sufficient for some applications, and enables low power consumption (miliwatt or microwatts). Microcontroller has the ability to maintain function while waiting for an interrupt; power consumption when idle (CPU clock and peripherals most off) may only nanowatts, so much of a microcontroller suitable for certain applications with battery / power supply that is more durable.
Microcontroller is used for the production of devices with the performance of automatic and controlled according to the function and logic, such as automobile engine control systems, remote controls, office machines, equipment, electrical equipment, and toys. By reducing the dimensions and size of the device then the costs can be reduced compared with a design that uses a separate microprocessor, memory, and input / output devices, microcontroller makes the process of making a digital devices become more economical.
Microcontroller AT89S51 type is MCS-51 microcontroller family with the exact same configuration with a fairly famous AT89C51, AT89S51 has a feature only ISP (In-System Programmable Flash Memory). This feature allows the microcontroller can be programmed directly in an electronic system without going through the Board or Downloader Programmer Board.
Microcontroller can be programmed directly through a cable ISP that is connected to the parallel port on a Personal Computer. With the above features, making use AT89S51 devices become more simple and does not require a lot of support ICs.
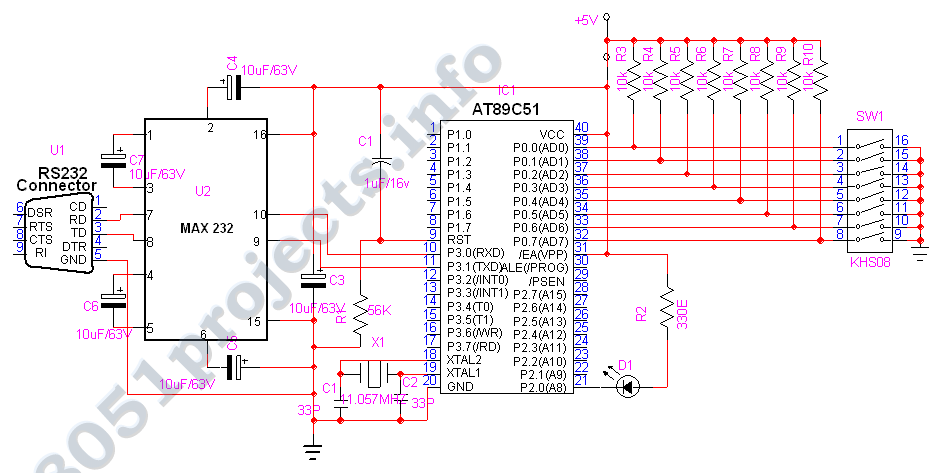
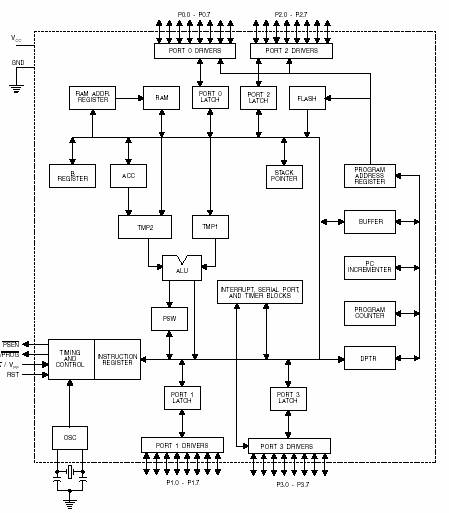
So the microcontroller AT89S51 has a privilege in terms of hardware. The block diagram of the microcontroller 89S51. Microcontroller AT89S51 has a pin numbered 40 and is generally packaged in a DIP (Dual Inline Package). Each pin on the microcontroller AT89S51 has a purpose as follows: Port 0 is port two functions that are on pins 32-39 of the AT89S51.
In a simple system design this port as the port I / O versatile. For a more complex design involving an external memory of this track dimultiplek to the data bus and address bus. Port 1 is reserved as I / O ports and are on pins 1-8. Some of the pins on this port has a specific function of P1. 5 (motion), P1. 6 (MISO), P1. 7 (SCK) is used to track download the program. is an output signal is found on pin 29. Its function is as a control signal to allow the microcontroller to read the program (code) from external memory.
Normally this pin is connected to pin EPROM. If the execution of the program from the internal ROM or from flash memory (Atmel AT89SXX), it is in the inactive state (high). ALE output signal on pin 30 which is the same function with ALE on microprocessor INTEL 8085, 8088 or 8086.
Demultiplek ALE signal is used for bus address and data bus. ALE signals generate pulses of 1 / 6 the oscillator frequency and can be used as a clock that can be used in general. There is signal input on pin 31 which can be logic low (ground) or logic high (+5 V). If given the logic high then the microcontroller will access the program from an internal ROM (EPROM / flash memory).
If given a logic low, the microcontroller will access the program from external memory. Provided on-chip oscillator driven by XTAL is connected to pin 18 and pin 19. Necessary stabilizing capacitor of 30 pF. Great XTAL value of about 3 MHz to 33 MHz. XTAL1 is the input to the reversal of the oscillator amplifier (inverting oscillator amplifier) and an internal clock input to the operation of the circuit. While XTAL2 i 🔗 External reference
The AT89S51 microcontroller is a versatile and cost-effective solution for embedded systems, particularly in applications where space and power efficiency are critical. It features a robust architecture that supports a variety of peripheral interfaces, making it suitable for controlling various devices. The ability to program the microcontroller in-system simplifies development and reduces the time required for product iterations.
The pin configuration of the AT89S51 is designed to facilitate easy integration into electronic systems. The dual inline package enhances its compatibility with standard breadboards and circuit boards, promoting ease of prototyping and deployment. The microcontroller's architecture includes built-in timers and serial interfaces, which can be used for communication with other devices, enhancing its functionality in complex applications.
Additionally, the low power consumption characteristics of the AT89S51 make it an ideal choice for battery-operated devices, where longevity is a key requirement. Its capability to operate at low frequencies without sacrificing performance allows it to be utilized in a wide range of applications, from simple control systems to more sophisticated automation tasks.
In summary, the AT89S51 microcontroller represents a powerful, efficient, and flexible component for modern electronic designs, providing essential features that support a broad spectrum of applications while maintaining cost-effectiveness and ease of use.A microcontroller (MCU) is a small computer in a single integrated circuit consisting of a CPU is relatively simple combined with support functions such as crystal oscillators, timers, sensors, serial and analog I / O etc. Microcontroller designed for small applications. Thus, in contrast to microprocessors used in personal computers and high perf ormance applications, simplicity is emphasized. Some microcontrollers can operate at clock frequencies as low as 32KHz, because it sufficient for some applications, and enables low power consumption (miliwatt or microwatts). Microcontroller has the ability to maintain function while waiting for an interrupt; power consumption when idle (CPU clock and peripherals most off) may only nanowatts, so much of a microcontroller suitable for certain applications with battery / power supply that is more durable.
Microcontroller is used for the production of devices with the performance of automatic and controlled according to the function and logic, such as automobile engine control systems, remote controls, office machines, equipment, electrical equipment, and toys. By reducing the dimensions and size of the device then the costs can be reduced compared with a design that uses a separate microprocessor, memory, and input / output devices, microcontroller makes the process of making a digital devices become more economical.
Microcontroller AT89S51 type is MCS-51 microcontroller family with the exact same configuration with a fairly famous AT89C51, AT89S51 has a feature only ISP (In-System Programmable Flash Memory). This feature allows the microcontroller can be programmed directly in an electronic system without going through the Board or Downloader Programmer Board.
Microcontroller can be programmed directly through a cable ISP that is connected to the parallel port on a Personal Computer. With the above features, making use AT89S51 devices become more simple and does not require a lot of support ICs.
So the microcontroller AT89S51 has a privilege in terms of hardware. The block diagram of the microcontroller 89S51. Microcontroller AT89S51 has a pin numbered 40 and is generally packaged in a DIP (Dual Inline Package). Each pin on the microcontroller AT89S51 has a purpose as follows: Port 0 is port two functions that are on pins 32-39 of the AT89S51.
In a simple system design this port as the port I / O versatile. For a more complex design involving an external memory of this track dimultiplek to the data bus and address bus. Port 1 is reserved as I / O ports and are on pins 1-8. Some of the pins on this port has a specific function of P1. 5 (motion), P1. 6 (MISO), P1. 7 (SCK) is used to track download the program. is an output signal is found on pin 29. Its function is as a control signal to allow the microcontroller to read the program (code) from external memory.
Normally this pin is connected to pin EPROM. If the execution of the program from the internal ROM or from flash memory (Atmel AT89SXX), it is in the inactive state (high). ALE output signal on pin 30 which is the same function with ALE on microprocessor INTEL 8085, 8088 or 8086.
Demultiplek ALE signal is used for bus address and data bus. ALE signals generate pulses of 1 / 6 the oscillator frequency and can be used as a clock that can be used in general. There is signal input on pin 31 which can be logic low (ground) or logic high (+5 V). If given the logic high then the microcontroller will access the program from an internal ROM (EPROM / flash memory).
If given a logic low, the microcontroller will access the program from external memory. Provided on-chip oscillator driven by XTAL is connected to pin 18 and pin 19. Necessary stabilizing capacitor of 30 pF. Great XTAL value of about 3 MHz to 33 MHz. XTAL1 is the input to the reversal of the oscillator amplifier (inverting oscillator amplifier) and an internal clock input to the operation of the circuit. While XTAL2 i 🔗 External reference