A small generator and network control circuit

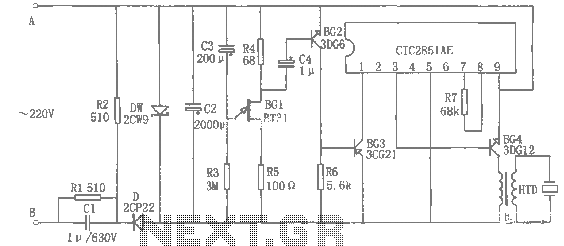
Circle i represents a two-phase grid connection line for an AC technology turbine shed, which consists of two lines. A voltage is generated between Ri through a Buck converter, with components R1 and R3 dividing the output. The sampled level is represented by lK, with voltages being equal. It is known that for a three-phase alternating current generator set, the voltage, frequency, and phase sequence must match the grid. If the AC voltage crosses zero, it indicates the frequency of the grid voltage is closely aligned with the generator set's output frequency. The branch voltage sampled at C251 (pin 2) is compared to the reference voltage at pin 3, which is set at 0.6V. When the voltage at pin 2 exceeds 0.6V, pin 1 outputs -12V, causing C2 to discharge rapidly through diodes Ds and D4. When the voltage at pin 2 drops below 0.6V, pin 1 outputs +12V. The circuit operates similarly to the Aa branch. When the voltage at C251 (pin 1) and pin 7 is high at 12V, the power from the wind turbine begins charging, which is delayed for a certain time. The BGi and BG components conduct, activating the AC contactor units to complete the operational cycle, which is indicated by the LED lighting up. Delay action refers to the sampling circuit voltage being too close to zero for the required duration. If the sampled voltage experiences a double zero crossing or a very short zero-crossing duration, it indicates that conditions are not met. The capacitor Cz charges a small amount before discharging immediately, preventing BGi from activating, and thus preventing grid connection. The W2 component introduces a one-second delay action to 0.5 seconds. The CI component ensures that Hj is activated when the sampled voltage crosses zero, preventing short circuit malfunctions.
The described circuit functions as a control mechanism for a two-phase AC generator connected to a grid. It employs a Buck converter to manage voltage levels, ensuring that the output remains stable and within operational limits. The comparative analysis between sampled voltages at various pins is crucial for maintaining synchronization with the grid. The use of reference voltages allows for precise control of when the output transitions between states, facilitating the generator's connection to the grid.
The circuit's design incorporates safety features, such as the delay mechanisms that prevent premature activation during transient conditions. This ensures that the generator only connects to the grid when all parameters are within acceptable ranges, thus protecting both the generator and the grid infrastructure from potential damage due to mismatched electrical characteristics.
In addition, the LED indicator serves as a visual feedback mechanism, confirming the operational status of the circuit. The inclusion of diodes for rapid discharge indicates a design consideration for managing transient voltages, which can occur during switching operations. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-engineered approach to integrating renewable energy sources into existing electrical grids, emphasizing reliability and safety. Circle i {JA, C two-phase grid connection line. a. c technology turbine shed two lines. A, a voltage between Ri by Buck, convex - Diu chain flow. R., R3. wl dividing aftercrop sampled level lK, C. Voltages c ask the same. We know that the three-phase alternating current generator set voltage, frequency, phase sequence must be the same grid to grid, if Aa. CclbJ voltage zero crossing, then the well pattern oval foot, l asked longer the ugly zero crossing, said the frequency of the grid voltage frequency voltage generator sets out closer, the more this town by the clock network.
Aa branch voltage sampled evacuation C251 (2) feet, and its (3) pin voltage is compared, (3) pin reference voltage is 0.6V. When (2) high-voltage pin F 0.6V. (i) pin output -12v, C2 through Ds, D4 rapid discharge. BGi. 8G2 cut i1.. : When (2) pin voltage is lower than 0.6V, (1) pin + J2V. Cc branch works with Aa branch with the same. When C251 (I) of the foot and (7) feet while high I2V, the power the wind,% c for charging, delay delayed after a certain time.
BGi, BG: conduction, J action, the AC contactor units, just to complete the work well, with the lighting issue when LEDi Well claws.. Delay action means that the sampling circuit voltage is too Bong Lang zero duration to meet the requirements.
If the sampled voltage is instantaneous asked double zero or zero-crossing duration is very short. Review just called to say conditions are not met. Cz electric charge a small amount and then immediately discharge, BGi not be turned on, and therefore can not network. Tone bamboo W2 make J a one second delay action to 0.5. FIG towel CI make Hj is anti Jt sampled voltage over zero when Q is too short circuit malfunction. (Jia-wen)
The described circuit functions as a control mechanism for a two-phase AC generator connected to a grid. It employs a Buck converter to manage voltage levels, ensuring that the output remains stable and within operational limits. The comparative analysis between sampled voltages at various pins is crucial for maintaining synchronization with the grid. The use of reference voltages allows for precise control of when the output transitions between states, facilitating the generator's connection to the grid.
The circuit's design incorporates safety features, such as the delay mechanisms that prevent premature activation during transient conditions. This ensures that the generator only connects to the grid when all parameters are within acceptable ranges, thus protecting both the generator and the grid infrastructure from potential damage due to mismatched electrical characteristics.
In addition, the LED indicator serves as a visual feedback mechanism, confirming the operational status of the circuit. The inclusion of diodes for rapid discharge indicates a design consideration for managing transient voltages, which can occur during switching operations. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-engineered approach to integrating renewable energy sources into existing electrical grids, emphasizing reliability and safety. Circle i {JA, C two-phase grid connection line. a. c technology turbine shed two lines. A, a voltage between Ri by Buck, convex - Diu chain flow. R., R3. wl dividing aftercrop sampled level lK, C. Voltages c ask the same. We know that the three-phase alternating current generator set voltage, frequency, phase sequence must be the same grid to grid, if Aa. CclbJ voltage zero crossing, then the well pattern oval foot, l asked longer the ugly zero crossing, said the frequency of the grid voltage frequency voltage generator sets out closer, the more this town by the clock network.
Aa branch voltage sampled evacuation C251 (2) feet, and its (3) pin voltage is compared, (3) pin reference voltage is 0.6V. When (2) high-voltage pin F 0.6V. (i) pin output -12v, C2 through Ds, D4 rapid discharge. BGi. 8G2 cut i1.. : When (2) pin voltage is lower than 0.6V, (1) pin + J2V. Cc branch works with Aa branch with the same. When C251 (I) of the foot and (7) feet while high I2V, the power the wind,% c for charging, delay delayed after a certain time.
BGi, BG: conduction, J action, the AC contactor units, just to complete the work well, with the lighting issue when LEDi Well claws.. Delay action means that the sampling circuit voltage is too Bong Lang zero duration to meet the requirements.
If the sampled voltage is instantaneous asked double zero or zero-crossing duration is very short. Review just called to say conditions are not met. Cz electric charge a small amount and then immediately discharge, BGi not be turned on, and therefore can not network. Tone bamboo W2 make J a one second delay action to 0.5. FIG towel CI make Hj is anti Jt sampled voltage over zero when Q is too short circuit malfunction. (Jia-wen)