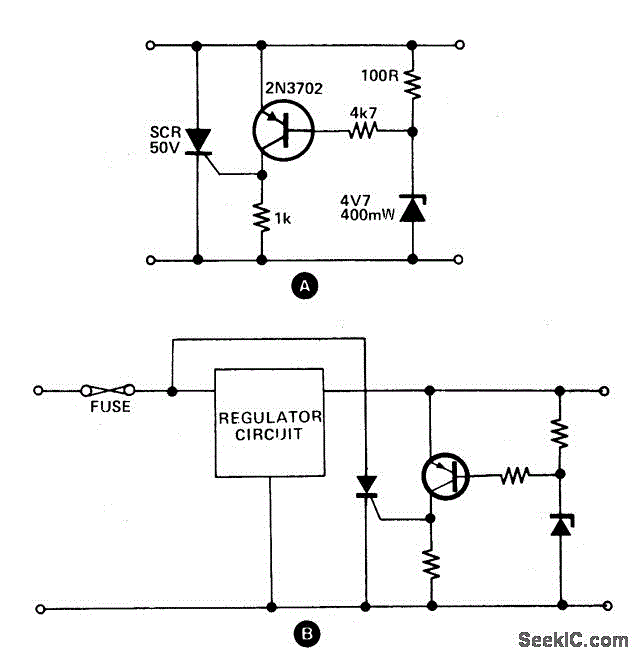
A Typical Crowbar
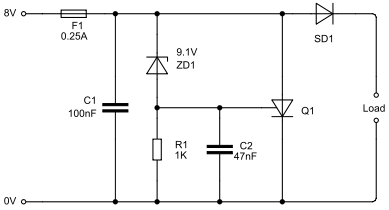
A crowbar circuit is a power supply protection circuit that rapidly short-circuits the supply line if the voltage and/or current exceeds defined limits.
A crowbar circuit serves as an essential protective mechanism in power supply systems. Its primary function is to safeguard sensitive electronic components from overvoltage or overcurrent conditions that could lead to damage or failure. When the voltage or current levels exceed predetermined thresholds, the crowbar circuit activates by creating a low-resistance path to ground, effectively short-circuiting the power supply line. This rapid response helps to prevent excessive power from reaching connected devices.
Typically, a crowbar circuit utilizes components such as thyristors or silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) to achieve this functionality. These components are chosen for their ability to handle high currents and voltages, ensuring reliable operation during fault conditions. The circuit may also include sensing elements, such as voltage dividers or current shunts, to monitor the supply conditions continuously.
In practical applications, the crowbar circuit is often configured with a fuse or circuit breaker in series with the power supply. This additional layer of protection ensures that, in the event of a fault, the fuse will blow or the breaker will trip, disconnecting the power supply and preventing further damage.
Design considerations for a crowbar circuit include the selection of appropriate threshold levels for activation, the response time of the circuit, and the choice of components to ensure compatibility with the overall system voltage and current ratings. Additionally, the layout of the circuit must minimize inductance and resistance to ensure swift operation when a fault condition occurs.
Overall, the crowbar circuit is a crucial element in enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic systems by providing robust protection against electrical anomalies.A crowbar circuit is a power supply protection circuit that rapidly short-circuits ("crowbars") the supply line if the voltage and/or current exceeds defined.. 🔗 External reference
A crowbar circuit serves as an essential protective mechanism in power supply systems. Its primary function is to safeguard sensitive electronic components from overvoltage or overcurrent conditions that could lead to damage or failure. When the voltage or current levels exceed predetermined thresholds, the crowbar circuit activates by creating a low-resistance path to ground, effectively short-circuiting the power supply line. This rapid response helps to prevent excessive power from reaching connected devices.
Typically, a crowbar circuit utilizes components such as thyristors or silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) to achieve this functionality. These components are chosen for their ability to handle high currents and voltages, ensuring reliable operation during fault conditions. The circuit may also include sensing elements, such as voltage dividers or current shunts, to monitor the supply conditions continuously.
In practical applications, the crowbar circuit is often configured with a fuse or circuit breaker in series with the power supply. This additional layer of protection ensures that, in the event of a fault, the fuse will blow or the breaker will trip, disconnecting the power supply and preventing further damage.
Design considerations for a crowbar circuit include the selection of appropriate threshold levels for activation, the response time of the circuit, and the choice of components to ensure compatibility with the overall system voltage and current ratings. Additionally, the layout of the circuit must minimize inductance and resistance to ensure swift operation when a fault condition occurs.
Overall, the crowbar circuit is a crucial element in enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic systems by providing robust protection against electrical anomalies.A crowbar circuit is a power supply protection circuit that rapidly short-circuits ("crowbars") the supply line if the voltage and/or current exceeds defined.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713