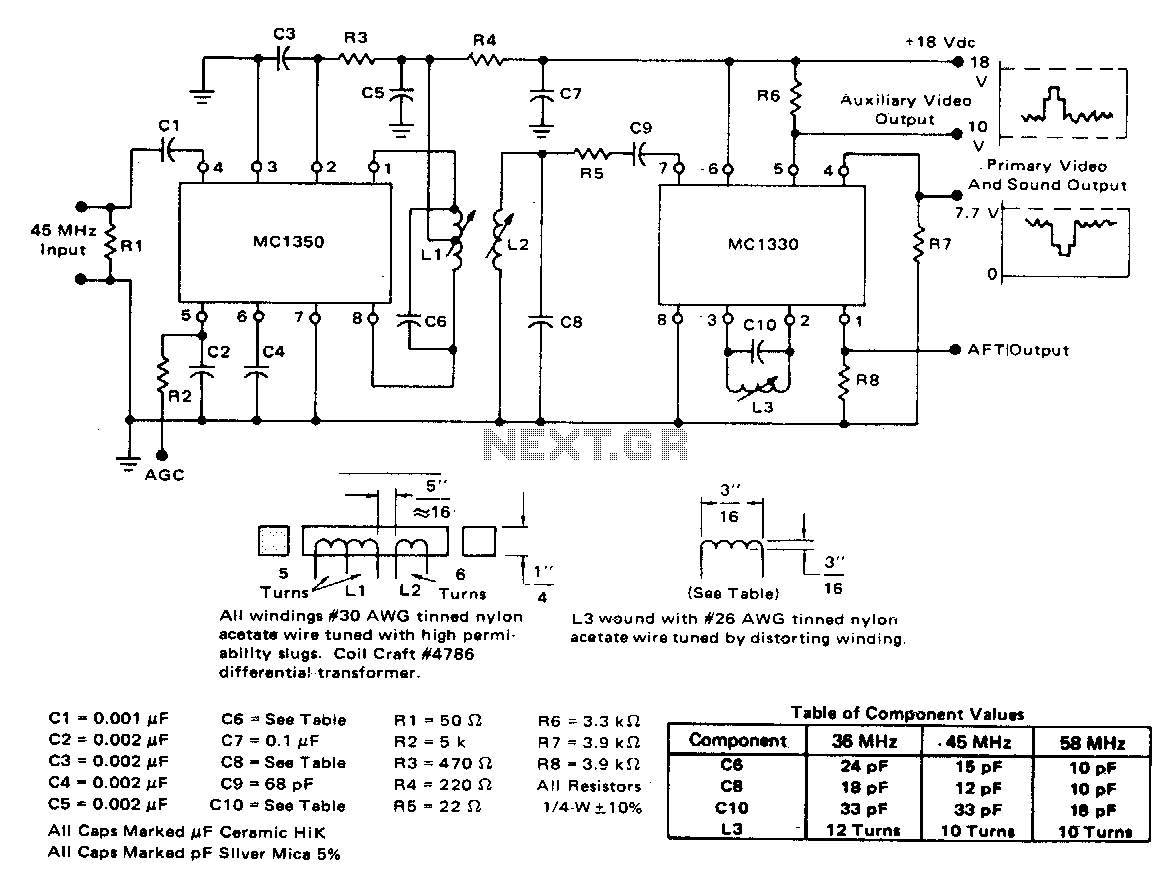
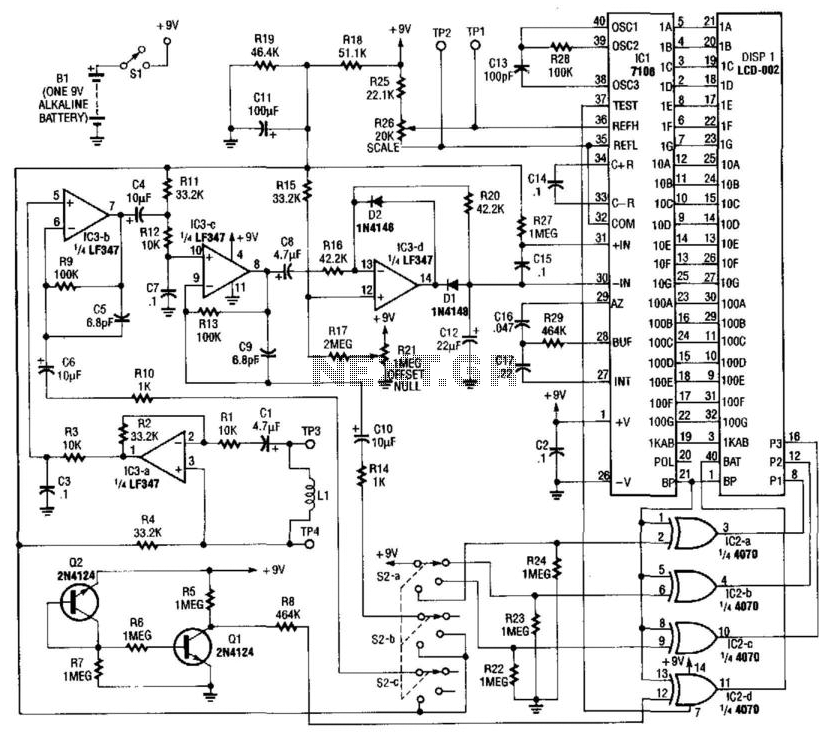
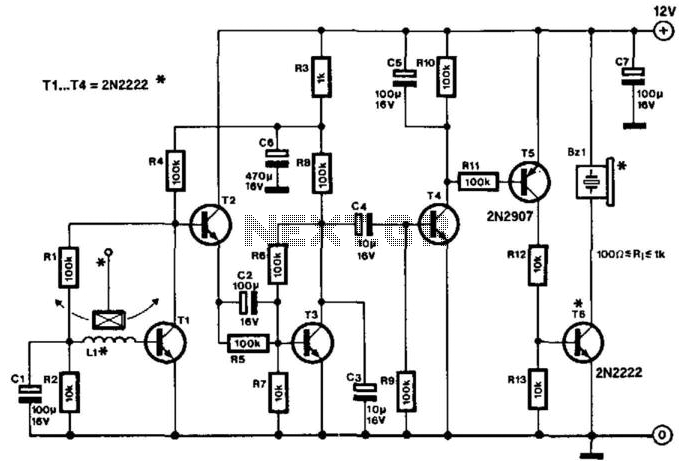
Absolute-Value Meter With Polarity Detector
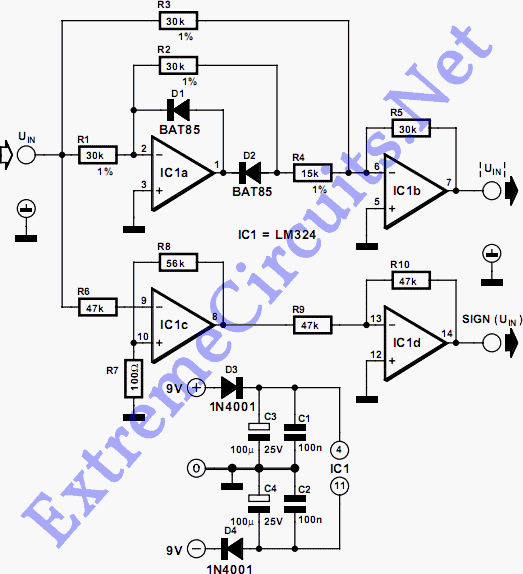
This circuit separates an input voltage signal into its components: (1) the absolute value and (2) the polarity or 'sign' (+ or -). It is designed to handle direct current (DC) signals.
The circuit operates by utilizing operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the desired signal processing. The first stage of the circuit involves rectification, where the absolute value of the input voltage is obtained. This is typically accomplished using a precision rectifier configuration, which allows for accurate rectification of small signals without the voltage drop associated with traditional diodes.
Following the rectification stage, the circuit employs a comparator or a simple logic circuit to determine the polarity of the input voltage. This is achieved by comparing the input signal against a reference voltage, usually set to zero volts. The output of this stage indicates whether the input voltage is positive or negative, thus providing the necessary sign information.
The final output of the circuit consists of two separate signals: one representing the absolute value of the input voltage and the other indicating the polarity. This dual-output configuration can be particularly useful in applications such as analog signal processing, where both the magnitude and direction of the signal are critical for further processing or control tasks.
Overall, this circuit design is fundamental in various electronic applications, including signal conditioning, measurement systems, and control circuits, where precise voltage analysis is required.This circuit breaks an input voltage signal down into its components: (1) the absolute value and (2) the polarity or ‘sign (+ or ). It will handle direc.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the desired signal processing. The first stage of the circuit involves rectification, where the absolute value of the input voltage is obtained. This is typically accomplished using a precision rectifier configuration, which allows for accurate rectification of small signals without the voltage drop associated with traditional diodes.
Following the rectification stage, the circuit employs a comparator or a simple logic circuit to determine the polarity of the input voltage. This is achieved by comparing the input signal against a reference voltage, usually set to zero volts. The output of this stage indicates whether the input voltage is positive or negative, thus providing the necessary sign information.
The final output of the circuit consists of two separate signals: one representing the absolute value of the input voltage and the other indicating the polarity. This dual-output configuration can be particularly useful in applications such as analog signal processing, where both the magnitude and direction of the signal are critical for further processing or control tasks.
Overall, this circuit design is fundamental in various electronic applications, including signal conditioning, measurement systems, and control circuits, where precise voltage analysis is required.This circuit breaks an input voltage signal down into its components: (1) the absolute value and (2) the polarity or ‘sign (+ or ). It will handle direc.. 🔗 External reference