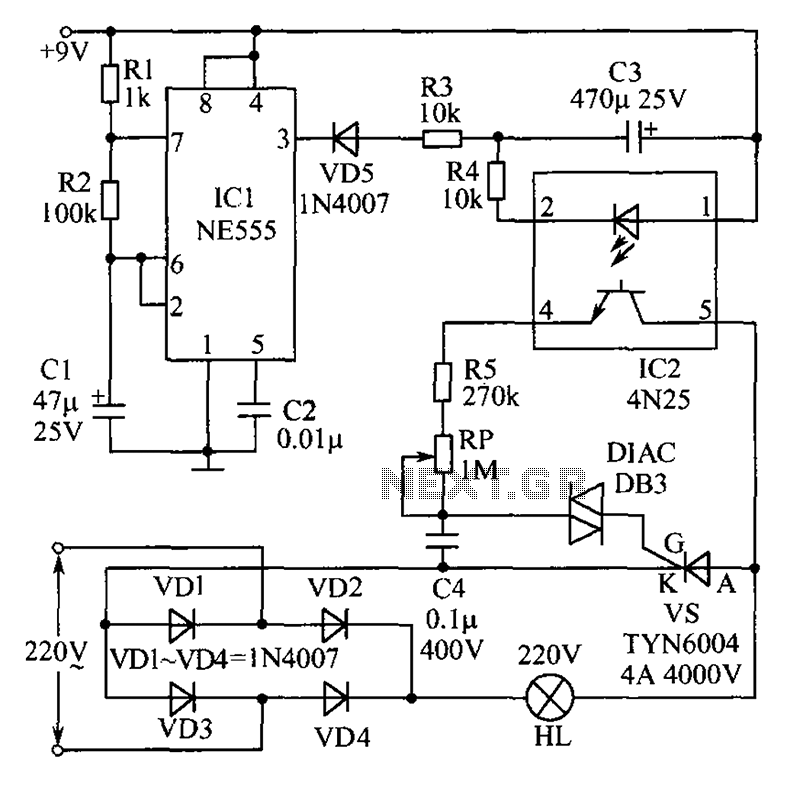
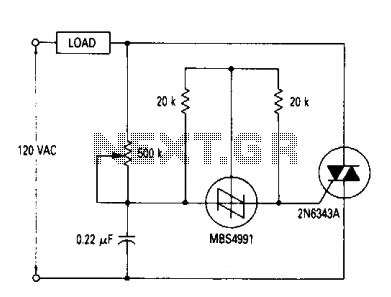
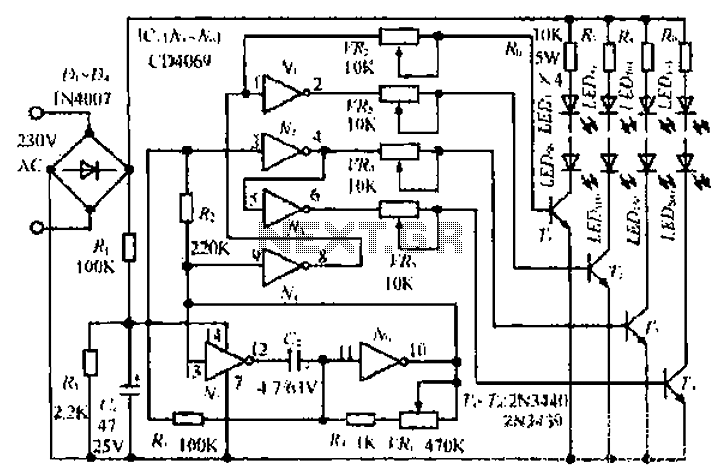
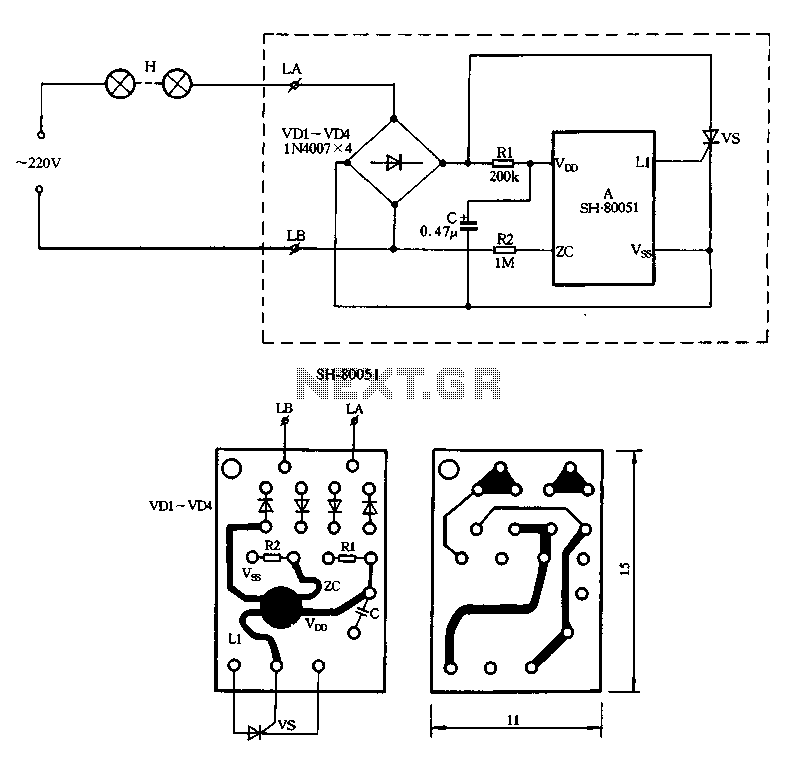
AC lights dimmer with triac
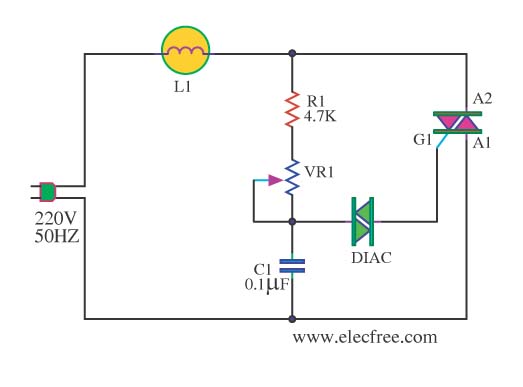
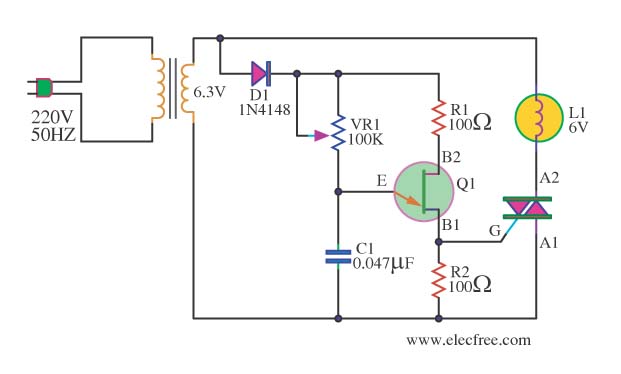
This circuit is designed to dim a light bulb with a maximum power rating of 100W. If the triac experiences high temperatures, it is essential to use a heat sink or allow for adequate heat dissipation. The diac functions as a diode that can be triggered in two different ways, providing bidirectional operation. The variable resistor VR1 is used to finely adjust the level of dimming. It is important to ensure that this circuit is enclosed in a box at all times while electricity is flowing through it. The operation of the circuit allows for the lamp L1 to be dimmed by adjusting the setting of VR1. This adjustment controls the charging speed of capacitor C1, as the triac will activate once C1 has charged to a sufficient voltage. With VR1 set to a lower value, C1 charges more quickly, resulting in a brighter lamp. Conversely, if VR1 is adjusted to a higher value, C1 charges more slowly, causing the lamp to emit a dimmer light. During the operation of the triac, the light bulb will dim according to the setting of VR1. Resistor R1 is included to protect VR1 from damage, while resistors R2 and capacitor C2 are utilized to filter out signal disturbances from both the circuit and external sources.
This circuit employs a triac-based dimmer design, which is commonly used for controlling the brightness of incandescent lamps. The triac is a semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered, allowing for precise control over the power delivered to the light bulb. The diac serves as a triggering device for the triac, ensuring that the triac only conducts when the voltage across C1 reaches a certain threshold. This configuration allows for a smooth dimming effect, as the charge time of C1, which is influenced by the resistance of VR1, determines when the triac will turn on during each AC cycle.
The variable resistor VR1 is critical for fine-tuning the dimming effect. By adjusting VR1, the user can change the resistance in the circuit, which directly affects the charging rate of C1. A lower resistance allows C1 to charge more quickly, leading to more frequent triggering of the triac and a brighter light output. Conversely, a higher resistance results in slower charging of C1, reducing the frequency of triac triggering and dimming the light.
Resistor R1 plays a protective role by limiting the current flowing through VR1, thereby preventing potential damage due to excessive current. The additional components, R2 and C2, are included to mitigate noise and signal disturbances that may arise from external sources or from the circuit itself. This filtering ensures stable operation and improves the overall performance of the dimmer circuit.
To enhance safety and reliability, the entire circuit should be housed in a suitable enclosure, preventing accidental contact with live components and ensuring that it operates safely under normal conditions. Proper heat management is also crucial; if the triac operates at high temperatures, the inclusion of a heat sink is recommended to dissipate heat effectively and prolong the lifespan of the device.This circuit has can to turn down a light bulb arrives at 100W. If Triac there is tall temperature should hold Heat Sink or let off the heat. The Diac be diode that perform be formed encourage or Trigger Diode 2 kinds are way or Bidirectional. The VR1 use for fine decorate turning down fire. Caution this circuit must is in a box closes all the tim e that have the electricity flows through. Operation of the circuit be Lamp L1 is adjusted by adjusting the light of VR1. This will serve to control the speed of charging of C1, Because triac will work. When C1 has charged to the voltage at the triac work. When adjusting the VR1 C1 will charge as little faster lamp is lit. If the adjustment of VR1 C1 will charge very slowly. The little light bulb. Because the triac does not work over the triac during the work. The light bulb will dim down by adjusting VR1. The R1 is placed for protection VR1 prevent damage. The R2, C2 is used to eliminate signal disturbance. Both produced and external circuit. 🔗 External reference
This circuit employs a triac-based dimmer design, which is commonly used for controlling the brightness of incandescent lamps. The triac is a semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered, allowing for precise control over the power delivered to the light bulb. The diac serves as a triggering device for the triac, ensuring that the triac only conducts when the voltage across C1 reaches a certain threshold. This configuration allows for a smooth dimming effect, as the charge time of C1, which is influenced by the resistance of VR1, determines when the triac will turn on during each AC cycle.
The variable resistor VR1 is critical for fine-tuning the dimming effect. By adjusting VR1, the user can change the resistance in the circuit, which directly affects the charging rate of C1. A lower resistance allows C1 to charge more quickly, leading to more frequent triggering of the triac and a brighter light output. Conversely, a higher resistance results in slower charging of C1, reducing the frequency of triac triggering and dimming the light.
Resistor R1 plays a protective role by limiting the current flowing through VR1, thereby preventing potential damage due to excessive current. The additional components, R2 and C2, are included to mitigate noise and signal disturbances that may arise from external sources or from the circuit itself. This filtering ensures stable operation and improves the overall performance of the dimmer circuit.
To enhance safety and reliability, the entire circuit should be housed in a suitable enclosure, preventing accidental contact with live components and ensuring that it operates safely under normal conditions. Proper heat management is also crucial; if the triac operates at high temperatures, the inclusion of a heat sink is recommended to dissipate heat effectively and prolong the lifespan of the device.This circuit has can to turn down a light bulb arrives at 100W. If Triac there is tall temperature should hold Heat Sink or let off the heat. The Diac be diode that perform be formed encourage or Trigger Diode 2 kinds are way or Bidirectional. The VR1 use for fine decorate turning down fire. Caution this circuit must is in a box closes all the tim e that have the electricity flows through. Operation of the circuit be Lamp L1 is adjusted by adjusting the light of VR1. This will serve to control the speed of charging of C1, Because triac will work. When C1 has charged to the voltage at the triac work. When adjusting the VR1 C1 will charge as little faster lamp is lit. If the adjustment of VR1 C1 will charge very slowly. The little light bulb. Because the triac does not work over the triac during the work. The light bulb will dim down by adjusting VR1. The R1 is placed for protection VR1 prevent damage. The R2, C2 is used to eliminate signal disturbance. Both produced and external circuit. 🔗 External reference