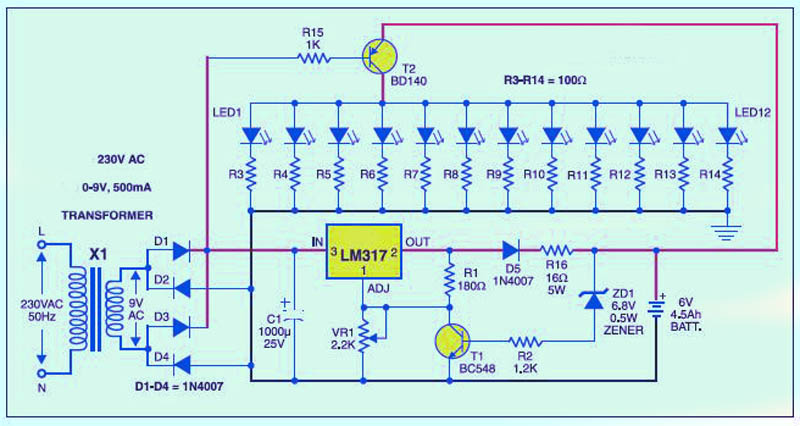
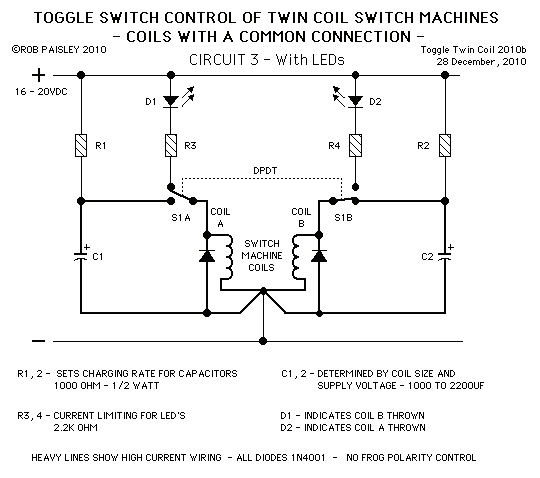
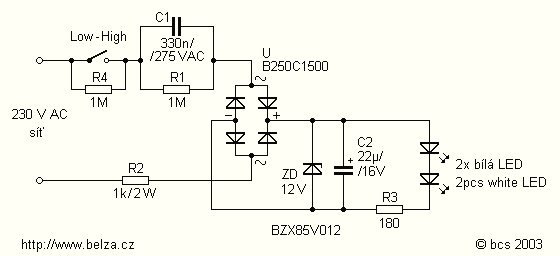
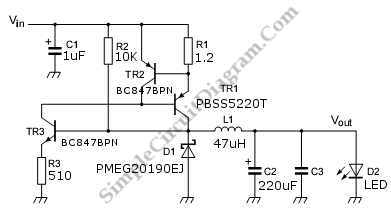
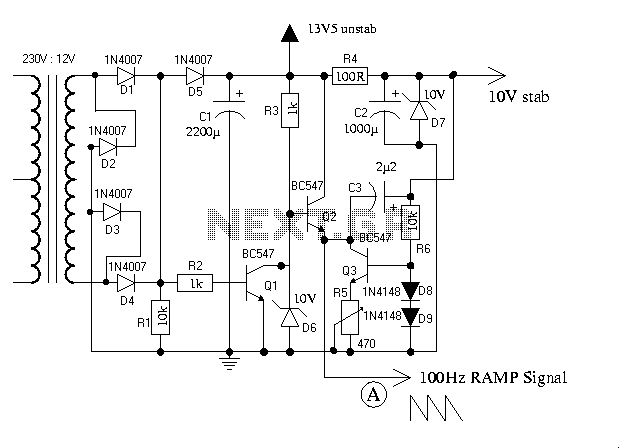
Adjustable light detection switch
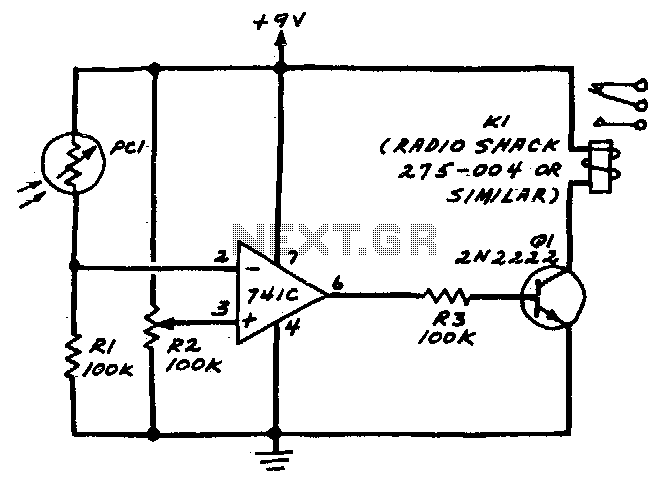
R2 sets the circuit's threshold. When the light intensity at the PCI's surface decreases, the resistance of PCI, a cadmium-sulfide photo-resistor, increases. This results in a decrease in voltage at the inverting input of the 741 operational amplifier. When the reference voltage at the non-inverting input of the 741 is appropriately adjusted via R2, the comparator transitions from a low to a high state when the PCI is darkened. This action activates Q1, which subsequently energizes relay K1.
The circuit described involves a light-sensitive control mechanism utilizing a cadmium-sulfide photo-resistor (PCI) as the primary sensing element. The resistance of the photo-resistor varies inversely with light intensity; as the light level diminishes, the resistance increases. This change in resistance alters the voltage at the inverting input of the operational amplifier (741), which functions as a comparator.
R2 is critical in establishing the threshold voltage at the non-inverting input of the 741. By adjusting R2, the reference voltage can be fine-tuned to ensure that the comparator responds accurately to the desired light level. When the light intensity drops below this threshold, the voltage at the inverting input decreases sufficiently to cause the output of the 741 to switch from a low state to a high state.
The output of the operational amplifier is connected to a transistor (Q1), which acts as a switch to control a relay (K1). When the output of the 741 transitions to high, Q1 is turned on, allowing current to flow through the relay coil. This energizes the relay, which can be used to control larger loads or activate other circuits based on the light sensing condition.
This configuration is commonly used in applications such as automatic lighting systems, where the circuit can turn lights on or off based on ambient light levels, providing an efficient and responsive control mechanism.R2 sets the circuit"s threshold. When the light intensity at PCI"s surface is decreased, the resistance of PCI a cadmium-sulfide photo-resistor is increased. This decreases the voltage at the inverting input of the 741. When the reference voltage at the 741"s noninverting input is properly adjusted via R2, the comparator will switch from low to high when PCI is darkened
This turns on Q1 which, in turn, pulls in relay Kl.
The circuit described involves a light-sensitive control mechanism utilizing a cadmium-sulfide photo-resistor (PCI) as the primary sensing element. The resistance of the photo-resistor varies inversely with light intensity; as the light level diminishes, the resistance increases. This change in resistance alters the voltage at the inverting input of the operational amplifier (741), which functions as a comparator.
R2 is critical in establishing the threshold voltage at the non-inverting input of the 741. By adjusting R2, the reference voltage can be fine-tuned to ensure that the comparator responds accurately to the desired light level. When the light intensity drops below this threshold, the voltage at the inverting input decreases sufficiently to cause the output of the 741 to switch from a low state to a high state.
The output of the operational amplifier is connected to a transistor (Q1), which acts as a switch to control a relay (K1). When the output of the 741 transitions to high, Q1 is turned on, allowing current to flow through the relay coil. This energizes the relay, which can be used to control larger loads or activate other circuits based on the light sensing condition.
This configuration is commonly used in applications such as automatic lighting systems, where the circuit can turn lights on or off based on ambient light levels, providing an efficient and responsive control mechanism.R2 sets the circuit"s threshold. When the light intensity at PCI"s surface is decreased, the resistance of PCI a cadmium-sulfide photo-resistor is increased. This decreases the voltage at the inverting input of the 741. When the reference voltage at the 741"s noninverting input is properly adjusted via R2, the comparator will switch from low to high when PCI is darkened
This turns on Q1 which, in turn, pulls in relay Kl.