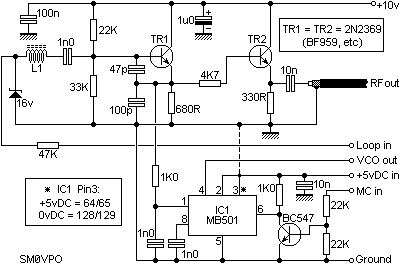
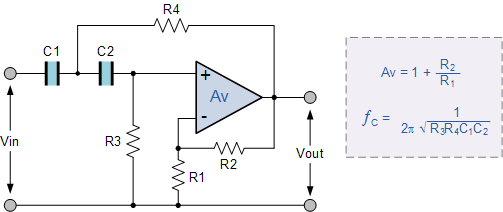
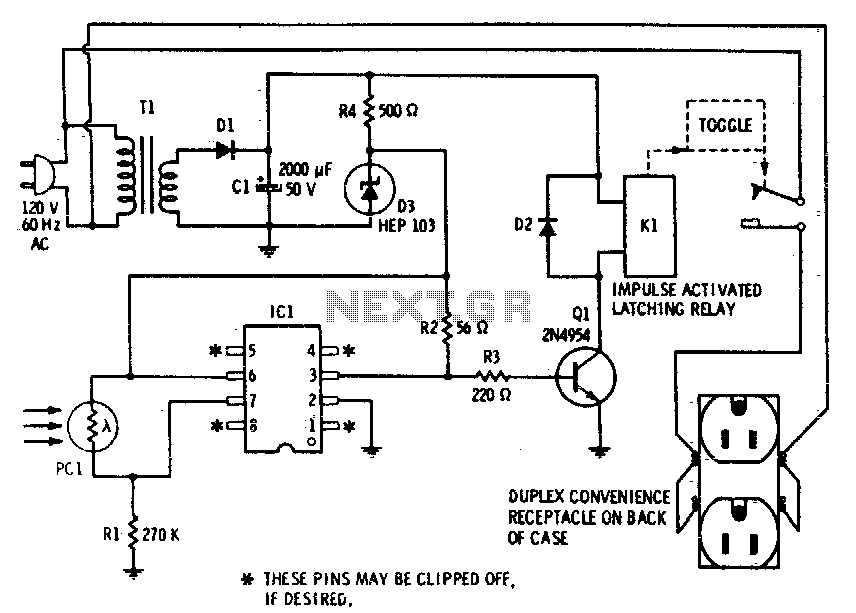
Discrete High Current Switch Mode LED Driver
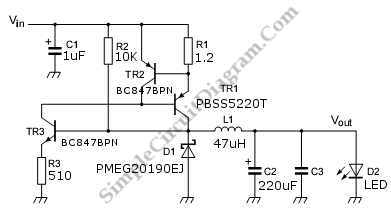
This is a discrete high-current switch-mode LED driver circuit. The fundamental principle of this circuit is based on the buck-converter topology. The efficiency of this circuit is 80%.
The discrete high-current switch-mode LED driver circuit utilizes a buck converter configuration to efficiently regulate the output current supplied to the LED load. The buck converter is designed to step down the input voltage while maintaining high efficiency, which is particularly important in LED applications where thermal management and power consumption are critical.
The circuit typically consists of a power switch (usually a MOSFET), an inductor, a diode, and output capacitors. The MOSFET operates as a switch, rapidly turning on and off to control the energy transferred to the inductor. When the MOSFET is turned on, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch turns off, the inductor releases its stored energy to the load through the diode, ensuring a continuous current flow to the LEDs.
The output current can be regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal controlling the MOSFET. This is achieved using a feedback mechanism that monitors the output current and adjusts the duty cycle accordingly to maintain the desired current level. The efficiency of the circuit, reported at 80%, indicates that 80% of the input power is effectively converted into output power, with the remaining 20% lost as heat, primarily in the switching elements and passive components.
To enhance performance, proper selection of the inductor and capacitors is crucial. The inductor must have a suitable current rating and low DC resistance to minimize losses. Output capacitors should have low equivalent series resistance (ESR) to reduce ripple voltage and improve stability.
Thermal management is also essential, as high currents can generate significant heat within the components. Adequate heat sinking or thermal vias may be required to ensure reliable operation. Overall, this circuit design is well-suited for applications requiring efficient LED driving with high current capabilities.This is a discrete high current switch mode LED driver circuit. The basics of this circuit is a buck-converter principle. The efficiency of this circuit is 80.. 🔗 External reference
The discrete high-current switch-mode LED driver circuit utilizes a buck converter configuration to efficiently regulate the output current supplied to the LED load. The buck converter is designed to step down the input voltage while maintaining high efficiency, which is particularly important in LED applications where thermal management and power consumption are critical.
The circuit typically consists of a power switch (usually a MOSFET), an inductor, a diode, and output capacitors. The MOSFET operates as a switch, rapidly turning on and off to control the energy transferred to the inductor. When the MOSFET is turned on, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch turns off, the inductor releases its stored energy to the load through the diode, ensuring a continuous current flow to the LEDs.
The output current can be regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal controlling the MOSFET. This is achieved using a feedback mechanism that monitors the output current and adjusts the duty cycle accordingly to maintain the desired current level. The efficiency of the circuit, reported at 80%, indicates that 80% of the input power is effectively converted into output power, with the remaining 20% lost as heat, primarily in the switching elements and passive components.
To enhance performance, proper selection of the inductor and capacitors is crucial. The inductor must have a suitable current rating and low DC resistance to minimize losses. Output capacitors should have low equivalent series resistance (ESR) to reduce ripple voltage and improve stability.
Thermal management is also essential, as high currents can generate significant heat within the components. Adequate heat sinking or thermal vias may be required to ensure reliable operation. Overall, this circuit design is well-suited for applications requiring efficient LED driving with high current capabilities.This is a discrete high current switch mode LED driver circuit. The basics of this circuit is a buck-converter principle. The efficiency of this circuit is 80.. 🔗 External reference