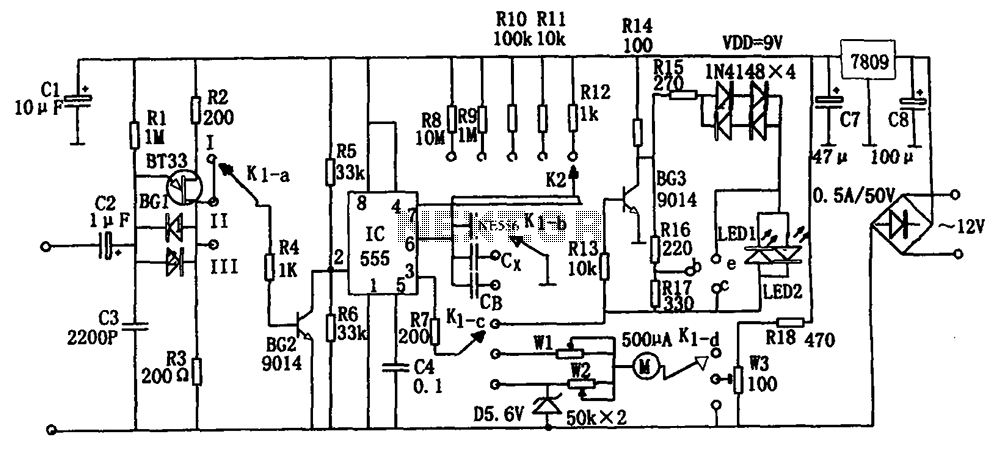
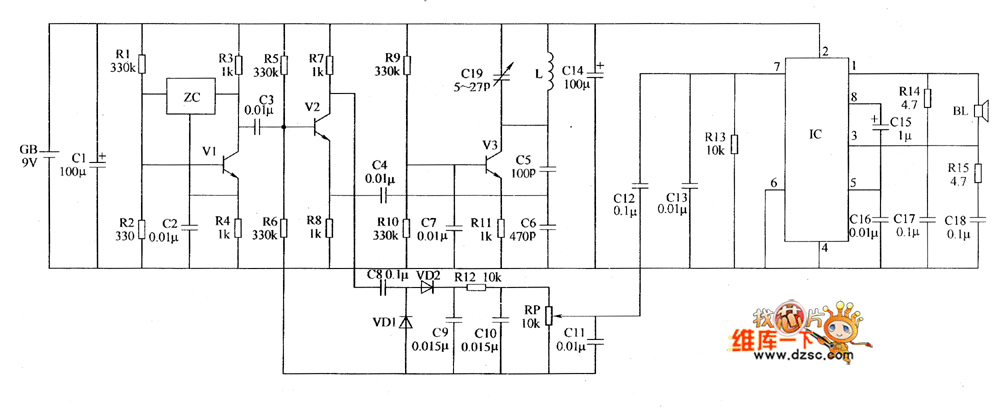
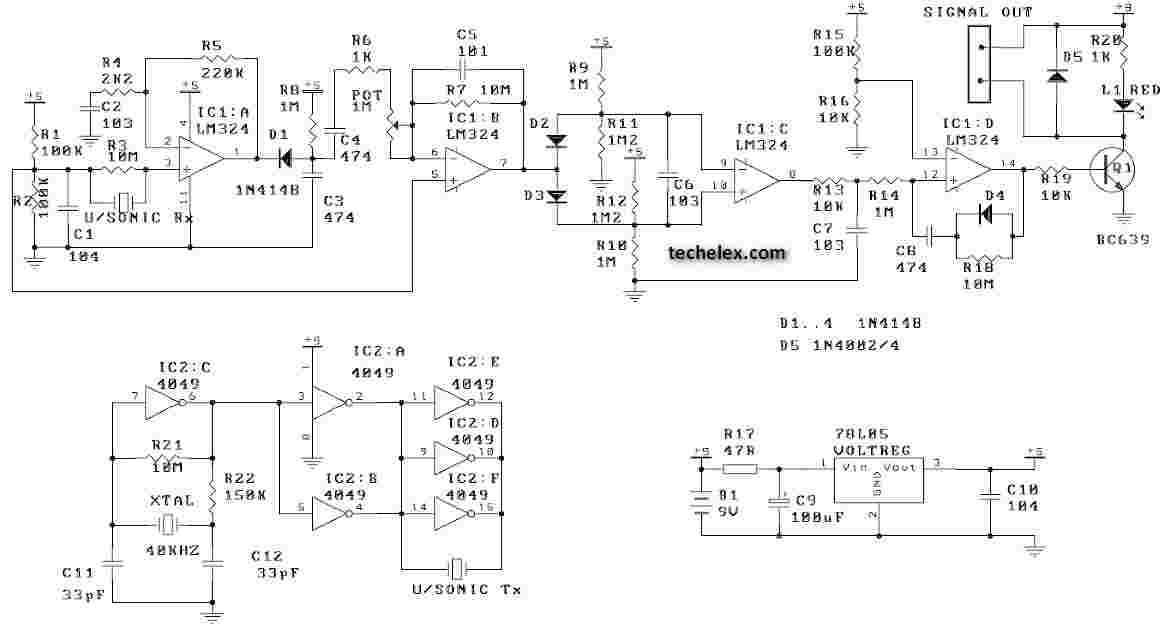
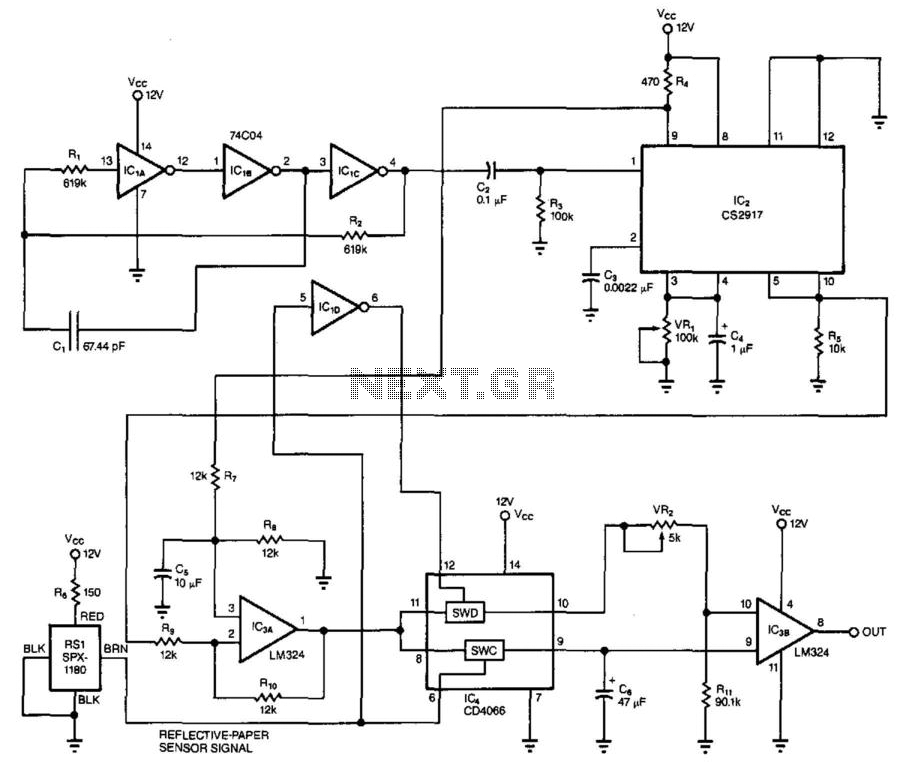
Air Flow Detector
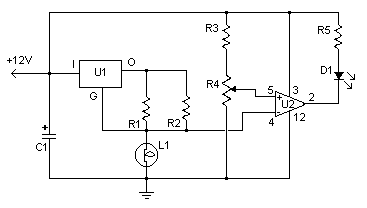
This simple circuit uses an incandescent lamp to detect airflow. With the filament exposed to air, a constant current source is used to slightly heat the filament. As it is heated, the resistance increases. As air flows over the filament it cools down, thus lowering its resistance. A comparator is used to detect this difference and light an LED. With a few changes, the circuit can be connected to a meter or ADC to provide an estimation on the amount of airflow.
The circuit operates on the principle of thermal resistance variation caused by airflow. The incandescent lamp's filament serves as both the heating element and the sensing element. The constant current source is critical as it ensures that the filament reaches a stable temperature, allowing for consistent operation. The heating effect causes the filament to reach a temperature where its resistance is predictable and can be accurately measured.
As airflow occurs over the filament, the cooling effect results in a decrease in temperature, which in turn lowers the resistance of the filament. This change in resistance is monitored by a comparator circuit. The comparator is configured to compare the voltage across the filament against a reference voltage. When the airflow cools the filament sufficiently to change its resistance, the voltage drop across the filament will fall below the reference voltage, triggering the comparator to activate an output signal.
In practical applications, the output of the comparator can drive an LED, providing a visual indication of airflow presence. For more advanced applications, the output can also be interfaced with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a digital meter. This allows for quantification of airflow, enabling the circuit to be used in various measurement and control systems.
To enhance the circuit's capabilities, additional components may be introduced, such as filters to stabilize the output signal or calibration circuits to adjust the sensitivity of the airflow detection. The design can be further optimized by selecting a filament material with appropriate thermal characteristics or by employing a microcontroller to process the comparator output and provide more sophisticated data analysis. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method for detecting and measuring airflow using basic electronic components.This simple circuit uses an incandescent lamp to detect airflow. With the filament exposed to air, a constant current source is used to slightly heat the filament. As it is heated, the resistance increases. As air flows over the filament it cools down, thus lowering it`s resistance. A comparator is used to detect this difference and light an LED. With a few changes, the circuit can be connected to a meter or ADC to provide an estimation on the amount of air flow. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates on the principle of thermal resistance variation caused by airflow. The incandescent lamp's filament serves as both the heating element and the sensing element. The constant current source is critical as it ensures that the filament reaches a stable temperature, allowing for consistent operation. The heating effect causes the filament to reach a temperature where its resistance is predictable and can be accurately measured.
As airflow occurs over the filament, the cooling effect results in a decrease in temperature, which in turn lowers the resistance of the filament. This change in resistance is monitored by a comparator circuit. The comparator is configured to compare the voltage across the filament against a reference voltage. When the airflow cools the filament sufficiently to change its resistance, the voltage drop across the filament will fall below the reference voltage, triggering the comparator to activate an output signal.
In practical applications, the output of the comparator can drive an LED, providing a visual indication of airflow presence. For more advanced applications, the output can also be interfaced with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a digital meter. This allows for quantification of airflow, enabling the circuit to be used in various measurement and control systems.
To enhance the circuit's capabilities, additional components may be introduced, such as filters to stabilize the output signal or calibration circuits to adjust the sensitivity of the airflow detection. The design can be further optimized by selecting a filament material with appropriate thermal characteristics or by employing a microcontroller to process the comparator output and provide more sophisticated data analysis. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method for detecting and measuring airflow using basic electronic components.This simple circuit uses an incandescent lamp to detect airflow. With the filament exposed to air, a constant current source is used to slightly heat the filament. As it is heated, the resistance increases. As air flows over the filament it cools down, thus lowering it`s resistance. A comparator is used to detect this difference and light an LED. With a few changes, the circuit can be connected to a meter or ADC to provide an estimation on the amount of air flow. 🔗 External reference