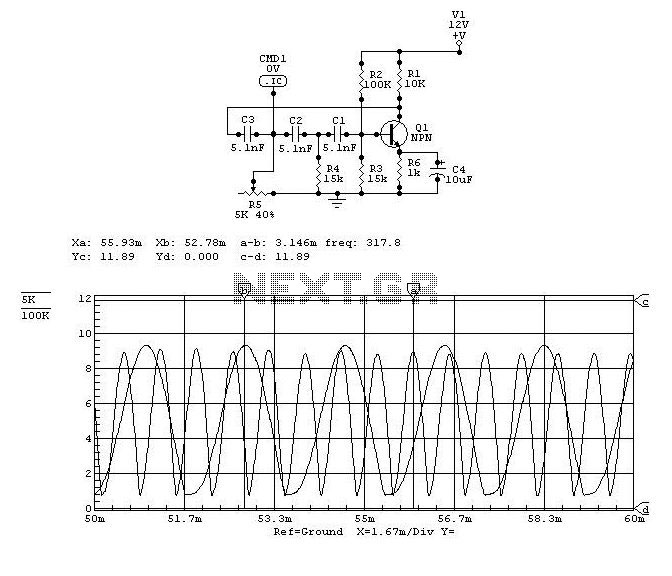
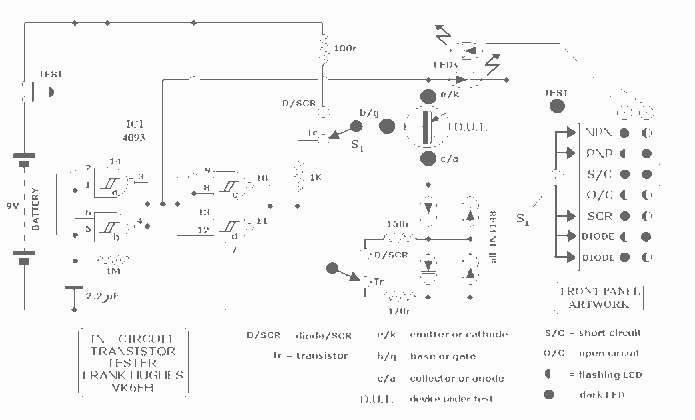
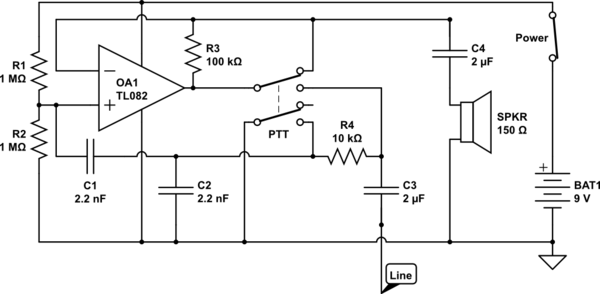
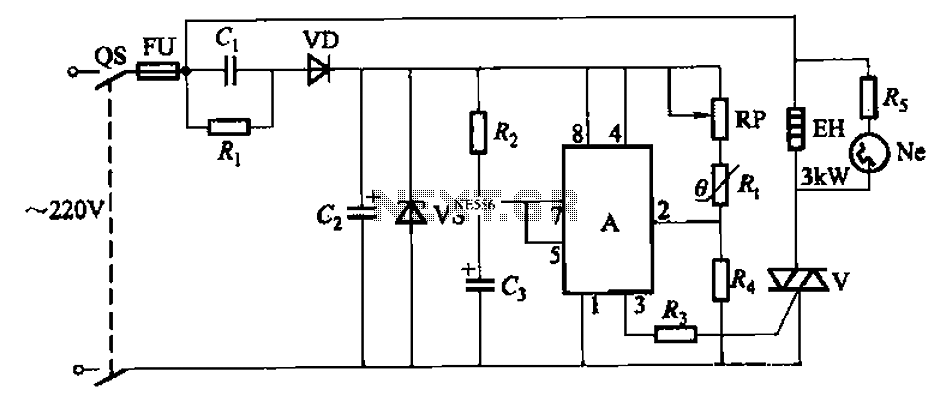
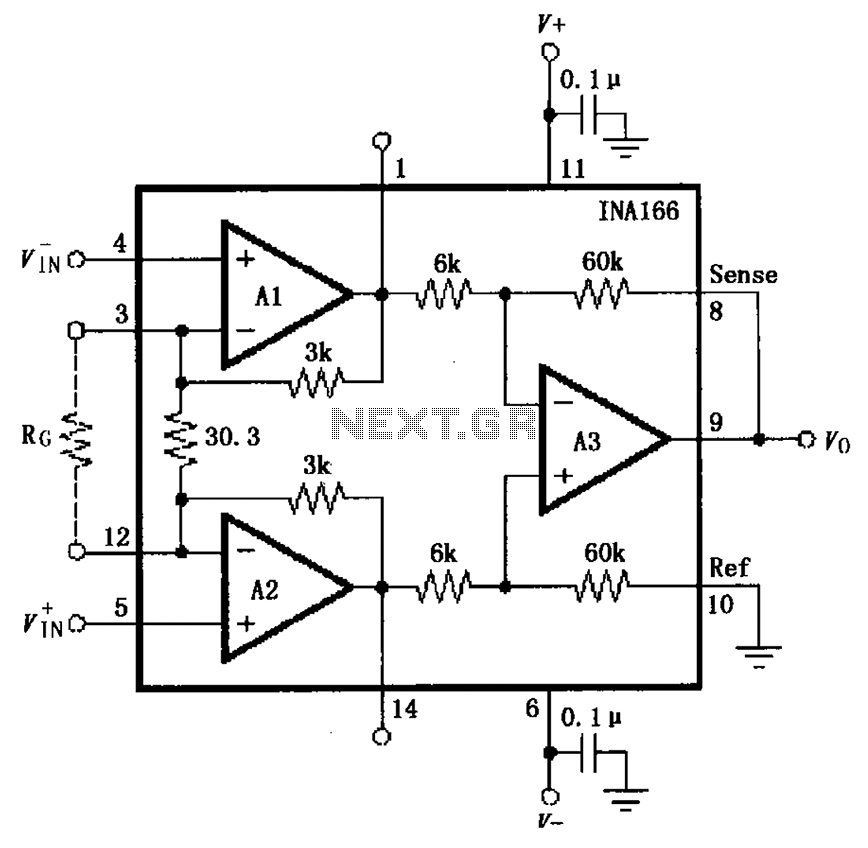
AM balanced diode circuit
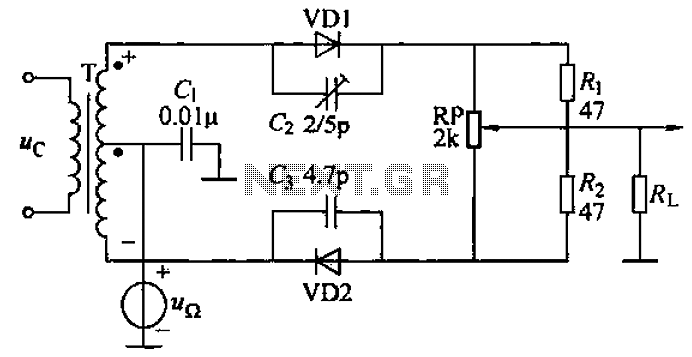
A common diode balanced modulator circuit is illustrated. It comprises two identical performance diodes and a center-tapped transformer configuration. The diodes used are VD1 and VD2, specifically 2AP9 models. The parameters for the circuit elements are detailed in FIG. 21-37. The role of the diodes is to balance the low-frequency modulation signal with the high-frequency carrier signal, resulting in a high-amplitude modulated signal output. This amplitude modulation circuit features a simple structure and produces minimal harmonic output, making it a widely used design for amplitude modulation applications.
The common diode balanced modulator circuit is an essential component in communication systems, particularly for amplitude modulation (AM) applications. The circuit's design utilizes two identical diodes, which ensures that the modulation process is symmetrical and efficient. The center-tapped transformer plays a crucial role in the circuit by providing the necessary phase shift and balancing the input signals.
In this configuration, the low-frequency modulation signal is applied to one side of the transformer, while the high-frequency carrier signal is applied to the other side. The diodes, VD1 and VD2, are configured to allow current flow in only one direction, effectively mixing the two signals. This results in the generation of upper and lower sidebands, which are characteristic of amplitude modulation.
The 2AP9 diodes are chosen for their reliable performance in radio frequency applications, ensuring that the circuit can handle the required power levels without distortion. The circuit's simplicity is an advantage, as it requires fewer components compared to other modulation techniques, leading to reduced costs and improved reliability.
The output of the balanced modulator is a high-amplitude modulated signal, which can then be further processed or transmitted. The minimal harmonic output is particularly beneficial in reducing interference and improving the overall quality of the transmitted signal. The circuit's design is adaptable, allowing for adjustments in the transformer turns ratio or diode biasing to optimize performance for specific applications. Overall, this balanced modulator circuit is a fundamental building block in the field of amplitude modulation, widely utilized for its effectiveness and efficiency in signal processing. Common diode balanced modulator circuit is shown. It consists of two identical performance diodes and a center-tapped transformer T composition. Diodes VD1, VD2 are 2AP9. Other elements parameters Parameter test value as shown in FIG. 21-37. Diode function is to balance the amplitude modulation circuit low-frequency modulation signal and high-frequency carrier signal through the circuit into a high-amplitude modulated signal output. The amplitude modulation circuit is simple structure, less harmonic output, is a common amplitude modulation circuit.
The common diode balanced modulator circuit is an essential component in communication systems, particularly for amplitude modulation (AM) applications. The circuit's design utilizes two identical diodes, which ensures that the modulation process is symmetrical and efficient. The center-tapped transformer plays a crucial role in the circuit by providing the necessary phase shift and balancing the input signals.
In this configuration, the low-frequency modulation signal is applied to one side of the transformer, while the high-frequency carrier signal is applied to the other side. The diodes, VD1 and VD2, are configured to allow current flow in only one direction, effectively mixing the two signals. This results in the generation of upper and lower sidebands, which are characteristic of amplitude modulation.
The 2AP9 diodes are chosen for their reliable performance in radio frequency applications, ensuring that the circuit can handle the required power levels without distortion. The circuit's simplicity is an advantage, as it requires fewer components compared to other modulation techniques, leading to reduced costs and improved reliability.
The output of the balanced modulator is a high-amplitude modulated signal, which can then be further processed or transmitted. The minimal harmonic output is particularly beneficial in reducing interference and improving the overall quality of the transmitted signal. The circuit's design is adaptable, allowing for adjustments in the transformer turns ratio or diode biasing to optimize performance for specific applications. Overall, this balanced modulator circuit is a fundamental building block in the field of amplitude modulation, widely utilized for its effectiveness and efficiency in signal processing. Common diode balanced modulator circuit is shown. It consists of two identical performance diodes and a center-tapped transformer T composition. Diodes VD1, VD2 are 2AP9. Other elements parameters Parameter test value as shown in FIG. 21-37. Diode function is to balance the amplitude modulation circuit low-frequency modulation signal and high-frequency carrier signal through the circuit into a high-amplitude modulated signal output. The amplitude modulation circuit is simple structure, less harmonic output, is a common amplitude modulation circuit.