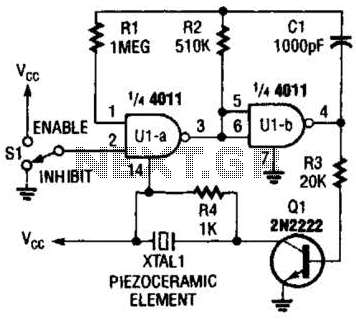
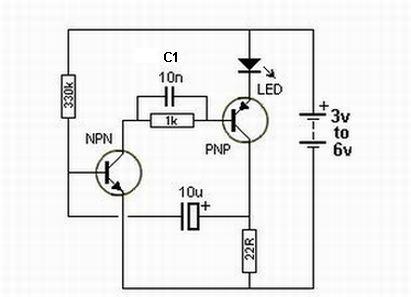
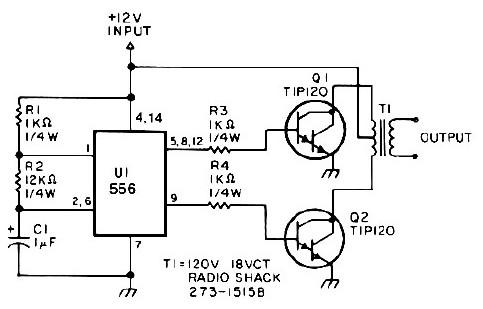
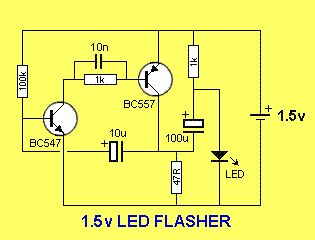
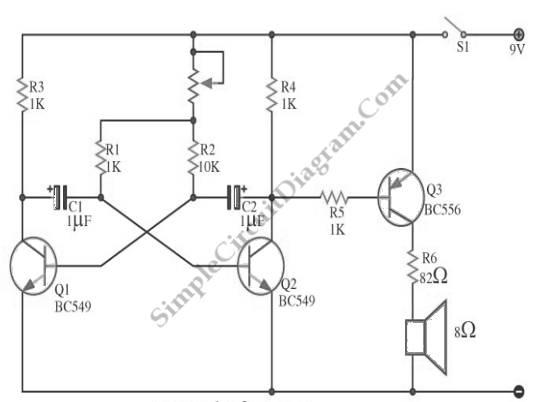
Simple Battery Charger Circuit Charges Upto 12 NiCD Cells

This circuit is designed to charge between one and twelve NiCd cells using a car battery. With switch S1 set to the normal position, it is capable of charging up to six cells.
The circuit operates by utilizing a car battery as the power source, providing the necessary voltage and current for charging NiCd cells. The configuration allows for a flexible number of cells to be charged, accommodating varying requirements from one to twelve cells. The inclusion of switch S1 enables the user to select the appropriate charging mode, optimizing the charging process based on the number of cells in use.
Typically, the circuit includes a charging regulator to ensure that the cells are charged safely and efficiently. This regulator monitors the voltage and current delivered to the cells, preventing overcharging, which can lead to cell damage or reduced lifespan. Additionally, diodes may be implemented to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the circuit components and the battery.
For charging one to six cells, the circuit may employ a simple series connection, while for charging more cells, a parallel configuration can be utilized. This flexibility is crucial for applications requiring different capacities and charging times.
The overall design should also consider thermal management, as charging can generate heat. Adequate heat dissipation mechanisms, such as heat sinks or ventilation, should be included to maintain optimal operating conditions.
In conclusion, this charging circuit provides a versatile solution for charging NiCd cells from a car battery, accommodating various configurations and ensuring safe operation through integrated protection mechanisms.This handy circuit can be used to charge from one to 12 NiCd cells from a car battery. Up to six cells can be charged with switch S1 in the normal posit.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a car battery as the power source, providing the necessary voltage and current for charging NiCd cells. The configuration allows for a flexible number of cells to be charged, accommodating varying requirements from one to twelve cells. The inclusion of switch S1 enables the user to select the appropriate charging mode, optimizing the charging process based on the number of cells in use.
Typically, the circuit includes a charging regulator to ensure that the cells are charged safely and efficiently. This regulator monitors the voltage and current delivered to the cells, preventing overcharging, which can lead to cell damage or reduced lifespan. Additionally, diodes may be implemented to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the circuit components and the battery.
For charging one to six cells, the circuit may employ a simple series connection, while for charging more cells, a parallel configuration can be utilized. This flexibility is crucial for applications requiring different capacities and charging times.
The overall design should also consider thermal management, as charging can generate heat. Adequate heat dissipation mechanisms, such as heat sinks or ventilation, should be included to maintain optimal operating conditions.
In conclusion, this charging circuit provides a versatile solution for charging NiCd cells from a car battery, accommodating various configurations and ensuring safe operation through integrated protection mechanisms.This handy circuit can be used to charge from one to 12 NiCd cells from a car battery. Up to six cells can be charged with switch S1 in the normal posit.. 🔗 External reference