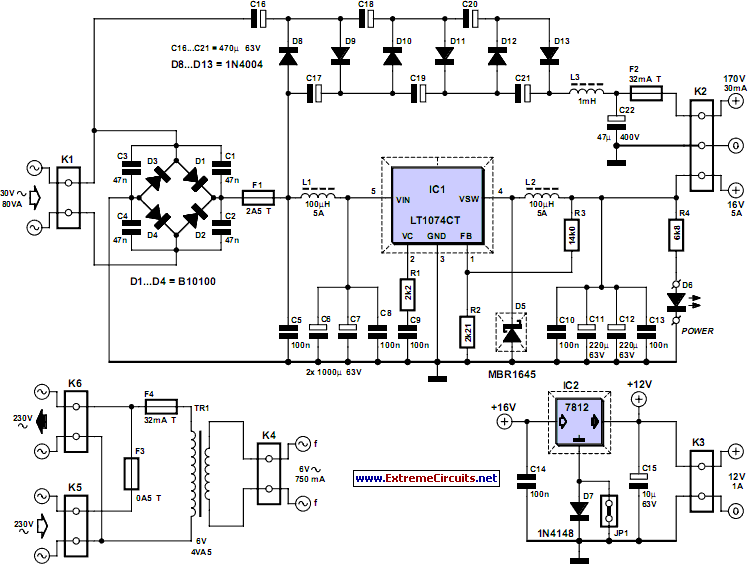
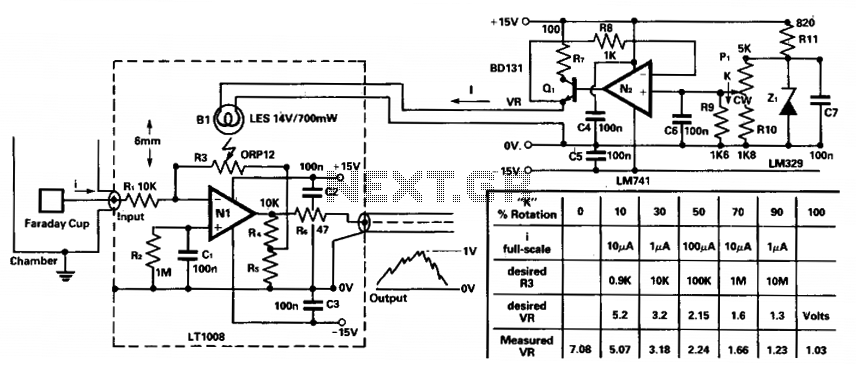
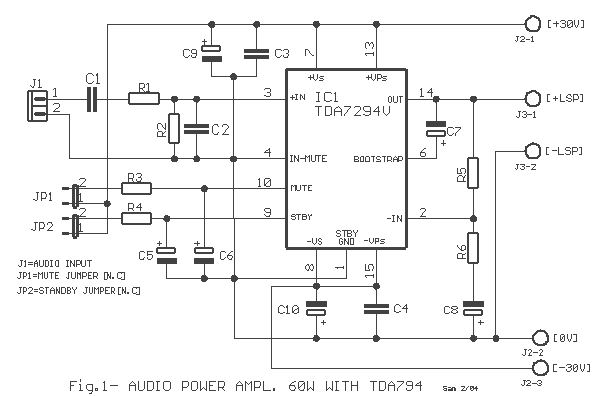
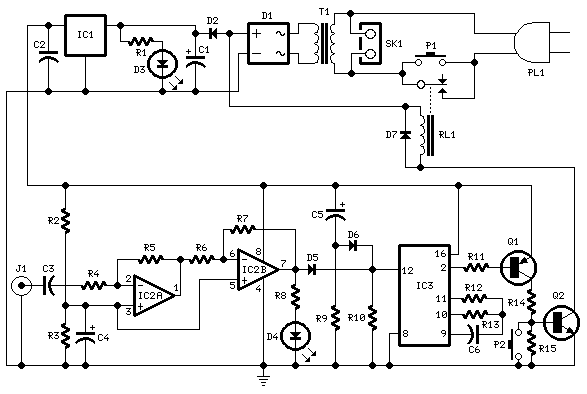
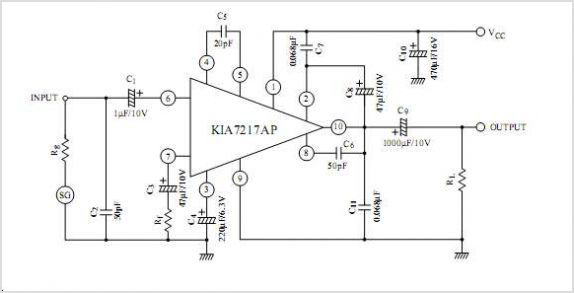
Amplifier circuits
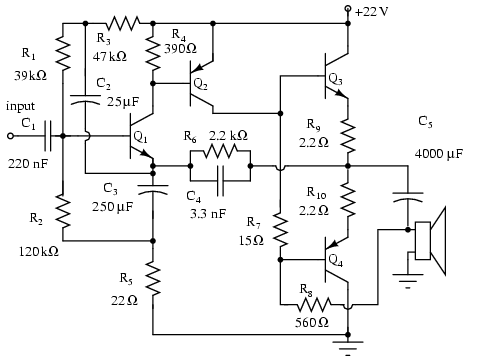
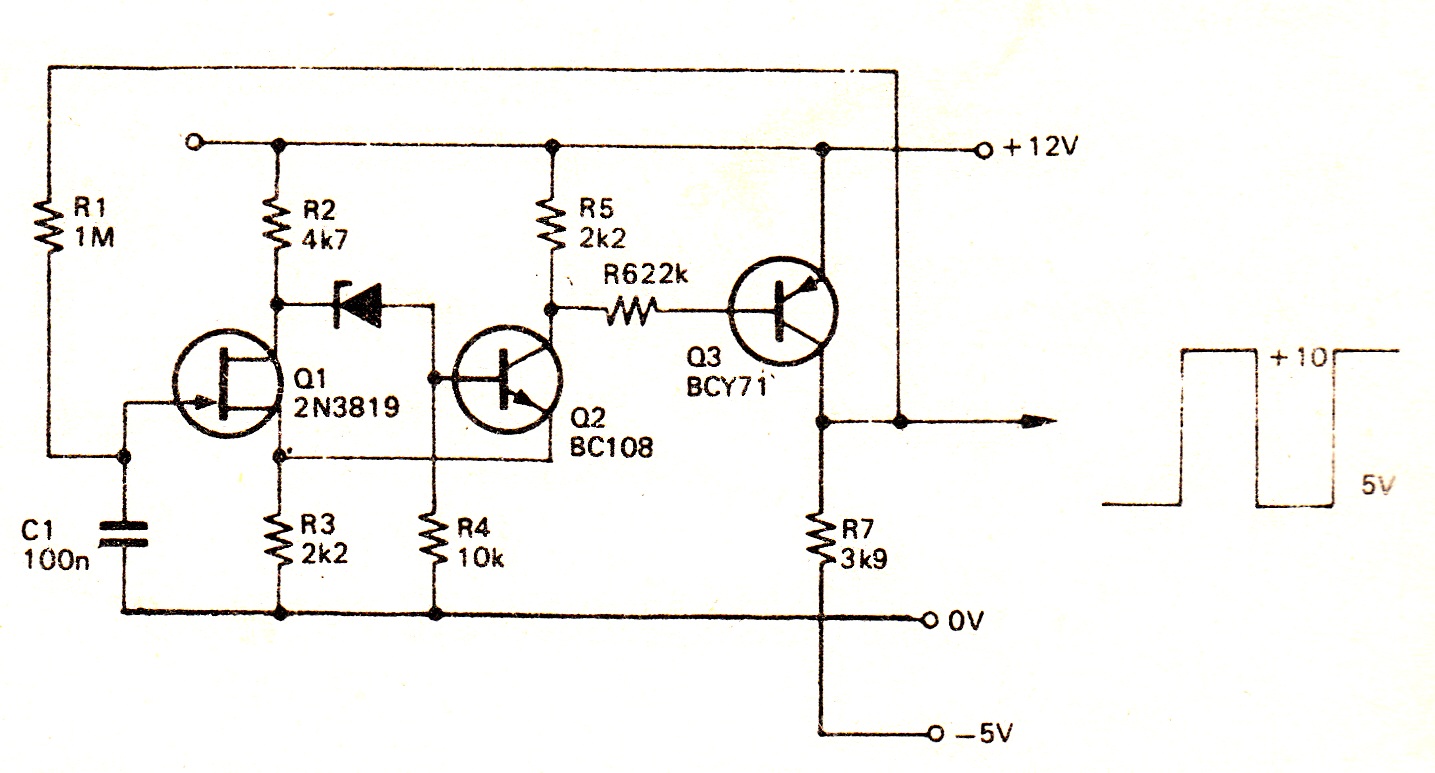
Note that Q3 and Q4 in the figure below are complementary, with Q3 being an NPN transistor and Q4 being a PNP transistor. This circuit is suitable for moderate power audio amplifiers. For a detailed explanation of this circuit, refer to the section on direct coupled complementary pairs in Chapter 4.
The described circuit utilizes a complementary push-pull configuration, which is commonly employed in audio amplifier designs to enhance efficiency and reduce distortion. In this setup, Q3 (NPN) and Q4 (PNP) transistors work together to amplify the audio signal. The complementary nature of these transistors allows for both halves of the audio waveform to be amplified, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity and achieving high fidelity in audio applications.
The circuit typically includes biasing resistors that ensure the transistors operate in their active regions, minimizing crossover distortion that can occur when transitioning between the two transistors. Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be implemented to stabilize the gain and improve linearity across a range of frequencies.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit must be designed to handle the required voltage and current levels for moderate power output, ensuring that the transistors remain within their safe operating areas. Heat dissipation must be managed effectively, often through the use of heat sinks, to prevent thermal runaway and ensure reliable long-term operation.
Overall, this complementary push-pull amplifier configuration is a robust solution for moderate power audio amplification, providing a good balance between performance, efficiency, and thermal management.Note, Q3 and Q4 in Figure below are complementary, NPN and PNP respectively. This circuit works well for moderate power audio amplifiers. For an explanation of this circuit see Direct coupled complementary-pair, Ch 4. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a complementary push-pull configuration, which is commonly employed in audio amplifier designs to enhance efficiency and reduce distortion. In this setup, Q3 (NPN) and Q4 (PNP) transistors work together to amplify the audio signal. The complementary nature of these transistors allows for both halves of the audio waveform to be amplified, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity and achieving high fidelity in audio applications.
The circuit typically includes biasing resistors that ensure the transistors operate in their active regions, minimizing crossover distortion that can occur when transitioning between the two transistors. Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be implemented to stabilize the gain and improve linearity across a range of frequencies.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit must be designed to handle the required voltage and current levels for moderate power output, ensuring that the transistors remain within their safe operating areas. Heat dissipation must be managed effectively, often through the use of heat sinks, to prevent thermal runaway and ensure reliable long-term operation.
Overall, this complementary push-pull amplifier configuration is a robust solution for moderate power audio amplification, providing a good balance between performance, efficiency, and thermal management.Note, Q3 and Q4 in Figure below are complementary, NPN and PNP respectively. This circuit works well for moderate power audio amplifiers. For an explanation of this circuit see Direct coupled complementary-pair, Ch 4. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713