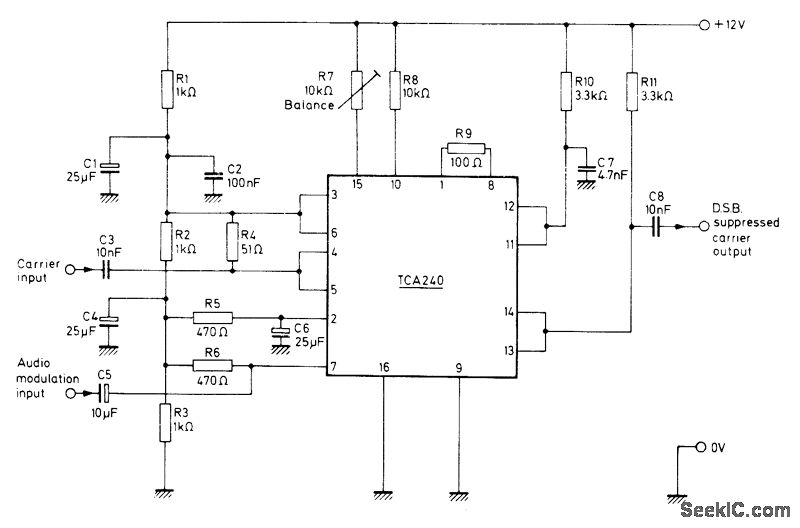
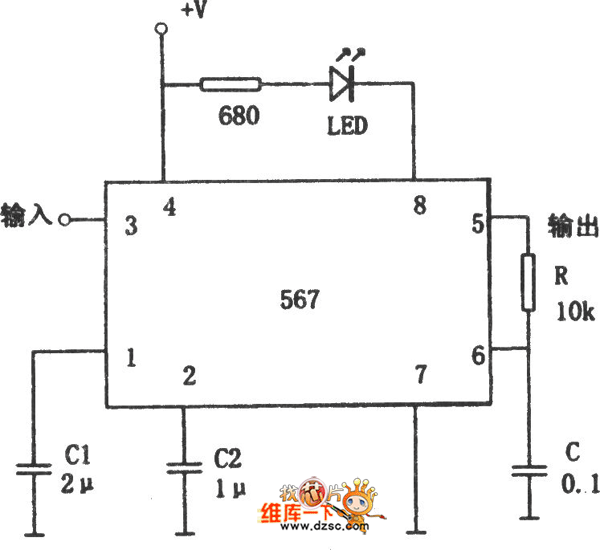
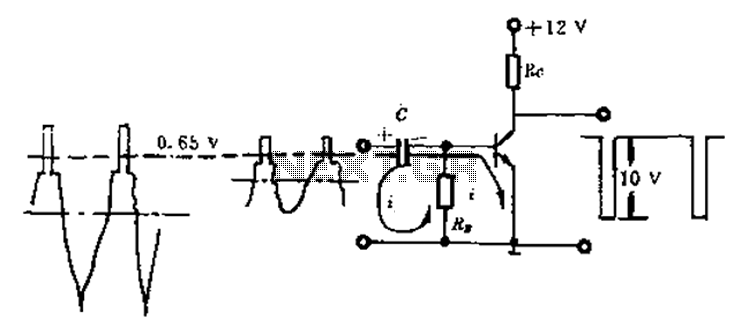
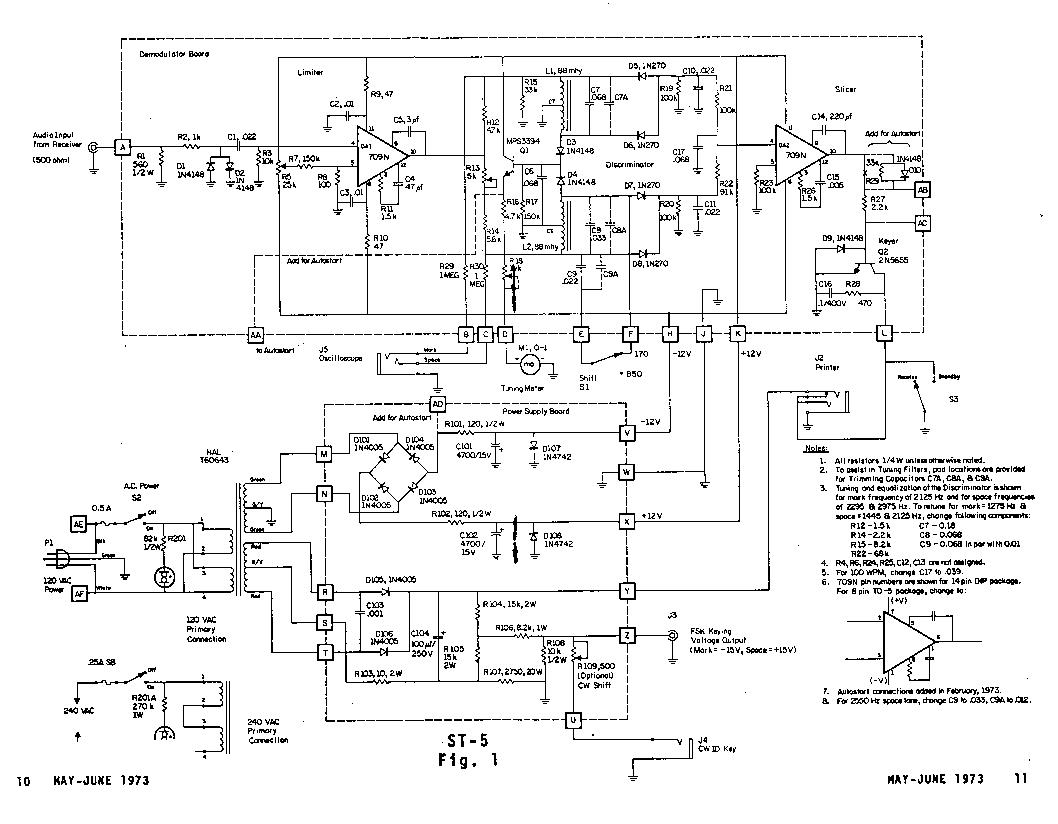
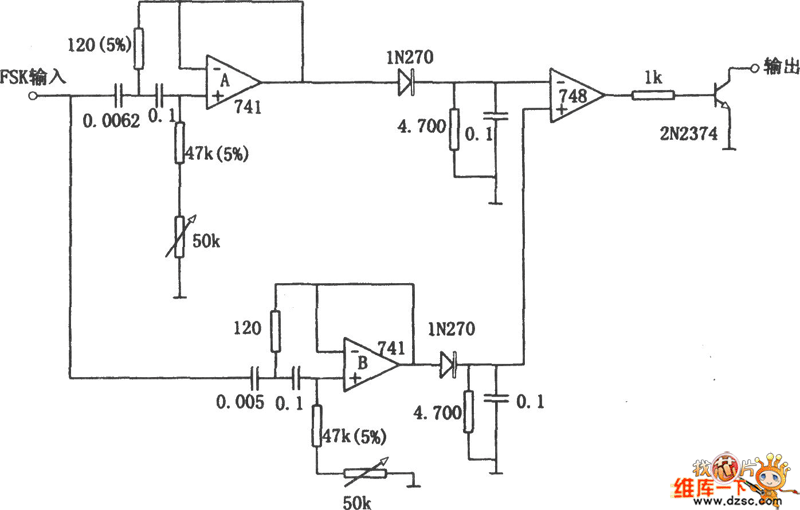
AMPLITUDE MODULATOR 1
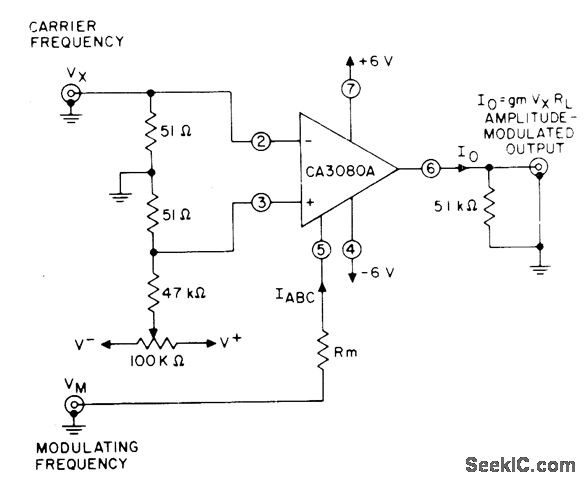
The circuit utilizes a controlled variation of amplifier bias current (IABC) in the CA3080A variable operational amplifier to achieve effective gain control of the signal. Changes in the amplitude of the modulating voltage (Vm) alter the bias current through resistor (Rm), resulting in amplitude modulation of the carrier signal.
The described circuit employs the CA3080A, a versatile operational amplifier known for its ability to handle various signal processing tasks. The operational amplifier is configured in a way that allows for dynamic adjustment of its gain based on the bias current, IABC. By manipulating this bias current, the circuit can achieve precise control over the amplification of input signals.
The modulating voltage (Vm) plays a crucial role in this configuration. As Vm varies, it influences the amount of current flowing through the resistor Rm. This change in current directly affects the biasing of the operational amplifier, thereby modulating the gain applied to the carrier signal. The result is an amplitude modulation effect, where the output signal's amplitude reflects the variations in the modulating voltage.
The circuit's design highlights the importance of feedback and stability in operational amplifier applications. Proper selection of resistor values and careful consideration of the power supply are essential to ensure optimal performance. The CA3080A's characteristics, such as its low distortion and wide bandwidth, make it suitable for applications requiring high-fidelity signal processing.
In summary, this circuit effectively demonstrates the principles of gain control and amplitude modulation using a variable operational amplifier, showcasing its utility in various electronic communication and signal processing applications. Proper implementation can lead to enhanced signal integrity and improved performance in systems relying on amplitude modulation techniques.Uses controlled variation of amplifier bias current IABC in CA3080A variable opamp to obtain effective gain control of signal. Variations in amplitude of modulating voltage Vm change bias current through Rm to give amplitude modulation of carrier.
-"Circuit Ideas for RCA Linear ICs, " RCA Solid State Division, Somerville, NJ, 1977, p 15. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs the CA3080A, a versatile operational amplifier known for its ability to handle various signal processing tasks. The operational amplifier is configured in a way that allows for dynamic adjustment of its gain based on the bias current, IABC. By manipulating this bias current, the circuit can achieve precise control over the amplification of input signals.
The modulating voltage (Vm) plays a crucial role in this configuration. As Vm varies, it influences the amount of current flowing through the resistor Rm. This change in current directly affects the biasing of the operational amplifier, thereby modulating the gain applied to the carrier signal. The result is an amplitude modulation effect, where the output signal's amplitude reflects the variations in the modulating voltage.
The circuit's design highlights the importance of feedback and stability in operational amplifier applications. Proper selection of resistor values and careful consideration of the power supply are essential to ensure optimal performance. The CA3080A's characteristics, such as its low distortion and wide bandwidth, make it suitable for applications requiring high-fidelity signal processing.
In summary, this circuit effectively demonstrates the principles of gain control and amplitude modulation using a variable operational amplifier, showcasing its utility in various electronic communication and signal processing applications. Proper implementation can lead to enhanced signal integrity and improved performance in systems relying on amplitude modulation techniques.Uses controlled variation of amplifier bias current IABC in CA3080A variable opamp to obtain effective gain control of signal. Variations in amplitude of modulating voltage Vm change bias current through Rm to give amplitude modulation of carrier.
-"Circuit Ideas for RCA Linear ICs, " RCA Solid State Division, Somerville, NJ, 1977, p 15. 🔗 External reference