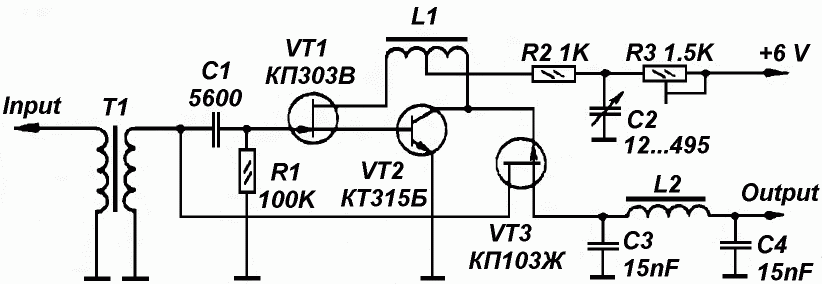
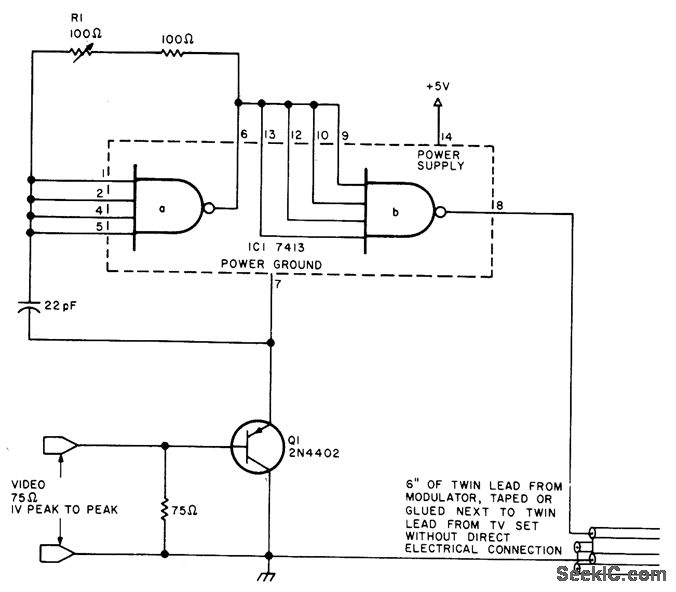
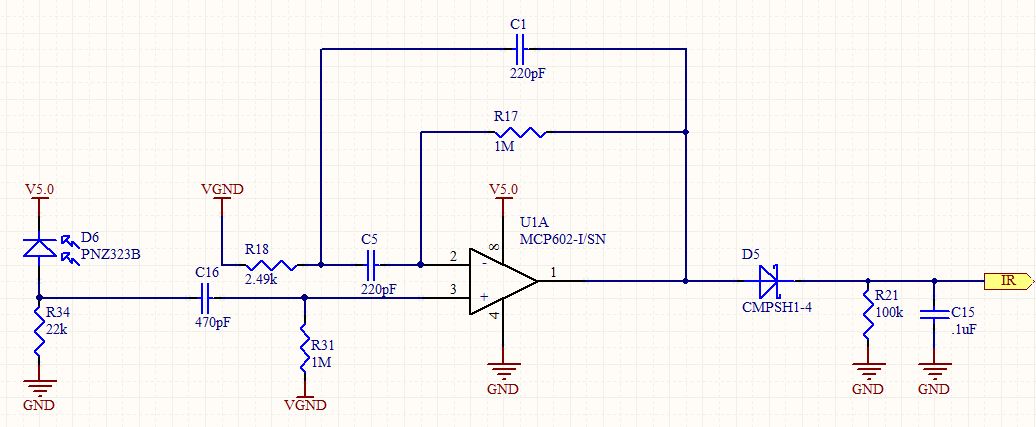
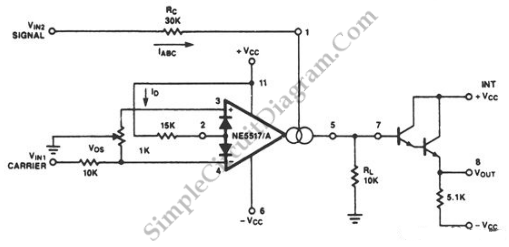
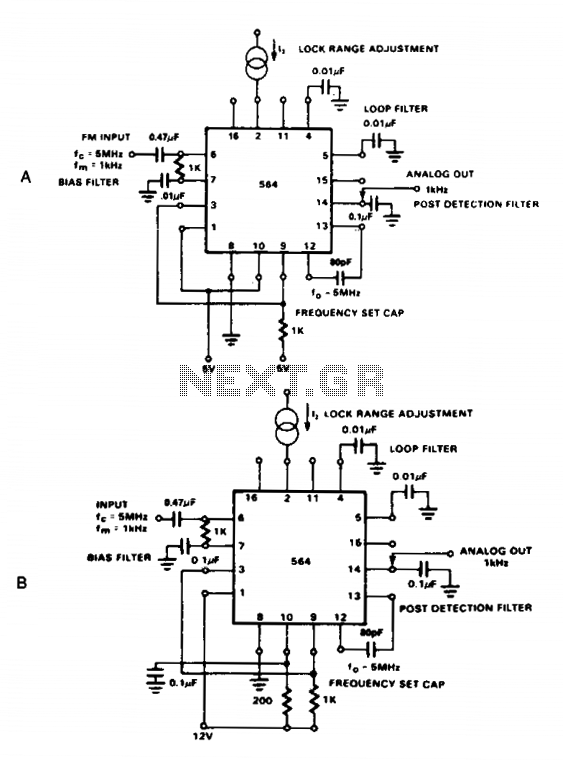
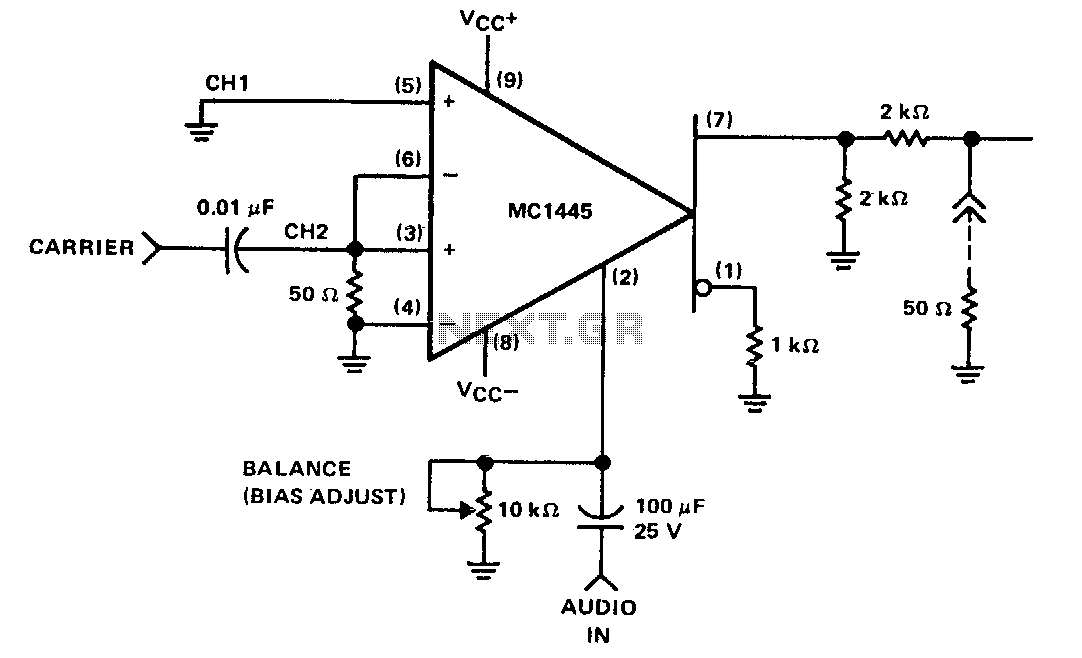
SUPPRESSED CARRIER MODULATOR
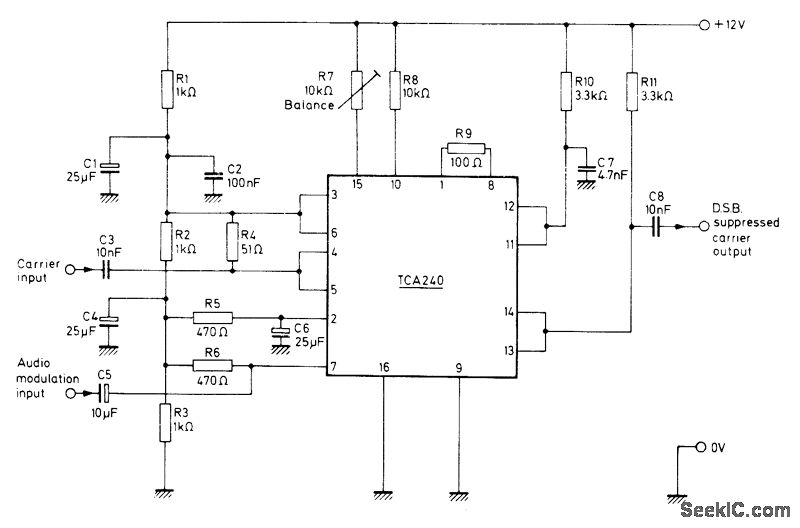
The Mullard TCA240 is a dual balanced modulator-demodulator that effectively suppresses the carrier frequency at the output, which is essential for Single Sideband (SSB) or Double Sideband (DSB) operation in transmitters. The bias resistor R7 is adjustable to achieve the minimum carrier output, thereby correcting any imbalance present in the system. Additionally, the TCA240 can function as a conventional Amplitude Modulation (AM) modulator if the biasing of the circuit sections is intentionally made unbalanced.
The Mullard TCA240 dual balanced modulator-demodulator is designed to facilitate efficient modulation and demodulation processes, particularly in communication systems requiring SSB or DSB signal formats. The device employs a balanced architecture that minimizes unwanted carrier signals, enhancing the clarity and quality of transmitted signals.
In practical applications, the TCA240 can be configured to operate in various modes depending on the biasing of its internal components. By adjusting the bias resistor R7, users can fine-tune the circuit to achieve optimal performance, ensuring that the carrier output is minimized to the desired level. This adjustment is critical in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in high-fidelity audio transmission or in radio frequency communication systems.
When utilized as an AM modulator, the TCA240's design allows for a deliberate imbalance in the circuit sections, which can be beneficial in specific scenarios where standard AM modulation characteristics are required. This versatility makes the TCA240 a valuable component in both modern and legacy communication systems, providing engineers with a reliable solution for various modulation needs.
The technical specifications and operational characteristics of the TCA240 are well-documented in Mullard's Technical Note 18, TP1489, published in London in 1975, which serves as a comprehensive guide for engineers and technicians working with this component.Mullard TCA240 dual balanced modulator-demodulator provides suppression of carrier frequency at output, as required for SSB or DSB operation of transmitter. Bias resistor R7 is adjusted for minimum carrier output to correct imbalance. Can be used as conventional AM modulator if biasing of circuit sections is deliberately unbalanced. -"Applications of the TCA240, " Mullard, London, 1975, Technical Note 18, TP1489. 🔗 External reference
The Mullard TCA240 dual balanced modulator-demodulator is designed to facilitate efficient modulation and demodulation processes, particularly in communication systems requiring SSB or DSB signal formats. The device employs a balanced architecture that minimizes unwanted carrier signals, enhancing the clarity and quality of transmitted signals.
In practical applications, the TCA240 can be configured to operate in various modes depending on the biasing of its internal components. By adjusting the bias resistor R7, users can fine-tune the circuit to achieve optimal performance, ensuring that the carrier output is minimized to the desired level. This adjustment is critical in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in high-fidelity audio transmission or in radio frequency communication systems.
When utilized as an AM modulator, the TCA240's design allows for a deliberate imbalance in the circuit sections, which can be beneficial in specific scenarios where standard AM modulation characteristics are required. This versatility makes the TCA240 a valuable component in both modern and legacy communication systems, providing engineers with a reliable solution for various modulation needs.
The technical specifications and operational characteristics of the TCA240 are well-documented in Mullard's Technical Note 18, TP1489, published in London in 1975, which serves as a comprehensive guide for engineers and technicians working with this component.Mullard TCA240 dual balanced modulator-demodulator provides suppression of carrier frequency at output, as required for SSB or DSB operation of transmitter. Bias resistor R7 is adjusted for minimum carrier output to correct imbalance. Can be used as conventional AM modulator if biasing of circuit sections is deliberately unbalanced. -"Applications of the TCA240, " Mullard, London, 1975, Technical Note 18, TP1489. 🔗 External reference