Audible Transistor Tester
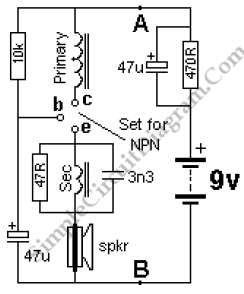
All types of transistors, including Darlington and power transistors, will be tested in this project. Connect the 9V battery in reverse at points A and B to conduct the tests.
In this project, a comprehensive testing setup for various transistor types is established. The circuit is designed to accommodate different transistor configurations, including standard bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), Darlington pairs, and power transistors.
To initiate testing, a 9V battery is employed as the power source. It is important to note that the battery should be connected in reverse at designated points A and B. This reverse connection is a critical aspect of the testing procedure, as it allows for the evaluation of the transistors under non-standard conditions, which can reveal important characteristics such as breakdown voltages and reverse bias behavior.
The testing circuit will likely include key components such as resistors, which are used to limit current and protect the transistors during testing. A series of test points may be integrated into the schematic to facilitate easy measurement of voltages and currents at various stages of the circuit. Additionally, a multimeter can be employed to measure the collector-emitter voltage (Vce), base-emitter voltage (Vbe), and collector current (Ic) for each transistor type.
For Darlington transistors specifically, the circuit will demonstrate the high current gain characteristics, making it essential to observe the input and output relationships. Power transistors will be tested under higher load conditions to ensure they can handle the required power dissipation without failure.
Overall, the project aims to provide a thorough understanding of transistor behavior across different configurations and operating conditions, contributing to the knowledge base of electronic circuit design and analysis.All types of transistors including Darlington and power will be tested in this project. Connect the 9v battery around the other way at points A and B to test.. 🔗 External reference
In this project, a comprehensive testing setup for various transistor types is established. The circuit is designed to accommodate different transistor configurations, including standard bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), Darlington pairs, and power transistors.
To initiate testing, a 9V battery is employed as the power source. It is important to note that the battery should be connected in reverse at designated points A and B. This reverse connection is a critical aspect of the testing procedure, as it allows for the evaluation of the transistors under non-standard conditions, which can reveal important characteristics such as breakdown voltages and reverse bias behavior.
The testing circuit will likely include key components such as resistors, which are used to limit current and protect the transistors during testing. A series of test points may be integrated into the schematic to facilitate easy measurement of voltages and currents at various stages of the circuit. Additionally, a multimeter can be employed to measure the collector-emitter voltage (Vce), base-emitter voltage (Vbe), and collector current (Ic) for each transistor type.
For Darlington transistors specifically, the circuit will demonstrate the high current gain characteristics, making it essential to observe the input and output relationships. Power transistors will be tested under higher load conditions to ensure they can handle the required power dissipation without failure.
Overall, the project aims to provide a thorough understanding of transistor behavior across different configurations and operating conditions, contributing to the knowledge base of electronic circuit design and analysis.All types of transistors including Darlington and power will be tested in this project. Connect the 9v battery around the other way at points A and B to test.. 🔗 External reference