Audio band-pass filter

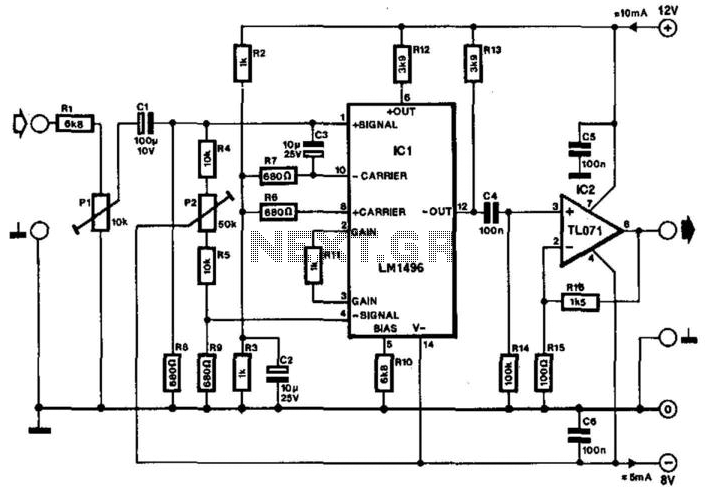
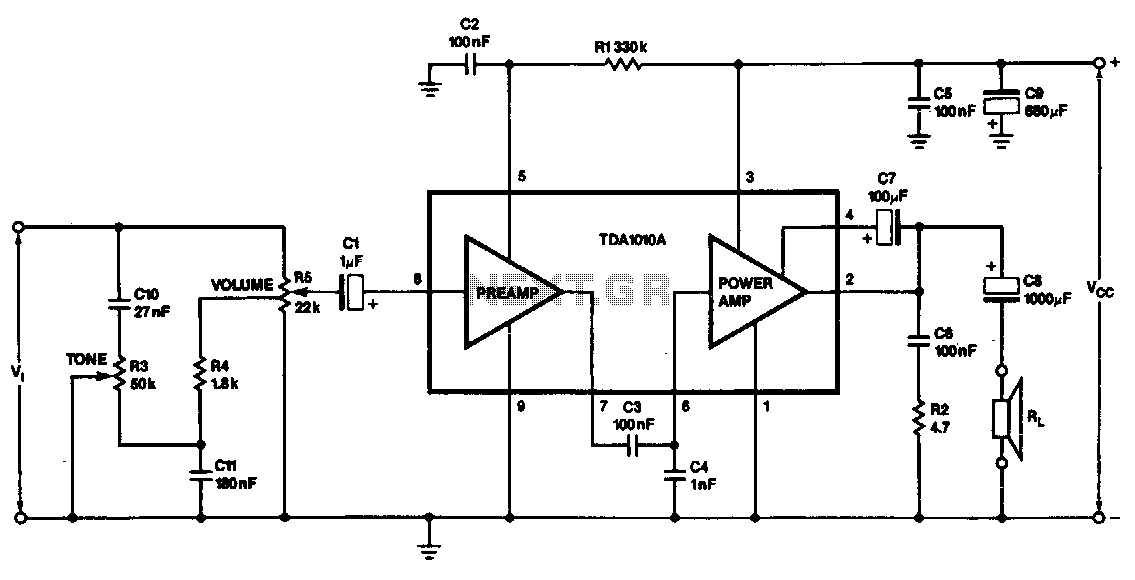
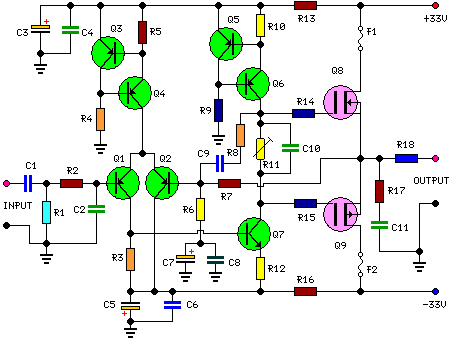
Band-pass filter used for a single channel, fH 50Hz, fL 13kHz.
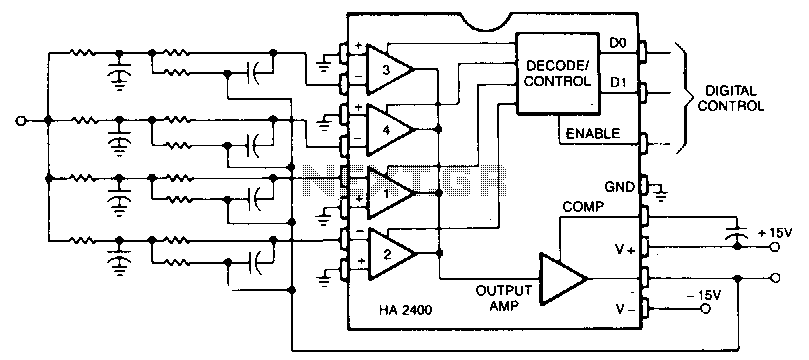
A band-pass filter (BPF) is an electronic circuit that allows signals within a specified frequency range to pass through while attenuating signals outside that range. In this case, the filter is designed for a single channel with a high cutoff frequency (fH) of 50 Hz and a low cutoff frequency (fL) of 13 kHz.
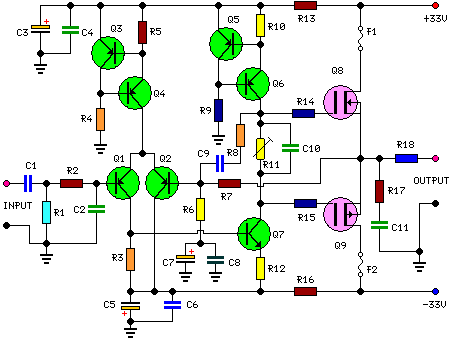
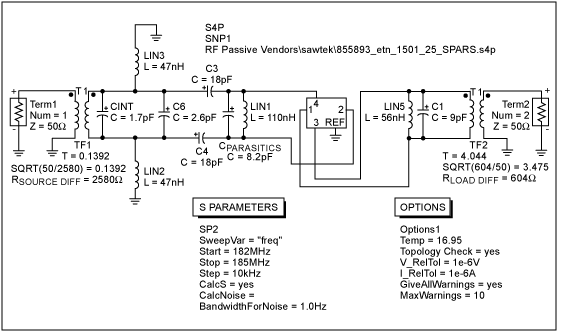
The design of this band-pass filter can be implemented using passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or through active components like operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the desired frequency response. The filter's configuration may involve either a series or parallel arrangement of these components to create a frequency-selective network.
For a passive band-pass filter, a typical design might consist of a high-pass filter (HPF) and a low-pass filter (LPF) connected in series. The HPF would use a capacitor in series with the input signal and a resistor to ground, allowing frequencies above 13 kHz to pass while blocking lower frequencies. The LPF would consist of a resistor in series and a capacitor to ground, allowing frequencies below 50 Hz to pass while attenuating higher frequencies.
In an active configuration, the use of op-amps can enhance the filter's performance by providing gain and improving the filter's selectivity. The op-amp can be configured in a band-pass arrangement that utilizes feedback and external components to set the cutoff frequencies precisely.
The specifications of this band-pass filter suggest it is suitable for applications where it is crucial to isolate signals within the 13 kHz to 50 Hz range, such as audio processing, communication systems, or instrumentation where unwanted frequencies must be filtered out to enhance signal clarity and integrity. Proper component selection and layout are critical to achieving the desired frequency response and minimizing distortion or noise in the output signal. Band-pass filter used for a single channel, fH 50Hz;, fl 13kHz.
A band-pass filter (BPF) is an electronic circuit that allows signals within a specified frequency range to pass through while attenuating signals outside that range. In this case, the filter is designed for a single channel with a high cutoff frequency (fH) of 50 Hz and a low cutoff frequency (fL) of 13 kHz.
The design of this band-pass filter can be implemented using passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or through active components like operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the desired frequency response. The filter's configuration may involve either a series or parallel arrangement of these components to create a frequency-selective network.
For a passive band-pass filter, a typical design might consist of a high-pass filter (HPF) and a low-pass filter (LPF) connected in series. The HPF would use a capacitor in series with the input signal and a resistor to ground, allowing frequencies above 13 kHz to pass while blocking lower frequencies. The LPF would consist of a resistor in series and a capacitor to ground, allowing frequencies below 50 Hz to pass while attenuating higher frequencies.
In an active configuration, the use of op-amps can enhance the filter's performance by providing gain and improving the filter's selectivity. The op-amp can be configured in a band-pass arrangement that utilizes feedback and external components to set the cutoff frequencies precisely.
The specifications of this band-pass filter suggest it is suitable for applications where it is crucial to isolate signals within the 13 kHz to 50 Hz range, such as audio processing, communication systems, or instrumentation where unwanted frequencies must be filtered out to enhance signal clarity and integrity. Proper component selection and layout are critical to achieving the desired frequency response and minimizing distortion or noise in the output signal. Band-pass filter used for a single channel, fH 50Hz;, fl 13kHz.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713