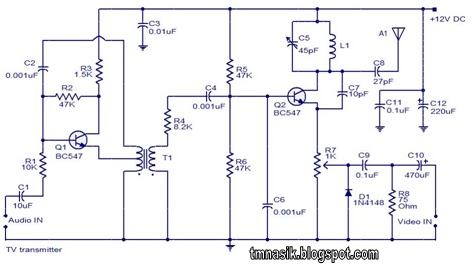
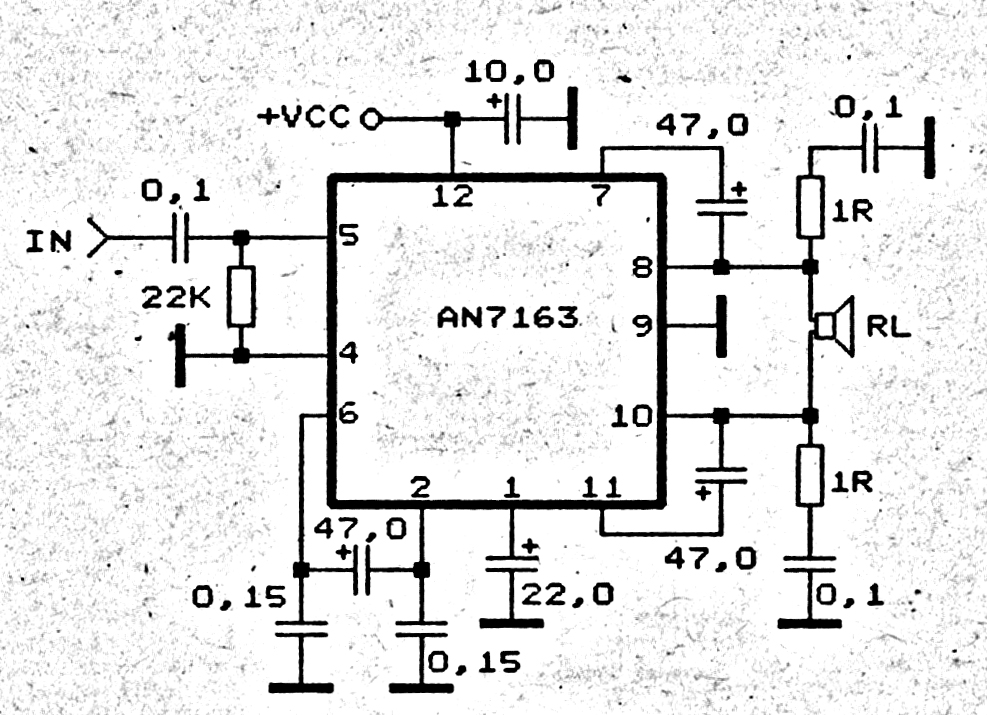
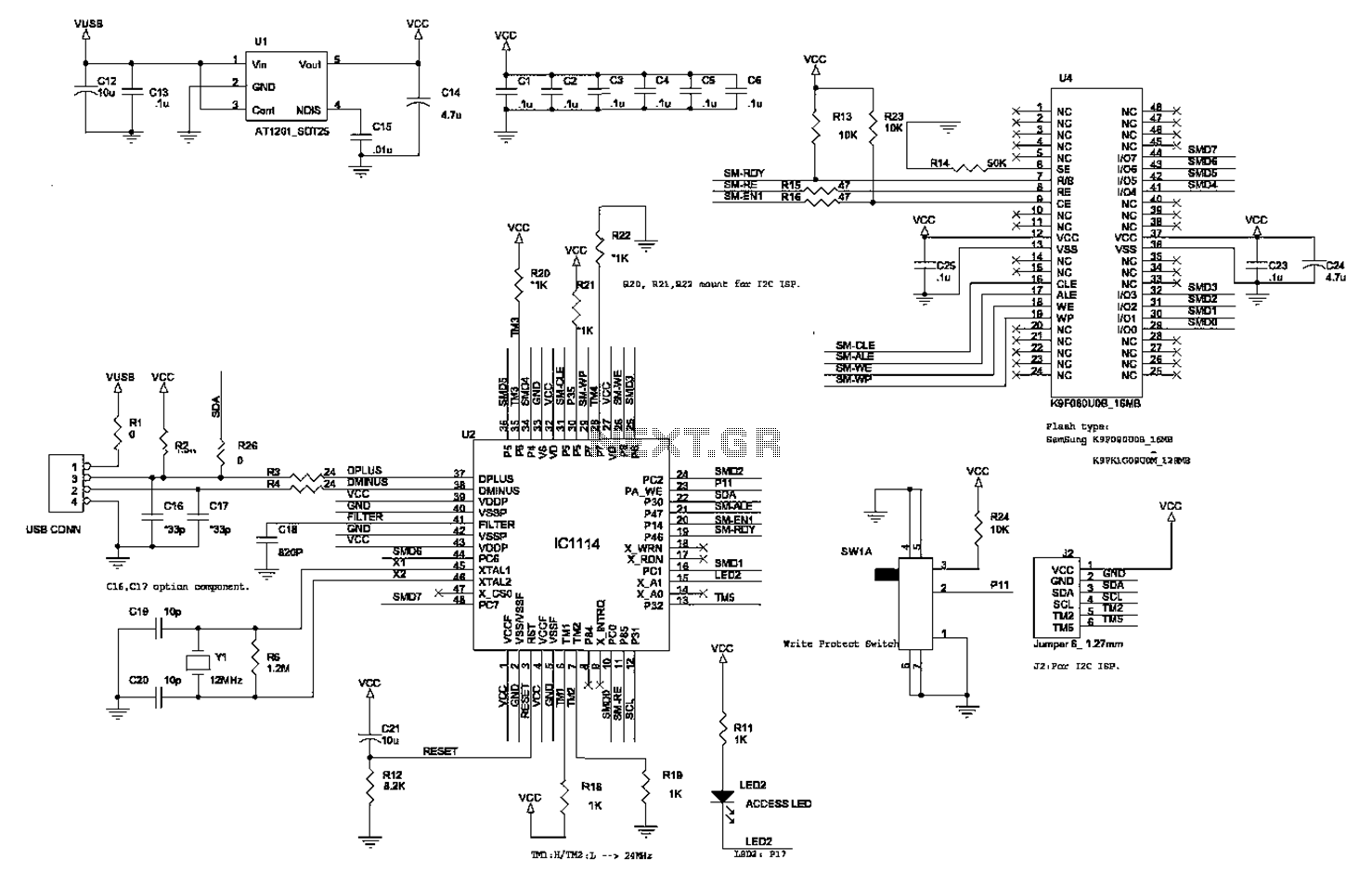
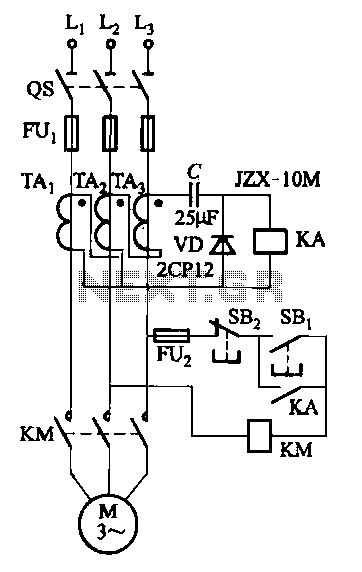
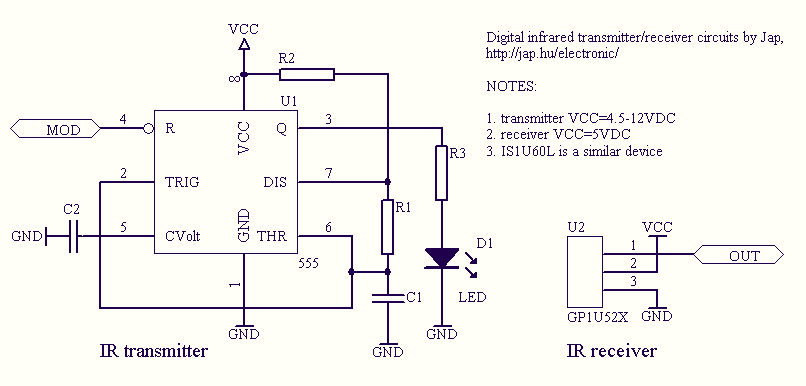
Audio Controlled Switch Circuit
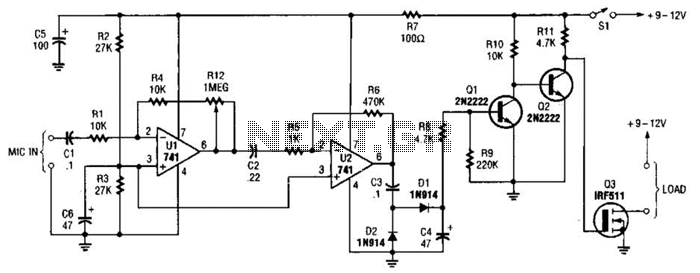
This audio-controlled switch integrates a pair of 741 operational amplifiers, two 2N2222 general-purpose transistors, an hcxFET, and several supporting components into a circuit capable of activating devices such as a tape recorder, a transmitter, or virtually any sound-activated equipment.
The audio-controlled switch circuit operates by detecting sound signals and converting them into a control signal that activates the connected devices. The core of the circuit comprises two 741 operational amplifiers configured in a non-inverting amplifier arrangement. These op-amps amplify the audio signal, enhancing the sensitivity of sound detection.
The amplified output from the op-amps is fed into a comparator stage, which determines whether the sound level exceeds a predefined threshold. This threshold is adjustable, allowing for customization based on the desired activation sensitivity. When the audio signal surpasses this threshold, the comparator output transitions from low to high.
This high output is then used to drive the base of the first 2N2222 transistor, which acts as a switch. The transistor is configured in common-emitter mode, providing significant current gain. When the transistor is turned on, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, activating the second 2N2222 transistor, which can drive the hcxFET.
The hcxFET serves as an electronic switch that can handle higher currents and voltages, making it suitable for controlling larger devices such as tape recorders or transmitters. The entire circuit is powered by a suitable DC power supply, with bypass capacitors included to filter out any noise and stabilize the voltage levels.
Additional support components, such as resistors and capacitors, are utilized for biasing the transistors, setting the gain of the op-amps, and filtering the audio signal. Proper selection of these components is crucial to ensure the circuit's performance and reliability in various audio environments. Overall, this audio-controlled switch provides a versatile solution for sound-activated applications, combining simplicity with effective control capabilities. This audio-controlled switch combines a pair of 741 op amps, two 2N2222 general-purpose transistors, a hcxFET, and a few support components to a circuit that can be used to turn on a tape recorder, a transmitter, or just about anything that uses sound.
The audio-controlled switch circuit operates by detecting sound signals and converting them into a control signal that activates the connected devices. The core of the circuit comprises two 741 operational amplifiers configured in a non-inverting amplifier arrangement. These op-amps amplify the audio signal, enhancing the sensitivity of sound detection.
The amplified output from the op-amps is fed into a comparator stage, which determines whether the sound level exceeds a predefined threshold. This threshold is adjustable, allowing for customization based on the desired activation sensitivity. When the audio signal surpasses this threshold, the comparator output transitions from low to high.
This high output is then used to drive the base of the first 2N2222 transistor, which acts as a switch. The transistor is configured in common-emitter mode, providing significant current gain. When the transistor is turned on, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, activating the second 2N2222 transistor, which can drive the hcxFET.
The hcxFET serves as an electronic switch that can handle higher currents and voltages, making it suitable for controlling larger devices such as tape recorders or transmitters. The entire circuit is powered by a suitable DC power supply, with bypass capacitors included to filter out any noise and stabilize the voltage levels.
Additional support components, such as resistors and capacitors, are utilized for biasing the transistors, setting the gain of the op-amps, and filtering the audio signal. Proper selection of these components is crucial to ensure the circuit's performance and reliability in various audio environments. Overall, this audio-controlled switch provides a versatile solution for sound-activated applications, combining simplicity with effective control capabilities. This audio-controlled switch combines a pair of 741 op amps, two 2N2222 general-purpose transistors, a hcxFET, and a few support components to a circuit that can be used to turn on a tape recorder, a transmitter, or just about anything that uses sound.