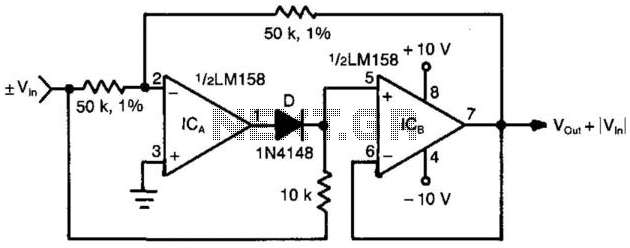
Audio vibration thaw circuit diagram
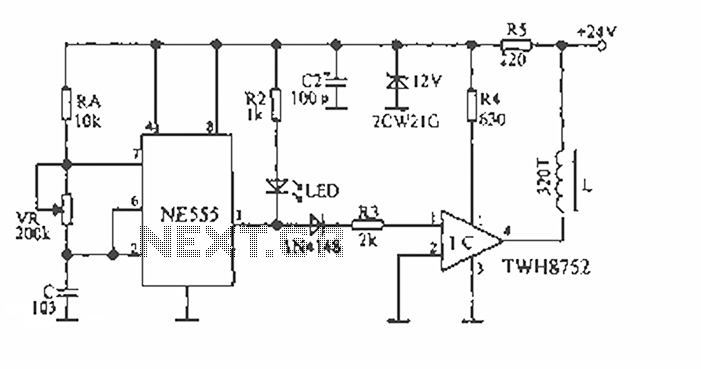
The device is designed to accelerate the defrosting process of fish, meat, and other foods by utilizing audio vibrations. This method allows for defrosting in warm water, significantly reducing the time required compared to conventional methods, while preserving the freshness of the food. The principle involves creating audio waves that cause the water and ice to collide, facilitating the penetration of water molecules into the ice and promoting faster melting. An iron container with a volume of approximately 0.1 m³ is used, with a solenoid placed at the bottom. The changes in magnetic field lines induce vibrations in the container, effectively transmitting them through the water. A 555 timer circuit generates a square wave oscillation, with a variable resistor (VR) to adjust the oscillation frequency. An LED indicates the operational status of the oscillation signal, which drives a high-power DC switch (TWH8752). The circuit is powered by a DC power supply derived from a step-down transformer, rectifier, and filter, providing around 100W of electrical power with a normal operating current of 4A.
The described device employs a sophisticated approach to enhance the defrosting process by leveraging the principles of acoustics and electromagnetism. The iron container, with its specified volume, is critical in ensuring that the audio vibrations effectively travel through the water, optimizing the thawing process. The solenoid, positioned strategically at the base of the container, is integral to generating the necessary vibrations. When energized, the solenoid's magnetic field fluctuates, causing the iron container to vibrate. This vibration creates a dynamic interaction between the ice and water, leading to an increased rate of heat transfer and promoting faster melting of the ice.
The 555 timer circuit plays a pivotal role in controlling the frequency of the audio vibrations. The ability to adjust the oscillation frequency via the variable resistor allows for fine-tuning of the defrosting process, catering to different types of food and their respective ice compositions. The LED indicator serves not only as a visual cue for operational status but also assists in troubleshooting by indicating whether the circuit is functioning correctly.
The high-power DC switch (TWH8752) is responsible for managing the current flow to the solenoid, ensuring that the vibrations are sustained and effective throughout the defrosting process. The power supply system, which includes a step-down transformer, rectifier, and filter, is designed to provide a stable and sufficient power output of approximately 100W. This ensures that the device can operate continuously without overheating or failure, maintaining an average current draw of 4A during normal operation.
This innovative approach to defrosting food not only reduces the time required but also minimizes the risk of compromising the quality and texture of the food, making it a valuable tool in both domestic and commercial kitchens.In the refrigerator before cooking after eating fish, meat and other food to be defrosted. The freeze was put into water, and the introduction of audio vibration can accelerate the defrosting process, thaw in warm water than conventional cut in half the time, and without damaging the freshness of food. Principle is to make audio thawing and freezing water was collided with each other, will be a combination of loose ice, water molecules penetrate the ice, the accelerated melting of ice.
Iron container with a volume of about 0.1m 3 square feet, put the solenoid L at the bottom of an opening, changes in the magnetic field lines make the cylinder bottom vibration and pass the water to achieve their goals. Circuit 555 generates a square wave oscillation, VR adjust the oscillation frequency, LED work instructions for the oscillation signal to the high-power DC switching TWH8752 1 feet, 4 feet connected to the electromagnet.
DC Power Supply After step-down transformer rectifier filter obtained electrical power capacity of about 100W, the normal operating current is 4A.
The described device employs a sophisticated approach to enhance the defrosting process by leveraging the principles of acoustics and electromagnetism. The iron container, with its specified volume, is critical in ensuring that the audio vibrations effectively travel through the water, optimizing the thawing process. The solenoid, positioned strategically at the base of the container, is integral to generating the necessary vibrations. When energized, the solenoid's magnetic field fluctuates, causing the iron container to vibrate. This vibration creates a dynamic interaction between the ice and water, leading to an increased rate of heat transfer and promoting faster melting of the ice.
The 555 timer circuit plays a pivotal role in controlling the frequency of the audio vibrations. The ability to adjust the oscillation frequency via the variable resistor allows for fine-tuning of the defrosting process, catering to different types of food and their respective ice compositions. The LED indicator serves not only as a visual cue for operational status but also assists in troubleshooting by indicating whether the circuit is functioning correctly.
The high-power DC switch (TWH8752) is responsible for managing the current flow to the solenoid, ensuring that the vibrations are sustained and effective throughout the defrosting process. The power supply system, which includes a step-down transformer, rectifier, and filter, is designed to provide a stable and sufficient power output of approximately 100W. This ensures that the device can operate continuously without overheating or failure, maintaining an average current draw of 4A during normal operation.
This innovative approach to defrosting food not only reduces the time required but also minimizes the risk of compromising the quality and texture of the food, making it a valuable tool in both domestic and commercial kitchens.In the refrigerator before cooking after eating fish, meat and other food to be defrosted. The freeze was put into water, and the introduction of audio vibration can accelerate the defrosting process, thaw in warm water than conventional cut in half the time, and without damaging the freshness of food. Principle is to make audio thawing and freezing water was collided with each other, will be a combination of loose ice, water molecules penetrate the ice, the accelerated melting of ice.
Iron container with a volume of about 0.1m 3 square feet, put the solenoid L at the bottom of an opening, changes in the magnetic field lines make the cylinder bottom vibration and pass the water to achieve their goals. Circuit 555 generates a square wave oscillation, VR adjust the oscillation frequency, LED work instructions for the oscillation signal to the high-power DC switching TWH8752 1 feet, 4 feet connected to the electromagnet.
DC Power Supply After step-down transformer rectifier filter obtained electrical power capacity of about 100W, the normal operating current is 4A.