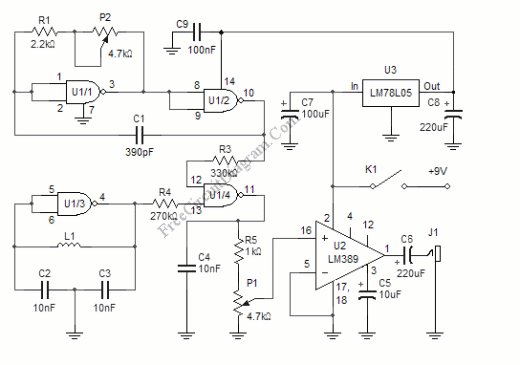
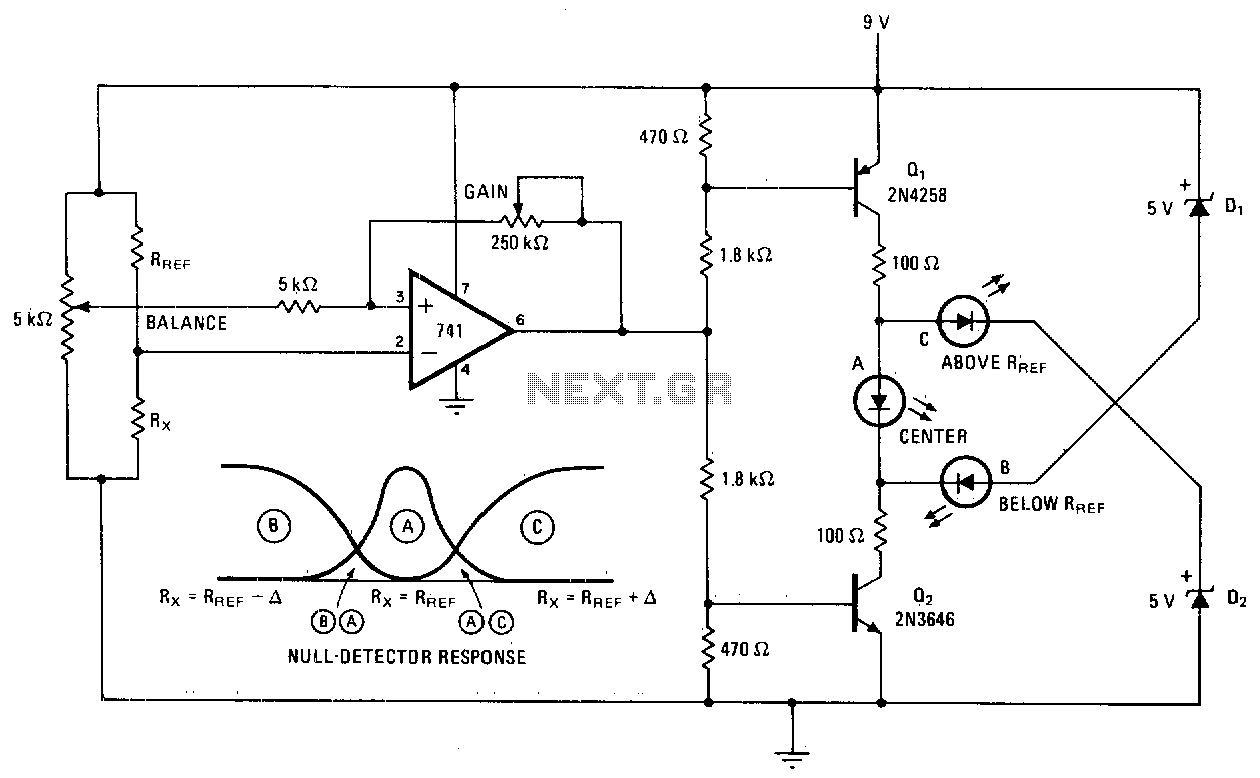
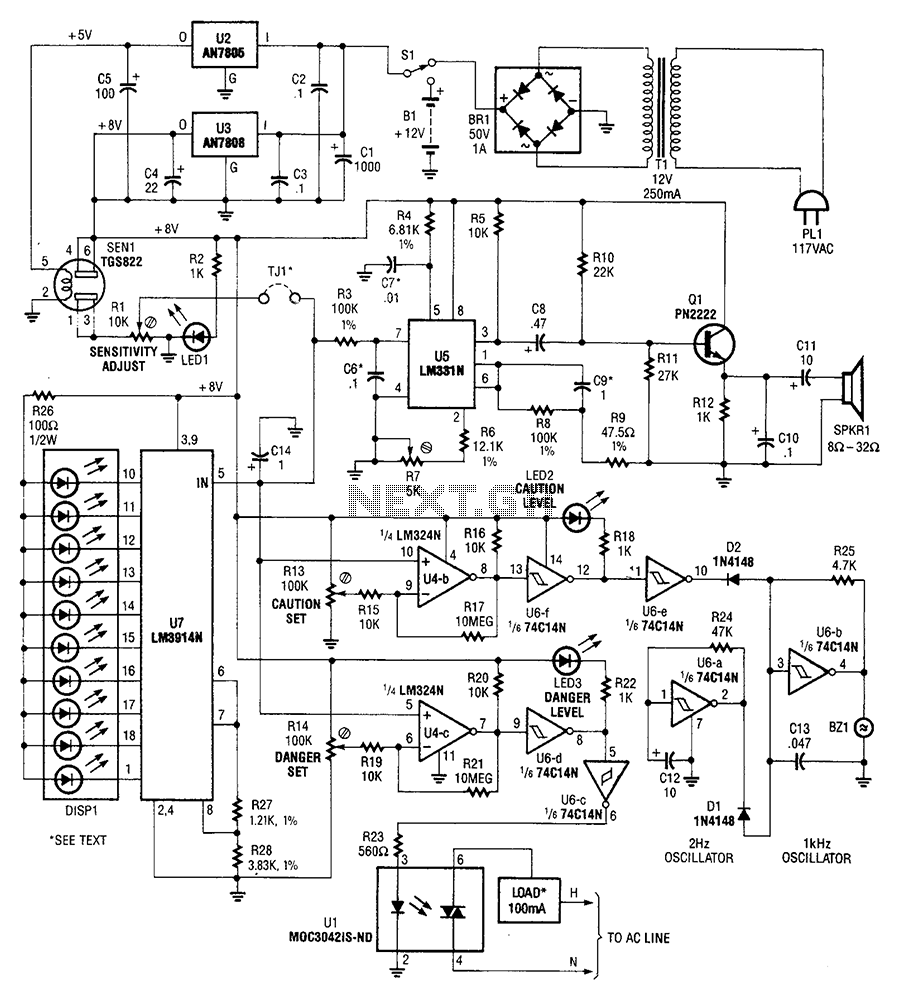
Beat Balance Metal Detector
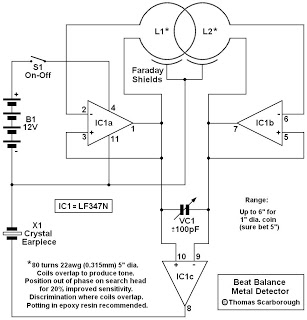
This is a metal detector circuit where the frequencies of two oscillators are mixed in a manner similar to a Beat Frequency Oscillator (BFO) to produce an audible heterodyne signal. At first glance, this design may appear to be a standard dual BFO metal detector. However, its distinguishing feature is that each coil influences the frequency of the adjacent oscillator through mutual coupling. This mutual interaction introduces the "balance" characteristic found in Induction Balance (IB) metal detectors, significantly enhancing sensitivity beyond that of traditional BFO designs.
The metal detector circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a transmitter coil generates an alternating magnetic field. When a metallic object is introduced into this field, eddy currents are induced in the object, which in turn generate their own magnetic field. This interaction modifies the frequency of the oscillators, allowing for the detection of metal objects.
The circuit typically consists of two main components: the transmitter and receiver coils. The transmitter coil is responsible for creating the magnetic field, while the receiver coil detects changes in the field caused by nearby metal objects. The mutual coupling between the coils is crucial, as it allows for the adjustment of the oscillation frequencies. This adjustment leads to a more refined detection capability, enabling the circuit to identify smaller or deeper metallic objects that standard BFO detectors may overlook.
In terms of design, the circuit may include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers to enhance signal processing and filtering. The output can be routed to an audio amplifier or a speaker, providing audible feedback to the user when a metal object is detected. The sensitivity and range of the detector can often be tuned by adjusting the values of the components in the circuit, allowing for customization based on the specific application or environment in which the metal detector will be used.
Overall, this metal detector circuit exemplifies a sophisticated application of mutual inductance principles, resulting in a highly effective tool for metal detection with improved performance over conventional designs.Here`s a metal detector circuit that frequencies of the two oscillators are then mixed in similar fashion to BFO, to produce an audible heterodyne. On the surface of it, this design would seem to represent little more than a twinned BFO metal detector.
What makes the metal detector different above all else ( check a simple metal detector ), and si gnificantly increases its range, is that each coil modifies the frequency of the adjacent oscillator through mutual coupling. This introduces the "balance" that is present in an IB metal detector, and boosts sensitivity well beyond that of BFO.
Disclaimer All files are found using legitimate search engine techniques. This site does not and will not condone hacking into sites to create the links it list. We will and do assume that all links found on the search engines we use are obtained in a legal manner and the webmasters are aware of the links listed on the search engines. If you find a URL that belongs to you, and you did not realize that it was "open to the public", please use the report button to notify the blogmaster of your request to remove it or it will remove within 24 hours.
This is not an invitation for webblog haters to spam with requests to remove content they feel that is objectionable and or unacceptable. Proof of URL ownership is required. NOTICE: This Blog Has Already Been Reviewed And Accepted By Blogger. com 🔗 External reference
The metal detector circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a transmitter coil generates an alternating magnetic field. When a metallic object is introduced into this field, eddy currents are induced in the object, which in turn generate their own magnetic field. This interaction modifies the frequency of the oscillators, allowing for the detection of metal objects.
The circuit typically consists of two main components: the transmitter and receiver coils. The transmitter coil is responsible for creating the magnetic field, while the receiver coil detects changes in the field caused by nearby metal objects. The mutual coupling between the coils is crucial, as it allows for the adjustment of the oscillation frequencies. This adjustment leads to a more refined detection capability, enabling the circuit to identify smaller or deeper metallic objects that standard BFO detectors may overlook.
In terms of design, the circuit may include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers to enhance signal processing and filtering. The output can be routed to an audio amplifier or a speaker, providing audible feedback to the user when a metal object is detected. The sensitivity and range of the detector can often be tuned by adjusting the values of the components in the circuit, allowing for customization based on the specific application or environment in which the metal detector will be used.
Overall, this metal detector circuit exemplifies a sophisticated application of mutual inductance principles, resulting in a highly effective tool for metal detection with improved performance over conventional designs.Here`s a metal detector circuit that frequencies of the two oscillators are then mixed in similar fashion to BFO, to produce an audible heterodyne. On the surface of it, this design would seem to represent little more than a twinned BFO metal detector.
What makes the metal detector different above all else ( check a simple metal detector ), and si gnificantly increases its range, is that each coil modifies the frequency of the adjacent oscillator through mutual coupling. This introduces the "balance" that is present in an IB metal detector, and boosts sensitivity well beyond that of BFO.
Disclaimer All files are found using legitimate search engine techniques. This site does not and will not condone hacking into sites to create the links it list. We will and do assume that all links found on the search engines we use are obtained in a legal manner and the webmasters are aware of the links listed on the search engines. If you find a URL that belongs to you, and you did not realize that it was "open to the public", please use the report button to notify the blogmaster of your request to remove it or it will remove within 24 hours.
This is not an invitation for webblog haters to spam with requests to remove content they feel that is objectionable and or unacceptable. Proof of URL ownership is required. NOTICE: This Blog Has Already Been Reviewed And Accepted By Blogger. com 🔗 External reference