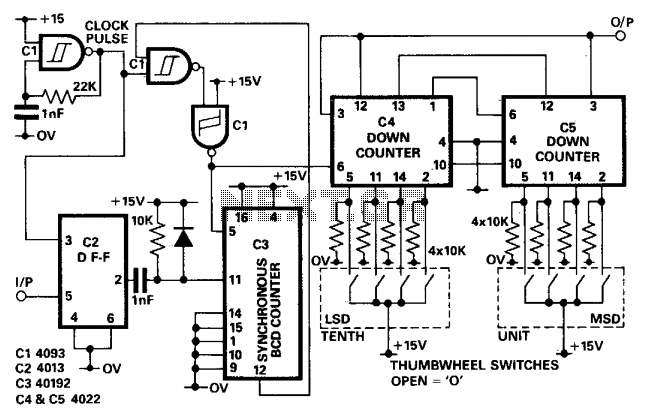
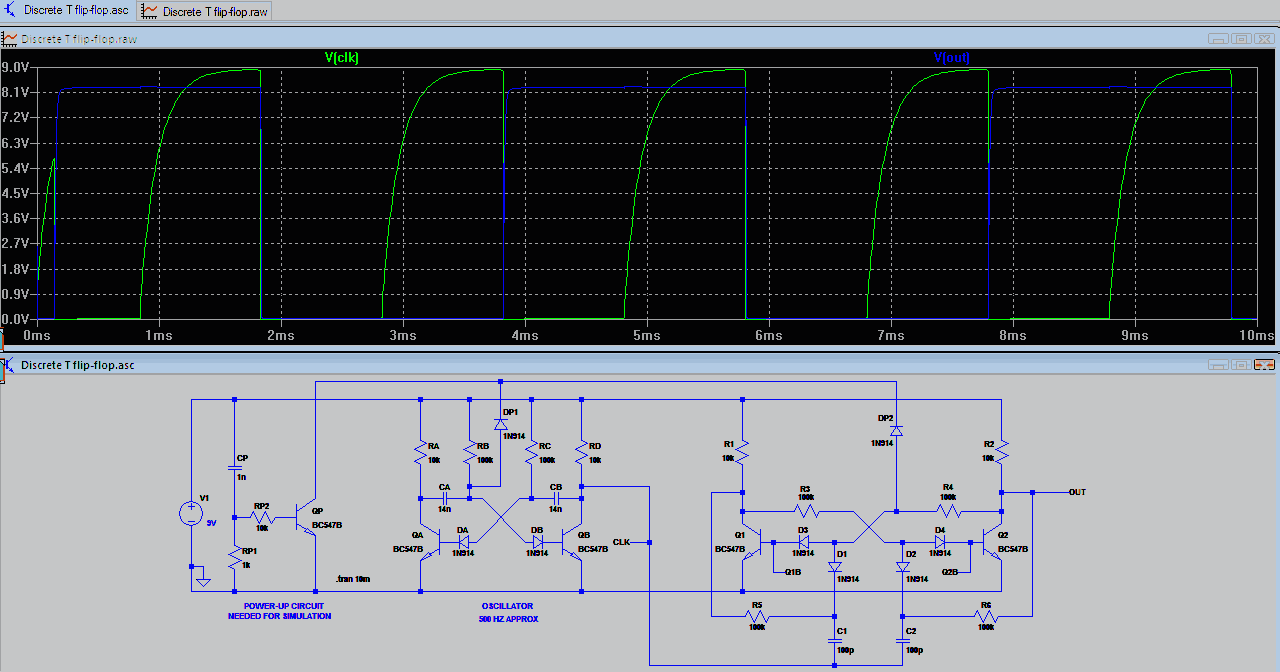
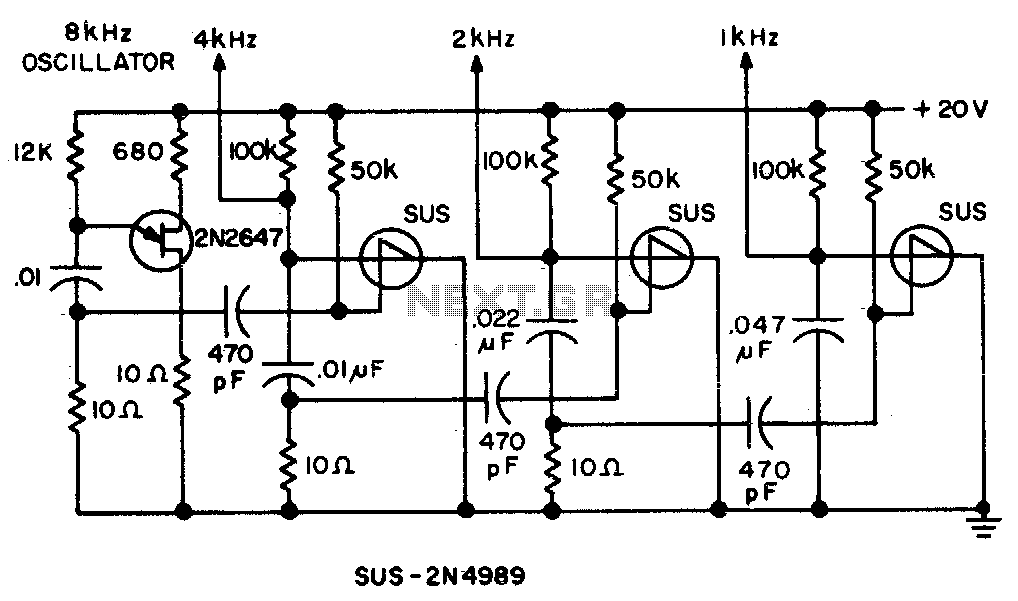
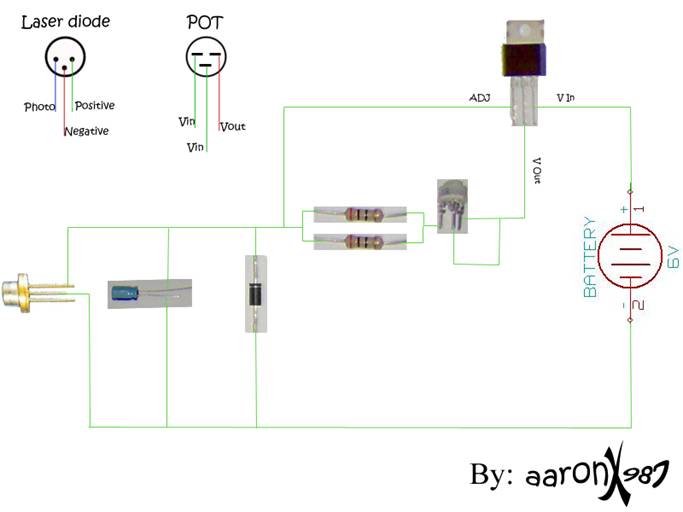
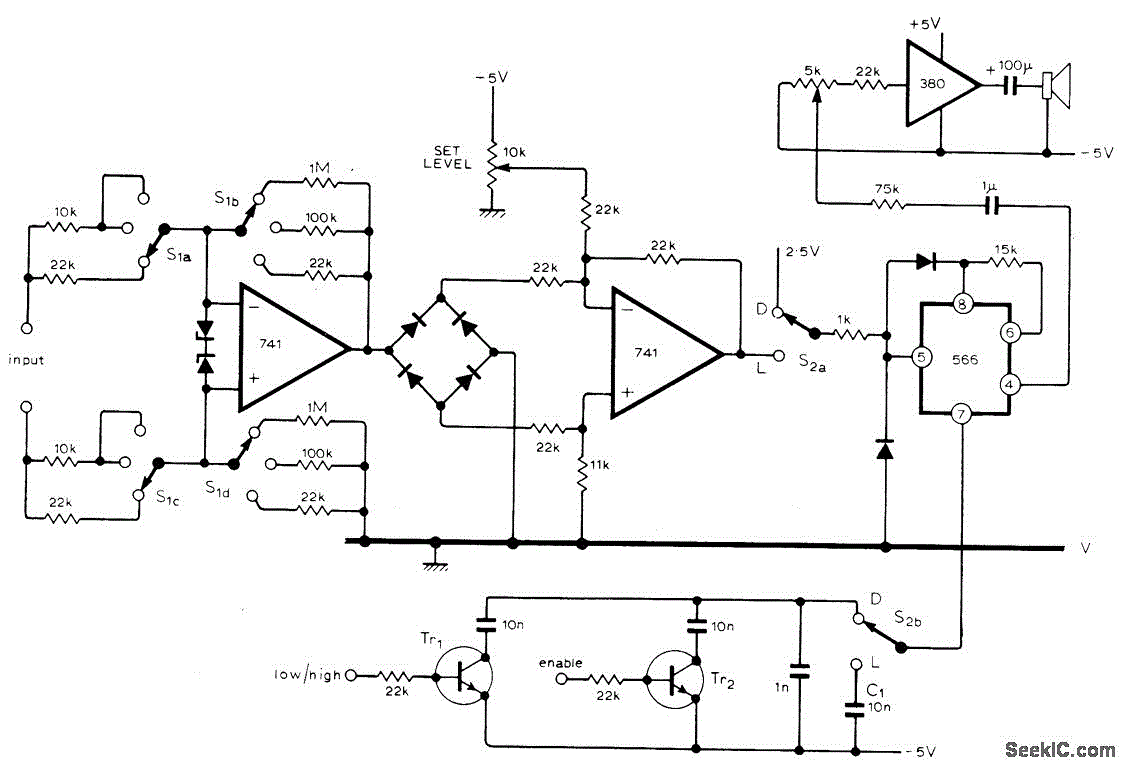
Binary divider chain
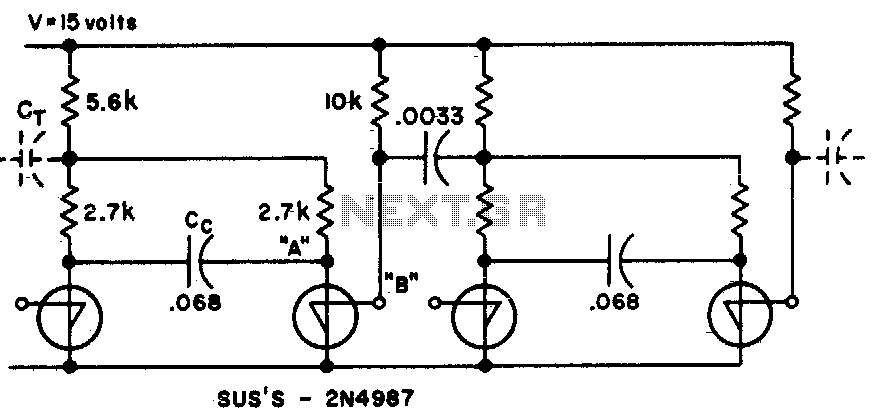
This circuit utilizes fewer components than traditional transistor flip-flops. The output at point "B" produces a transient-free waveform.
The circuit in question is designed to provide a simplified approach to signal processing by minimizing the number of components involved compared to conventional transistor flip-flops. This reduction in component count not only enhances reliability but also decreases the overall footprint of the circuit, making it suitable for compact applications.
The output at point "B" is noteworthy for its transient-free waveform, which indicates that the circuit is capable of delivering a stable signal without the usual spikes or dips that can occur during transitions. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in digital applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in clock generation or data communication.
In terms of operation, the circuit likely employs a combination of passive and active elements, such as resistors, capacitors, and potentially a single active device like a CMOS or a specific type of logic gate that can achieve the desired flip-flop behavior. The careful selection of these components enables the circuit to maintain its performance while ensuring that the output remains clean and free from undesirable transients.
The transient-free nature of the output can be attributed to the circuit's design, which may include features such as proper timing control and feedback mechanisms that stabilize the output signal. This makes the circuit particularly useful in applications where precision and reliability are critical, such as in timing circuits or digital signal processing systems.
Overall, this circuit represents an efficient solution for applications requiring reliable signal processing with minimal component usage, ensuring both performance and space efficiency.This circuit uses fewer components than transistor flip flops Output at "B" gives a transient-free waveform.
The circuit in question is designed to provide a simplified approach to signal processing by minimizing the number of components involved compared to conventional transistor flip-flops. This reduction in component count not only enhances reliability but also decreases the overall footprint of the circuit, making it suitable for compact applications.
The output at point "B" is noteworthy for its transient-free waveform, which indicates that the circuit is capable of delivering a stable signal without the usual spikes or dips that can occur during transitions. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in digital applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in clock generation or data communication.
In terms of operation, the circuit likely employs a combination of passive and active elements, such as resistors, capacitors, and potentially a single active device like a CMOS or a specific type of logic gate that can achieve the desired flip-flop behavior. The careful selection of these components enables the circuit to maintain its performance while ensuring that the output remains clean and free from undesirable transients.
The transient-free nature of the output can be attributed to the circuit's design, which may include features such as proper timing control and feedback mechanisms that stabilize the output signal. This makes the circuit particularly useful in applications where precision and reliability are critical, such as in timing circuits or digital signal processing systems.
Overall, this circuit represents an efficient solution for applications requiring reliable signal processing with minimal component usage, ensuring both performance and space efficiency.This circuit uses fewer components than transistor flip flops Output at "B" gives a transient-free waveform.