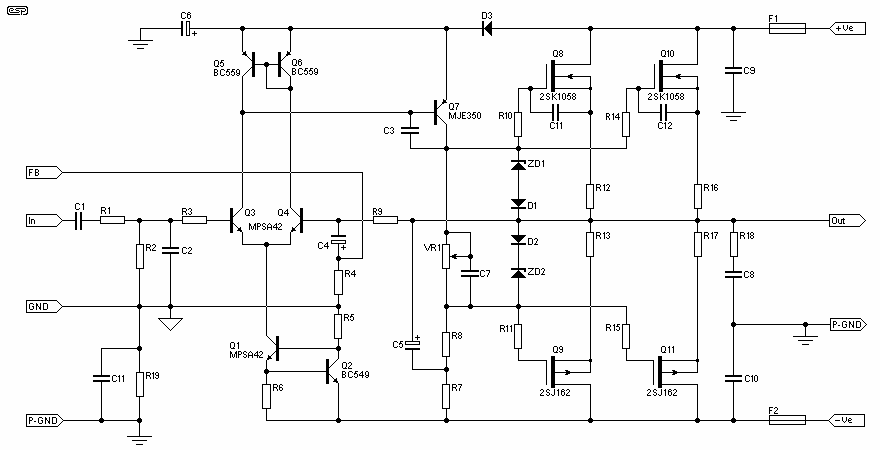
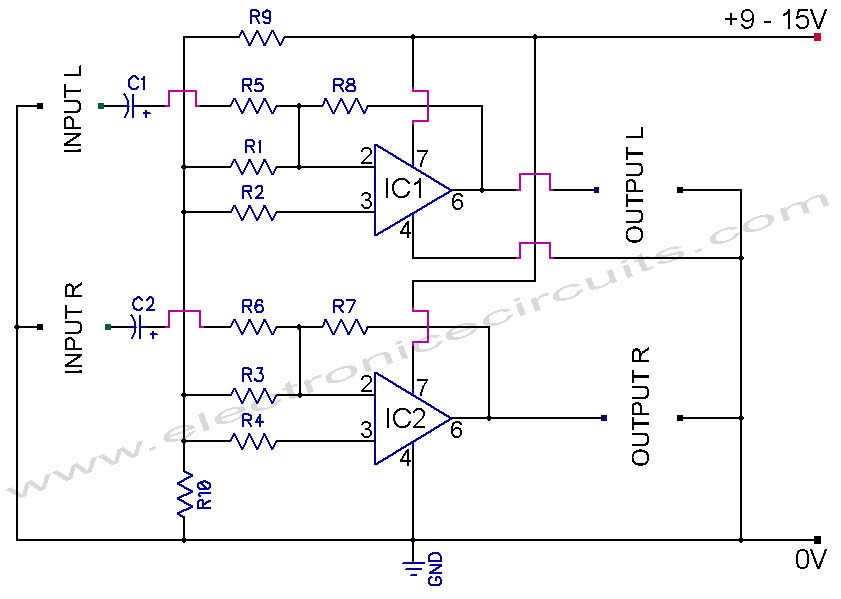
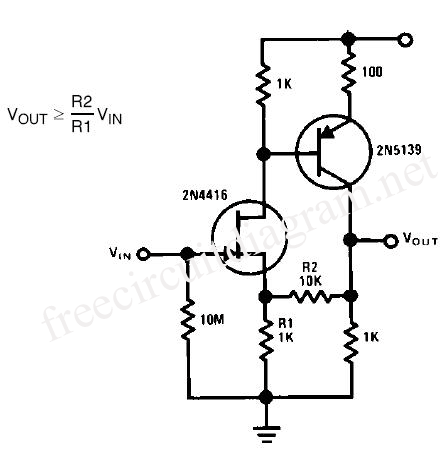
BMW40 Ibus tuner Amp Modification
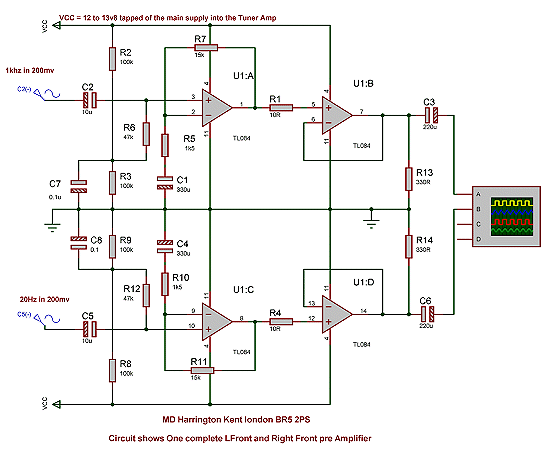
How the circuit works. The circuit comprises a non-inverting amplifier with a final output buffer stage or voltage follower for impedance matching.
The described circuit functions as a non-inverting amplifier, which is designed to amplify an input voltage while maintaining its phase. This configuration is ideal for applications where a high input impedance and low output impedance are required. The non-inverting amplifier utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the desired gain, which can be set by external resistors.
In this circuit, the gain (Av) is determined by the resistors connected to the op-amp, following the formula Av = 1 + (Rf/Rin), where Rf is the feedback resistor and Rin is the resistor connected to the input. This allows for precise control over the amplification level.
Following the amplification stage, a voltage follower or buffer stage is employed. This is typically implemented using another op-amp configured in a unity-gain configuration. The purpose of the buffer is to provide impedance matching between the high-impedance output of the amplifier and the load, which may have a lower impedance. The voltage follower ensures that the output voltage remains equal to the input voltage while providing the necessary current drive capability without affecting the performance of the preceding amplifier stage.
The entire circuit is powered by a dual power supply, providing both positive and negative voltage rails to the op-amps, which is essential for proper operation. Bypass capacitors are also included near the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation.
In summary, this circuit effectively amplifies an input voltage while maintaining integrity and providing the necessary impedance matching for subsequent stages or loads. It is commonly used in audio processing, sensor signal conditioning, and other applications requiring precise voltage amplification.How the circuit worksh1. Your title here The circuit comprises a non inverting amplifier with a final output buffer stage or voltage follower for impedance matchin.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a non-inverting amplifier, which is designed to amplify an input voltage while maintaining its phase. This configuration is ideal for applications where a high input impedance and low output impedance are required. The non-inverting amplifier utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the desired gain, which can be set by external resistors.
In this circuit, the gain (Av) is determined by the resistors connected to the op-amp, following the formula Av = 1 + (Rf/Rin), where Rf is the feedback resistor and Rin is the resistor connected to the input. This allows for precise control over the amplification level.
Following the amplification stage, a voltage follower or buffer stage is employed. This is typically implemented using another op-amp configured in a unity-gain configuration. The purpose of the buffer is to provide impedance matching between the high-impedance output of the amplifier and the load, which may have a lower impedance. The voltage follower ensures that the output voltage remains equal to the input voltage while providing the necessary current drive capability without affecting the performance of the preceding amplifier stage.
The entire circuit is powered by a dual power supply, providing both positive and negative voltage rails to the op-amps, which is essential for proper operation. Bypass capacitors are also included near the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation.
In summary, this circuit effectively amplifies an input voltage while maintaining integrity and providing the necessary impedance matching for subsequent stages or loads. It is commonly used in audio processing, sensor signal conditioning, and other applications requiring precise voltage amplification.How the circuit worksh1. Your title here The circuit comprises a non inverting amplifier with a final output buffer stage or voltage follower for impedance matchin.. 🔗 External reference