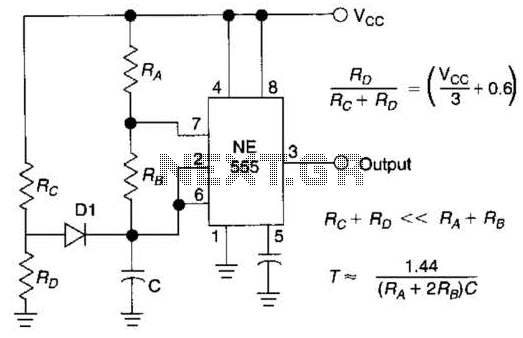
Buffer leakage current measurement circuit diagram OPA111 INA117
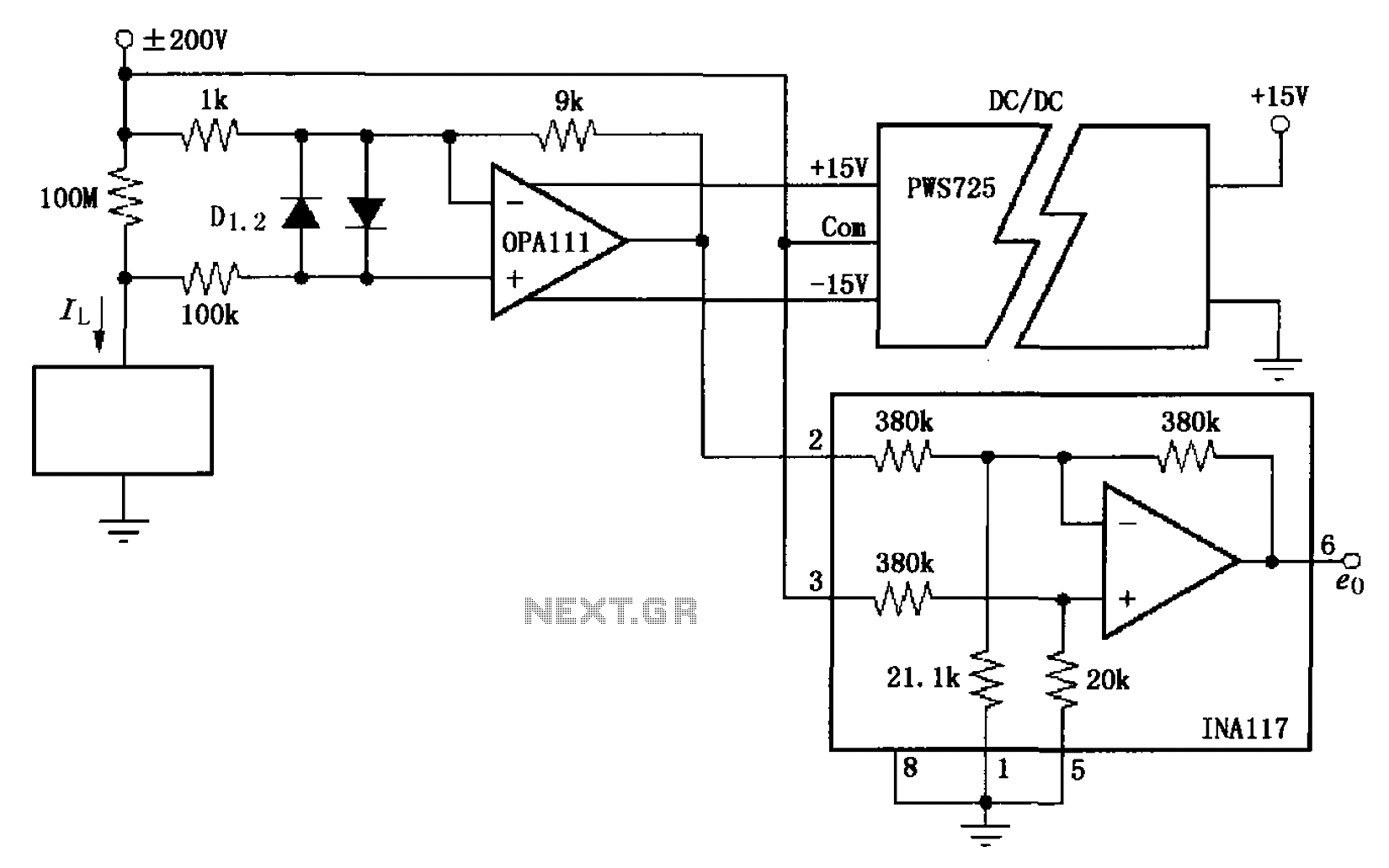
The circuit illustrated in FIG OPA111 is designed for measuring input buffer leakage current. The transistors D1 and D2, which are 2N3904 types, short the base and collector contacts while leaving the emitter open. When a power supply of up to 200V is applied to the device under test, the leakage current passes through a 100MΩ sampling resistor, creating a voltage drop across it. This voltage drop is then fed into the input of an INA117 amplifier, resulting in an output voltage represented as eo IL 109 (1V/nA). To accurately measure low leakage currents and minimize measurement errors caused by shunt effects, the circuit employs a high input resistance buffer. Additionally, the OPA111 operational amplifier is powered by an isolated power supply, enabling the circuit to handle a common-mode range of 200V.
The OPA111 circuit configuration serves as a precise tool for measuring low-level leakage currents in high-voltage applications. The transistors D1 and D2, both configured as a Darlington pair, help maintain a high input impedance while ensuring minimal leakage current into the measurement path. This configuration is critical for applications where even minute currents can significantly affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices.
The 100MΩ sampling resistor is a key component in this setup, as it converts the leakage current into a measurable voltage drop. The INA117 instrumentation amplifier is selected for its high input impedance and low offset voltage, which are essential for accurate readings of small voltage changes that correspond to the leakage current. The output voltage from the INA117 is scaled to provide a clear and interpretable output, allowing for straightforward analysis.
The use of an isolated power supply for the OPA111 operational amplifier is particularly advantageous in this design. It ensures that the high voltage applied to the device under test does not affect the integrity of the measurement circuit. The ability to handle a common-mode voltage of up to 200V means that this circuit can be used in various high-voltage applications without the risk of damage or inaccurate readings.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for accurately measuring leakage currents in high-voltage environments, leveraging high-impedance components and careful circuit design to ensure precision and reliability. As shown in FIG OPA111 constituted by the input buffer leakage current measuring circuit. D1, D2 of the transistor 2N3904, which will short the base and collector contact (open emitter). Up to 200V power is applied to the device under test, leakage current flows through 100M sampling resistor, forming a voltage drop across the sampling resistor, the voltage drop after the buffer input to the INA117 amplifier output, the output voltage eo IL 109 (1V/nA). Because you want to measure low leakage current, measurement circuit to prevent shunt caused by measurement error, so the use of high input resistance measurements constitute a buffer circuit.
With an isolated power supply OPA111 op amp power supply, so the circuit allows 200V common-mode range.
The OPA111 circuit configuration serves as a precise tool for measuring low-level leakage currents in high-voltage applications. The transistors D1 and D2, both configured as a Darlington pair, help maintain a high input impedance while ensuring minimal leakage current into the measurement path. This configuration is critical for applications where even minute currents can significantly affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices.
The 100MΩ sampling resistor is a key component in this setup, as it converts the leakage current into a measurable voltage drop. The INA117 instrumentation amplifier is selected for its high input impedance and low offset voltage, which are essential for accurate readings of small voltage changes that correspond to the leakage current. The output voltage from the INA117 is scaled to provide a clear and interpretable output, allowing for straightforward analysis.
The use of an isolated power supply for the OPA111 operational amplifier is particularly advantageous in this design. It ensures that the high voltage applied to the device under test does not affect the integrity of the measurement circuit. The ability to handle a common-mode voltage of up to 200V means that this circuit can be used in various high-voltage applications without the risk of damage or inaccurate readings.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for accurately measuring leakage currents in high-voltage environments, leveraging high-impedance components and careful circuit design to ensure precision and reliability. As shown in FIG OPA111 constituted by the input buffer leakage current measuring circuit. D1, D2 of the transistor 2N3904, which will short the base and collector contact (open emitter). Up to 200V power is applied to the device under test, leakage current flows through 100M sampling resistor, forming a voltage drop across the sampling resistor, the voltage drop after the buffer input to the INA117 amplifier output, the output voltage eo IL 109 (1V/nA). Because you want to measure low leakage current, measurement circuit to prevent shunt caused by measurement error, so the use of high input resistance measurements constitute a buffer circuit.
With an isolated power supply OPA111 op amp power supply, so the circuit allows 200V common-mode range.