building regulated 5v dc power supply
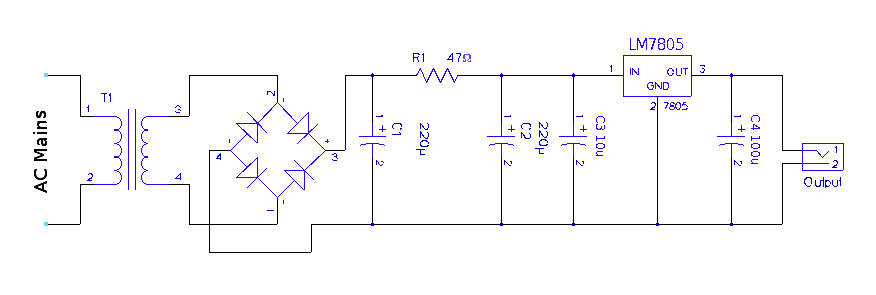
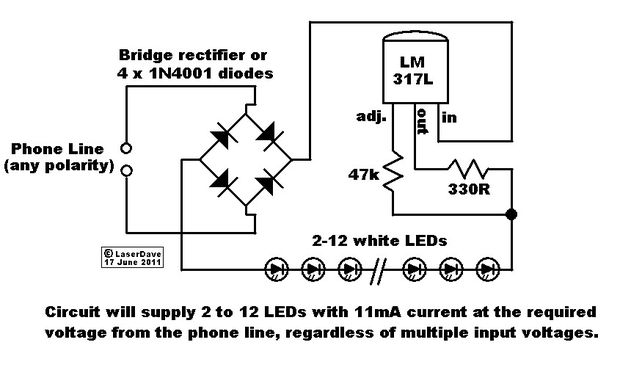
A regulated 5-volt DC supply is essential for powering microcontroller and TTL-based circuits. The output of most wall adapters is often too rippled and impure for use in digital circuits. An inexpensive power supply can be constructed using discrete components and a fixed voltage regulator IC. The circuit consists of three main blocks: the rectifier, filter, and regulator. The rectifier transforms the mains AC voltage into a suitable DC voltage. However, the output of the rectifier is an impure DC signal, necessitating a filter to clean the signal, followed by a regulator to provide a precise 5 volts, regardless of the load connected to the output. The circuit includes a transformer and a diode bridge, utilizing standard silicon 1N4007 diodes. A 12V transformer is selected, as the regulator IC requires at least 7.5V of input voltage to function effectively. A pi-filter is employed, consisting of two 220 µF capacitors and a resistor. Pi-filters are well-suited for light load applications like digital circuits. It is crucial to check the polarity of the capacitors before connecting them. The resistor is rated to dissipate up to 5W of power; while smaller 3W resistors may be used, their availability could be a concern. Avoid using 0.25W or 0.5W resistors. Voltage regulation is achieved using the three-terminal voltage regulator IC LM7805, which provides a stable 5V DC output against significant fluctuations in input voltage and load. The regulator includes internal protection circuits that activate during overload conditions. For pin configuration, position the regulator with its face towards you and legs pointing upward; the right pin is the input, the middle pin is ground, and the leftmost pin is the output. A 6.3mm or 3.5mm female mono TRS connector, commonly referred to as an audio jack, serves as the output port, enabling power delivery via standard audio cables. The completed circuit can fit into a 2.5 by 1.5-inch PCB, excluding the output jack and plug. A small switch can also be integrated at the output for convenient operation. The IC may be heat-sinked using multiple layers of aluminum foil to dissipate heat, or if enclosed in a metal box, the IC can be pinned to the box's sides; however, this is not strictly necessary.
The power supply circuit is designed to ensure reliable operation of microcontrollers and TTL-based circuits by providing a clean and stable 5V output. The rectifier stage employs a diode bridge configuration, converting the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC). The choice of the 12V transformer is critical, as it ensures that the voltage remains above the minimum input voltage required by the LM7805 regulator, which is essential for maintaining stable output.
The pi-filter configuration, consisting of capacitors and a resistor, effectively smooths the rectified output, reducing ripple voltage and enhancing the overall performance of the power supply. The use of 220 µF capacitors is appropriate for filtering, as they provide sufficient capacitance to handle transient loads typical in digital circuits.
The LM7805 voltage regulator is a robust choice for this application, featuring built-in thermal overload protection and short-circuit protection, enhancing the reliability of the power supply. The clear identification of pinouts facilitates easy integration into the circuit, ensuring that users can connect the regulator without confusion.
The output connector, a standard audio jack, is a practical solution for interfacing with various devices. This design allows for flexibility in power distribution, making it suitable for a range of applications in electronics. The compact PCB layout optimizes space, allowing for easy enclosure and integration into larger electronic systems.
Overall, this power supply circuit is an effective solution for providing a stable and regulated voltage source for microcontroller and TTL-based applications, ensuring that digital circuits operate efficiently and reliably.A regulated 5 volt DC supply is essential for powering micro-controller and TTL based circuits. The output of most wall-warts and adapters is to rippled and impure for use in digital circuits. Lets build an inexpensive power supply using some discrete components and a fixed voltage regulator IC. The circuit consists of three main blocks, the recti fier, filter and regulator. The rectifier is used to transform the mains AC voltage to a suitable DC voltage. The output of the rectifier is however an impure DC signal so we use a filter to clean the signal and finally a regulator to deliver precisely 5 volts, irrespective of the load connected to the output. It consists of a transformer and a diode bridge. The diodes are standard silicon 1N4007 diodes. We have chosen a 12V transformer because the regulator IC needs at-least 7. 5V of input voltage to function properly. We use a pi-filter here. The two 220 µF capacitors and resistor form the filter. Pi-filters are great for light load applications like digital circuits. Be sure to check the polarity of the capacitors before connecting them. The resistor shown above is one rated to dissipate up-to 5W of power across it. You may use smaller 3W resistors, but availability may be an issue. Don`t use the tiny 0. 25 W or 0. 5W ones though. The voltage is regulated by three terminal voltage regulator IC LM7805. This regulator provides stable 5V DC output against large fluctuations in input voltage and load. It also has internal protection circuits which `brownout` the device when overloaded. To decide the pin-outs, hold the regulator with its face towards you and legs pointing upward, the pin to the right is the input, middle pin is ground and left most pin is output.
A 6. 3mm or 3. 5mm female mono TRS connector (tip, ring, sleeve), also known as an `audio jack` serves as a great output port. The power can then be delivered via standard audio cables. The finished circuit fits neatly into a 2 by 1. 5 PCB, excluding the output jack and plug. You can also include a small switch at the out-put for easy operation. The IC can be heatsink-ed on multiple layers of aluminum foil to dissipate the heat, or if you are enclosing this in a metal box, pin the IC to the sides of the box.
This is not entirely necessary though. 🔗 External reference
The power supply circuit is designed to ensure reliable operation of microcontrollers and TTL-based circuits by providing a clean and stable 5V output. The rectifier stage employs a diode bridge configuration, converting the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC). The choice of the 12V transformer is critical, as it ensures that the voltage remains above the minimum input voltage required by the LM7805 regulator, which is essential for maintaining stable output.
The pi-filter configuration, consisting of capacitors and a resistor, effectively smooths the rectified output, reducing ripple voltage and enhancing the overall performance of the power supply. The use of 220 µF capacitors is appropriate for filtering, as they provide sufficient capacitance to handle transient loads typical in digital circuits.
The LM7805 voltage regulator is a robust choice for this application, featuring built-in thermal overload protection and short-circuit protection, enhancing the reliability of the power supply. The clear identification of pinouts facilitates easy integration into the circuit, ensuring that users can connect the regulator without confusion.
The output connector, a standard audio jack, is a practical solution for interfacing with various devices. This design allows for flexibility in power distribution, making it suitable for a range of applications in electronics. The compact PCB layout optimizes space, allowing for easy enclosure and integration into larger electronic systems.
Overall, this power supply circuit is an effective solution for providing a stable and regulated voltage source for microcontroller and TTL-based applications, ensuring that digital circuits operate efficiently and reliably.A regulated 5 volt DC supply is essential for powering micro-controller and TTL based circuits. The output of most wall-warts and adapters is to rippled and impure for use in digital circuits. Lets build an inexpensive power supply using some discrete components and a fixed voltage regulator IC. The circuit consists of three main blocks, the recti fier, filter and regulator. The rectifier is used to transform the mains AC voltage to a suitable DC voltage. The output of the rectifier is however an impure DC signal so we use a filter to clean the signal and finally a regulator to deliver precisely 5 volts, irrespective of the load connected to the output. It consists of a transformer and a diode bridge. The diodes are standard silicon 1N4007 diodes. We have chosen a 12V transformer because the regulator IC needs at-least 7. 5V of input voltage to function properly. We use a pi-filter here. The two 220 µF capacitors and resistor form the filter. Pi-filters are great for light load applications like digital circuits. Be sure to check the polarity of the capacitors before connecting them. The resistor shown above is one rated to dissipate up-to 5W of power across it. You may use smaller 3W resistors, but availability may be an issue. Don`t use the tiny 0. 25 W or 0. 5W ones though. The voltage is regulated by three terminal voltage regulator IC LM7805. This regulator provides stable 5V DC output against large fluctuations in input voltage and load. It also has internal protection circuits which `brownout` the device when overloaded. To decide the pin-outs, hold the regulator with its face towards you and legs pointing upward, the pin to the right is the input, middle pin is ground and left most pin is output.
A 6. 3mm or 3. 5mm female mono TRS connector (tip, ring, sleeve), also known as an `audio jack` serves as a great output port. The power can then be delivered via standard audio cables. The finished circuit fits neatly into a 2 by 1. 5 PCB, excluding the output jack and plug. You can also include a small switch at the out-put for easy operation. The IC can be heatsink-ed on multiple layers of aluminum foil to dissipate the heat, or if you are enclosing this in a metal box, pin the IC to the sides of the box.
This is not entirely necessary though. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713