Bus masters diagram
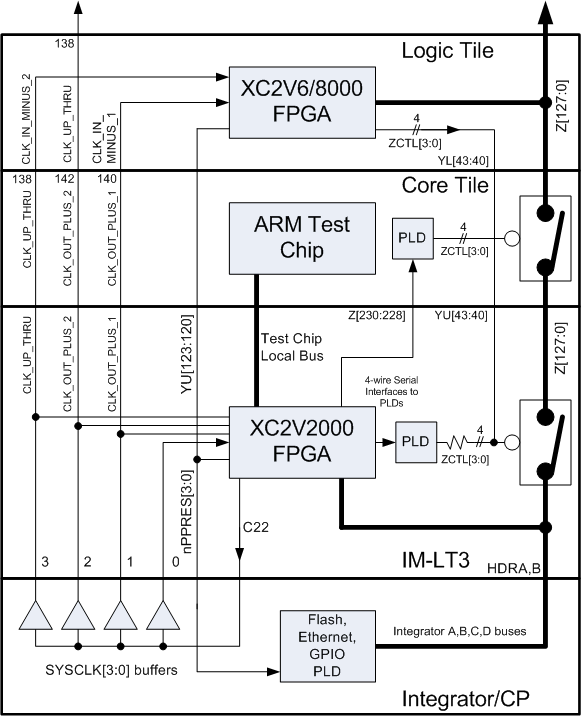
It is possible to add bus masters to the system, but a different bus architecture would be required since the Integrator/CP uses the AHB-Lite bus protocol, which allows only one bus master (the ARM CPU core). One way to add bus masters in a Logic Tile would be to instantiate a bridge in the IM-LT3 FPGA and split the Z[127:0] bus at the IM-LT3. The custom masters (and slaves) could then exist on the upper segment of this bus, while the Integrator/CP's AHB-Lite System bus would continue to exist on the lower segment of the bus.
The proposed system enhancement involves modifying the existing AHB-Lite bus architecture to accommodate multiple bus masters. The AHB-Lite protocol is inherently designed for single master operation, which limits its flexibility in multi-master configurations. To implement additional bus masters, a bridging mechanism within the IM-LT3 FPGA is suggested. This entails the division of the Z[127:0] bus into two segments: an upper segment dedicated to custom bus masters and slaves, and a lower segment reserved for the existing AHB-Lite System bus controlled by the ARM CPU core.
The implementation of this architecture requires careful consideration of signal integrity and timing, as the introduction of additional masters may lead to increased contention for bus resources. The bridge in the IM-LT3 FPGA will facilitate communication between the two bus segments, ensuring that data can be routed effectively without conflicts. It is essential to design the bridge with appropriate arbitration logic to manage access to the bus and prevent data collisions.
Additionally, the custom bus masters will need to be compatible with the existing bus protocol to ensure seamless integration. This may involve implementing specific interfaces or protocols that allow these masters to communicate effectively with the AHB-Lite System bus.
In conclusion, while the integration of multiple bus masters within the AHB-Lite architecture poses challenges, the proposed solution of utilizing a bridge within the IM-LT3 FPGA offers a viable pathway to enhance system capabilities. This configuration not only expands the functionality of the Logic Tile but also maintains the integrity and performance of the existing AHB-Lite protocol.It is possible to add bus masters to the system, but a different bus architecture would be required, since the Integrator/CP uses the AHB-Lite bus protocol, which allows only one bus master (the ARM CPU core). One way to add bus masters in a Logic Tile would be to instantiate a bridge in the IM-LT3 FPGA, and splitting the Z[127:0] bus at the IM-LT3.
The custom masters (and slaves) could then exist on the upper segment of this bus, and the Integrator/CP's AHB-Lite System bus would continue to exist on the lower segment of the bus. 🔗 External reference
The proposed system enhancement involves modifying the existing AHB-Lite bus architecture to accommodate multiple bus masters. The AHB-Lite protocol is inherently designed for single master operation, which limits its flexibility in multi-master configurations. To implement additional bus masters, a bridging mechanism within the IM-LT3 FPGA is suggested. This entails the division of the Z[127:0] bus into two segments: an upper segment dedicated to custom bus masters and slaves, and a lower segment reserved for the existing AHB-Lite System bus controlled by the ARM CPU core.
The implementation of this architecture requires careful consideration of signal integrity and timing, as the introduction of additional masters may lead to increased contention for bus resources. The bridge in the IM-LT3 FPGA will facilitate communication between the two bus segments, ensuring that data can be routed effectively without conflicts. It is essential to design the bridge with appropriate arbitration logic to manage access to the bus and prevent data collisions.
Additionally, the custom bus masters will need to be compatible with the existing bus protocol to ensure seamless integration. This may involve implementing specific interfaces or protocols that allow these masters to communicate effectively with the AHB-Lite System bus.
In conclusion, while the integration of multiple bus masters within the AHB-Lite architecture poses challenges, the proposed solution of utilizing a bridge within the IM-LT3 FPGA offers a viable pathway to enhance system capabilities. This configuration not only expands the functionality of the Logic Tile but also maintains the integrity and performance of the existing AHB-Lite protocol.It is possible to add bus masters to the system, but a different bus architecture would be required, since the Integrator/CP uses the AHB-Lite bus protocol, which allows only one bus master (the ARM CPU core). One way to add bus masters in a Logic Tile would be to instantiate a bridge in the IM-LT3 FPGA, and splitting the Z[127:0] bus at the IM-LT3.
The custom masters (and slaves) could then exist on the upper segment of this bus, and the Integrator/CP's AHB-Lite System bus would continue to exist on the lower segment of the bus. 🔗 External reference