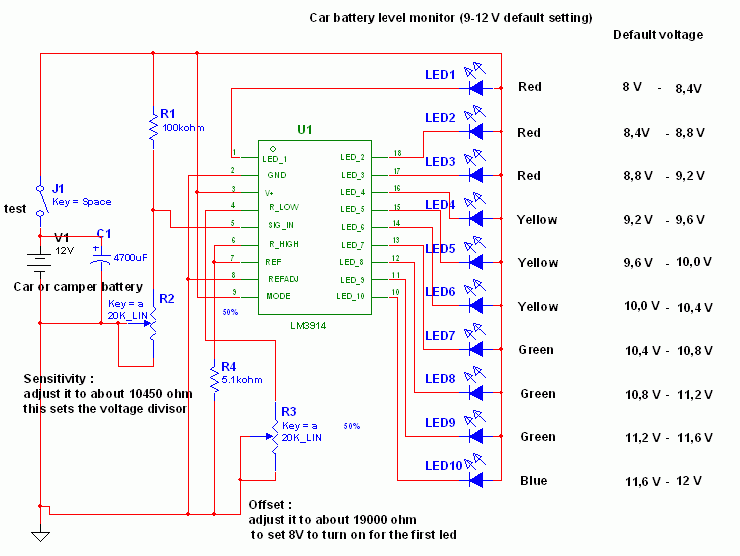
Car Lights Monitor
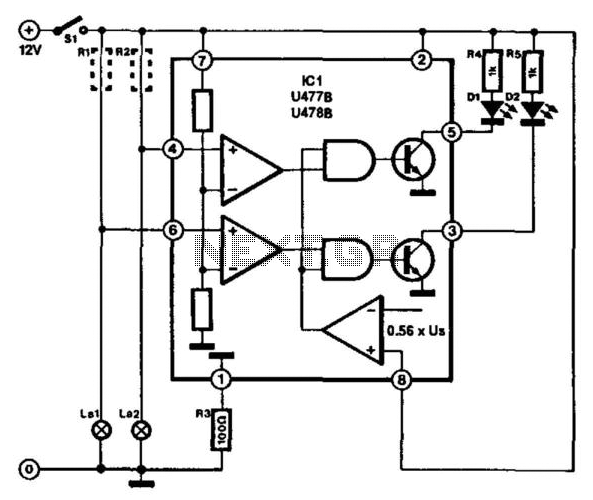
This circuit is designed for monitoring automotive lighting. Two specialized integrated circuits (ICs) from Telefunken are used to measure the current through a light bulb. Detecting whether current flows through a bulb is an effective method to determine its operational status. A small resistor is connected in series with the bulb, creating a small voltage drop when the bulb is illuminated (R1 and R2 in the diagram). Each IC can handle only two bulbs, necessitating the use of three or four ICs per vehicle. The junction of the bulb and resistor connects to one of the IC inputs (pin 4 or pin 6). The voltage across the resistor is compared within the IC to an internal reference voltage. Depending on the IC type, the required voltage drop is approximately 16 mV (U477B) or 100 mV (U478B). This minimal voltage drop does not impact the brightness of the bulb. The series resistor value can be calculated easily; for example, with a brake light (typically 21 W), the current through the bulb, assuming a 12-V battery, is 21 W / 12 V = 1.75 A. The necessary resistance is then 16 mΩ for U477B or 100 mΩ for U478B. These resistors can be constructed from resistance wire available from electrical suppliers, or standard circuit wire with a diameter of 0.7 mm, which has a specific resistance of about 100 mΩ per meter, may also be utilized. In many vehicles, the existing wiring may provide sufficient resistance to function as the series resistor. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) can be connected to the outputs of the IC (pins 3 and 5) to indicate when a car light is not functioning properly.
The automotive lighting monitoring circuit employs two Telefunken ICs, specifically designed to detect current flow through light bulbs, thereby indicating their operational status. The circuit's design utilizes a series resistor placed alongside the bulb to create a measurable voltage drop when the bulb is activated. This voltage drop is critical for the IC's functionality, as it allows the IC to compare the voltage against an internal reference, ensuring accurate detection of the bulb's status.
For practical implementation, the circuit requires careful selection of the series resistor's value based on the bulb's power rating and the vehicle's battery voltage. The calculations provided illustrate the relationship between the bulb's wattage, the supply voltage, and the required resistance to achieve the necessary voltage drop for each specific IC model. The use of resistance wire or standard circuit wire for the series resistor provides flexibility in sourcing materials, while also accommodating the potential for existing vehicle wiring to suffice as the series resistor.
The output pins of the ICs allow for the integration of visual indicators, such as LEDs, which serve as alerts for bulb failures. This feature enhances the circuit's utility, providing immediate feedback to the vehicle operator regarding the status of critical lighting components. Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for automotive lighting monitoring, leveraging precise measurements and effective signaling to ensure vehicle safety. This circuit is for the purpose of monitoring automotive lighting. Two special ICs are available from Telefunken that ar e designed to measure the current through a light bulb. In practice, detecting whether a current flows through a bulb or not is a most suitable way of determining whether the bulb still works. If a small resistance is connected in series with a bulb, a small voltage drop will develop across it when the bulb lights (R1 and R2 in the diagram).
Each IC can cope with only two bulbs, so three or four ICs are needed per car. The junction of the bulb and resistor is connected to one of the inputs (pin 4 or pin 6) of the IC. The potential across the resistor is compared in the IC with an internal reference voltage. Depending on which of the two ICs is used, the voltage drop must be about 16 mV (U477B) or 100 mV (U478B). This voltage drop is so small that it will not affect the brightness of the relevant bulb. The value of the series resistor is determined quite easily. If, for instance, it is in series with the brake light (normally 21 W), the current through the bulb, assuming that the vehicle has a 12-V battery, is 21-r 12 = 1.75 A.
The resistance must then be of 16^-1.75 = 9 mQ (U477B) or 100-r 1.75 = 57 mU (U478B). These resistors can be made from a length of resistance wire (available from most electrical retailers). Failing that, standard circuit wire of 0.7 mm diameter can be used. This has a specific resistance of about 100 mQ per meter. However, in most cars, the existing wiring will have sufficient resistance to serve as series resistor.
LEDs can be connected to the outputs of the IC (pins 3 and 5). These will only light if the relevant car light fails to work properly. 🔗 External reference
The automotive lighting monitoring circuit employs two Telefunken ICs, specifically designed to detect current flow through light bulbs, thereby indicating their operational status. The circuit's design utilizes a series resistor placed alongside the bulb to create a measurable voltage drop when the bulb is activated. This voltage drop is critical for the IC's functionality, as it allows the IC to compare the voltage against an internal reference, ensuring accurate detection of the bulb's status.
For practical implementation, the circuit requires careful selection of the series resistor's value based on the bulb's power rating and the vehicle's battery voltage. The calculations provided illustrate the relationship between the bulb's wattage, the supply voltage, and the required resistance to achieve the necessary voltage drop for each specific IC model. The use of resistance wire or standard circuit wire for the series resistor provides flexibility in sourcing materials, while also accommodating the potential for existing vehicle wiring to suffice as the series resistor.
The output pins of the ICs allow for the integration of visual indicators, such as LEDs, which serve as alerts for bulb failures. This feature enhances the circuit's utility, providing immediate feedback to the vehicle operator regarding the status of critical lighting components. Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for automotive lighting monitoring, leveraging precise measurements and effective signaling to ensure vehicle safety. This circuit is for the purpose of monitoring automotive lighting. Two special ICs are available from Telefunken that ar e designed to measure the current through a light bulb. In practice, detecting whether a current flows through a bulb or not is a most suitable way of determining whether the bulb still works. If a small resistance is connected in series with a bulb, a small voltage drop will develop across it when the bulb lights (R1 and R2 in the diagram).
Each IC can cope with only two bulbs, so three or four ICs are needed per car. The junction of the bulb and resistor is connected to one of the inputs (pin 4 or pin 6) of the IC. The potential across the resistor is compared in the IC with an internal reference voltage. Depending on which of the two ICs is used, the voltage drop must be about 16 mV (U477B) or 100 mV (U478B). This voltage drop is so small that it will not affect the brightness of the relevant bulb. The value of the series resistor is determined quite easily. If, for instance, it is in series with the brake light (normally 21 W), the current through the bulb, assuming that the vehicle has a 12-V battery, is 21-r 12 = 1.75 A.
The resistance must then be of 16^-1.75 = 9 mQ (U477B) or 100-r 1.75 = 57 mU (U478B). These resistors can be made from a length of resistance wire (available from most electrical retailers). Failing that, standard circuit wire of 0.7 mm diameter can be used. This has a specific resistance of about 100 mQ per meter. However, in most cars, the existing wiring will have sufficient resistance to serve as series resistor.
LEDs can be connected to the outputs of the IC (pins 3 and 5). These will only light if the relevant car light fails to work properly. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713