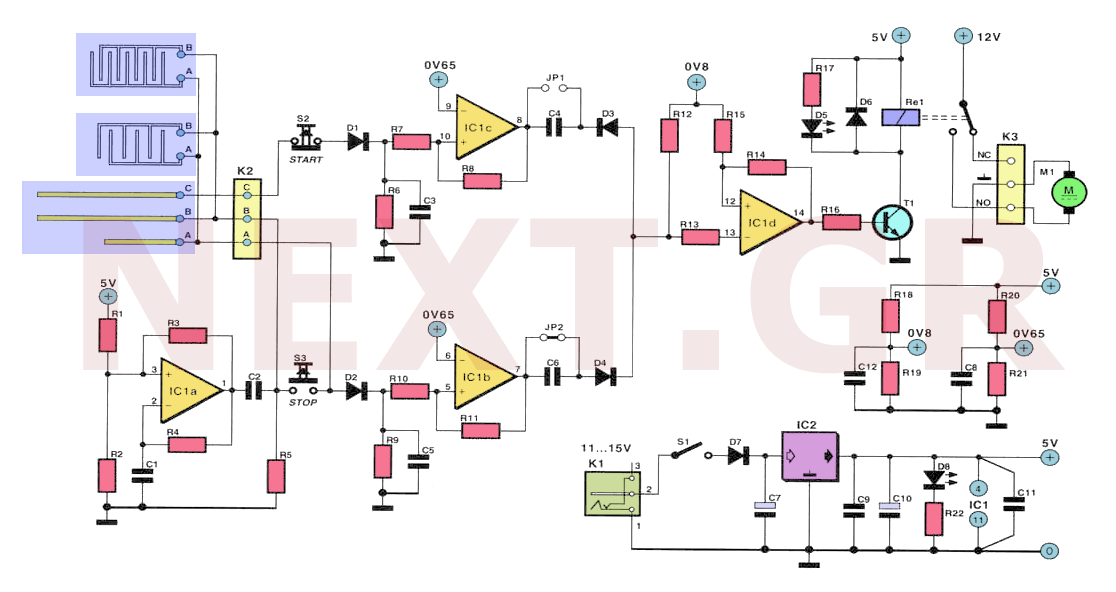
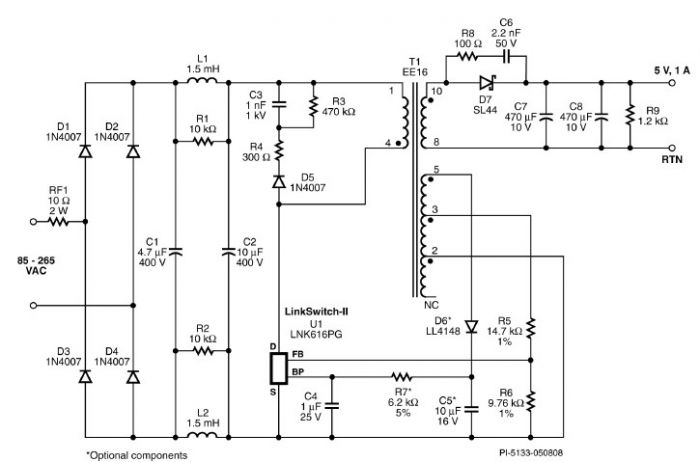
car parking sensor circuit using infra
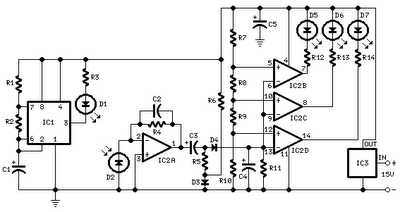
All distances mentioned can vary depending on the infrared transmitting and receiving LEDs used and are significantly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces greatly reduce the device's sensitivity. This circuit can also be applied in various applications such as liquid level detection and proximity devices. The infrared photodiode D2 should be of a type that includes an optical sunlight filter; these components are typically housed in black plastic cases. Some resemble TO92 transistors; in such cases, it is important to note that the sensitive surface is the curved side, not the flat side. It is advisable to enclose all the circuitry near the infrared LEDs within a compact box. The three signaling LEDs can be positioned away from the main box at a height that makes them easily visible to the car driver. The optimal setup is achieved by bringing D2 closer to D1 (without a reflecting object) until D5 illuminates, then slightly moving it away until D5 is clearly off. Typically, the ideal distance between D1 and D2 is in the range of 1.5 to 3 cm.
The described circuit utilizes infrared (IR) LEDs for transmission and reception, which can be applied in various sensing applications. The performance of the circuit is influenced by the type of infrared LEDs selected, with specific attention given to their wavelength and output power. The sensitivity of the system is notably impacted by the color of the reflecting surface; lighter surfaces tend to enhance sensitivity, while darker surfaces, particularly black, significantly diminish it.
The integration of an infrared photodiode (D2) with an optical sunlight filter is crucial for ensuring reliable operation in environments with ambient light. The design recommendation indicates that this photodiode should be housed in a black plastic casing to minimize interference from external light sources. The photodiode's sensitivity is maximized when the curved surface is oriented correctly, as it is designed to capture more incoming infrared light effectively.
The circuit should be compact, with all components, including the infrared LEDs, housed together to reduce the influence of external factors and maintain signal integrity. The signaling LEDs, which indicate the status of the system, should be placed at an elevated position for optimal visibility, ensuring that they can be easily seen by the operator, such as a car driver.
For calibration, the procedure involves adjusting the distance between the transmitting LED (D1) and the photodiode (D2). The optimal distance is critical for achieving the desired response from the signaling LED (D5). This adjustment should be performed carefully, starting from a close proximity and gradually increasing the distance until D5 turns off, indicating the effective range has been surpassed. Typically, the ideal operational distance between D1 and D2 is maintained within 1.5 to 3 cm, ensuring reliable detection and signaling for the intended applications.
This circuit design offers flexibility for various applications, including liquid level detection and proximity sensing, making it a versatile choice for engineers and developers in the field of electronics.All distances mentioned before can vary, depending on infra-red transmitting and receiving LEDs used and are mostly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces lower greatly the device sensitivity. Obviously, you can use this circuit in other applications like liquids level detection, proximity devices etc.
The infra-red Photo Diode D2, should be of the type incorporating an optical sunlight filter: these components appear in black plastic cases. Some of them resemble TO92 transistors: in this case, please note that the sensitive surface is the curved, not the flat one.
It is wiser to place all the circuitry near the infra-red LEDs in a small box. The 3 signaling LEDs can be placed far from the main box at an height making them well visible by the car driver. The best setup is obtained bringing D2 nearer to D1 (without a reflecting object) until D5 illuminates; then moving it a bit until D5 is clearly off.
Usually D1-D2 optimum distance lies in the range 1. 5-3 cm. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes infrared (IR) LEDs for transmission and reception, which can be applied in various sensing applications. The performance of the circuit is influenced by the type of infrared LEDs selected, with specific attention given to their wavelength and output power. The sensitivity of the system is notably impacted by the color of the reflecting surface; lighter surfaces tend to enhance sensitivity, while darker surfaces, particularly black, significantly diminish it.
The integration of an infrared photodiode (D2) with an optical sunlight filter is crucial for ensuring reliable operation in environments with ambient light. The design recommendation indicates that this photodiode should be housed in a black plastic casing to minimize interference from external light sources. The photodiode's sensitivity is maximized when the curved surface is oriented correctly, as it is designed to capture more incoming infrared light effectively.
The circuit should be compact, with all components, including the infrared LEDs, housed together to reduce the influence of external factors and maintain signal integrity. The signaling LEDs, which indicate the status of the system, should be placed at an elevated position for optimal visibility, ensuring that they can be easily seen by the operator, such as a car driver.
For calibration, the procedure involves adjusting the distance between the transmitting LED (D1) and the photodiode (D2). The optimal distance is critical for achieving the desired response from the signaling LED (D5). This adjustment should be performed carefully, starting from a close proximity and gradually increasing the distance until D5 turns off, indicating the effective range has been surpassed. Typically, the ideal operational distance between D1 and D2 is maintained within 1.5 to 3 cm, ensuring reliable detection and signaling for the intended applications.
This circuit design offers flexibility for various applications, including liquid level detection and proximity sensing, making it a versatile choice for engineers and developers in the field of electronics.All distances mentioned before can vary, depending on infra-red transmitting and receiving LEDs used and are mostly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces lower greatly the device sensitivity. Obviously, you can use this circuit in other applications like liquids level detection, proximity devices etc.
The infra-red Photo Diode D2, should be of the type incorporating an optical sunlight filter: these components appear in black plastic cases. Some of them resemble TO92 transistors: in this case, please note that the sensitive surface is the curved, not the flat one.
It is wiser to place all the circuitry near the infra-red LEDs in a small box. The 3 signaling LEDs can be placed far from the main box at an height making them well visible by the car driver. The best setup is obtained bringing D2 nearer to D1 (without a reflecting object) until D5 illuminates; then moving it a bit until D5 is clearly off.
Usually D1-D2 optimum distance lies in the range 1. 5-3 cm. 🔗 External reference