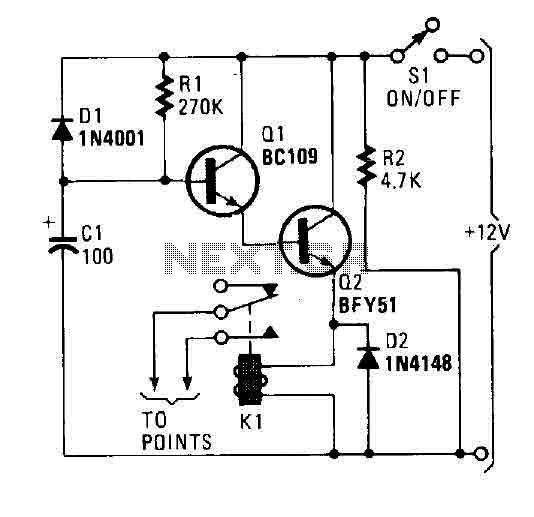
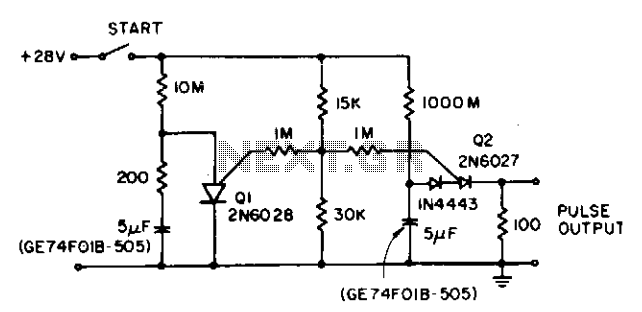
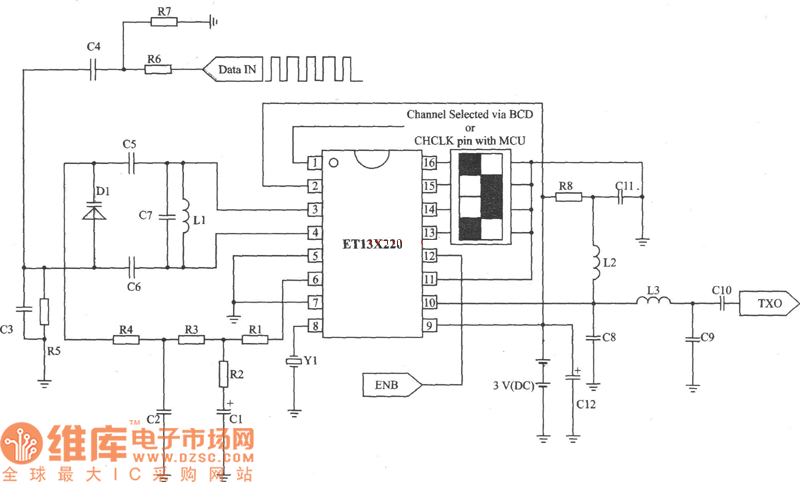
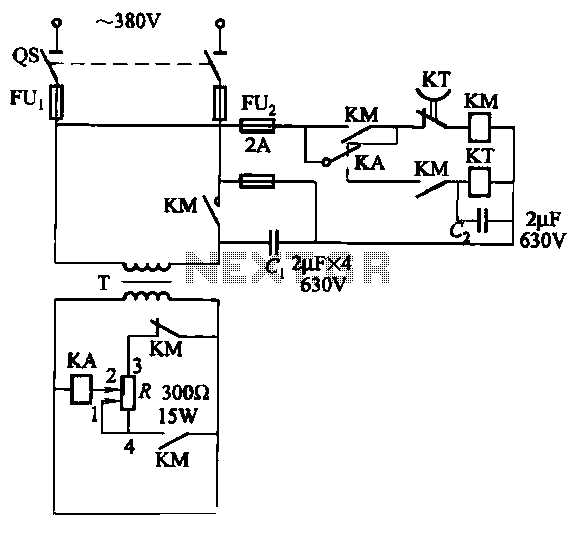
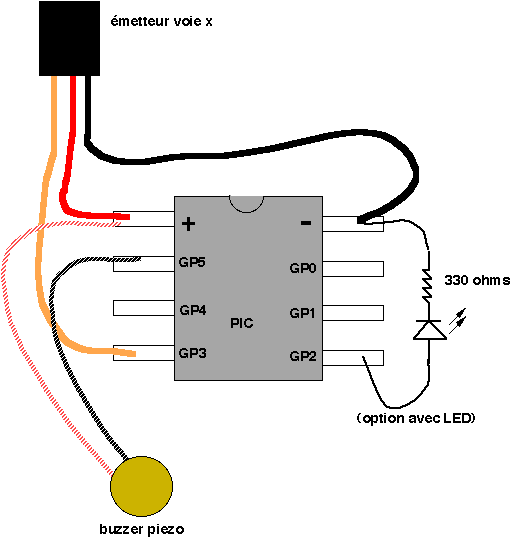
CB85-10 leakage protection circuit

CB85-10 leakage protection circuit diagram, T for the trip coil, SB is the test button, Ri is simulated human resistance.
The CB85-10 leakage protection circuit is designed to enhance safety by detecting leakage currents and disconnecting the electrical supply to prevent electric shocks. The circuit includes a trip coil (T), which is the actuator responsible for opening the circuit when a leakage is detected. The test button (SB) allows users to simulate a fault condition to verify the functionality of the protection circuit. The simulated human resistance (Ri) represents the resistance of a human body, which is critical for determining the threshold at which the circuit will activate.
In this schematic, the trip coil is connected to a relay that interrupts the power supply when a leakage current exceeds a predetermined level. The test button is strategically placed in the circuit to facilitate routine testing, ensuring that the leakage protection system is operational. The simulated human resistance is typically set to approximate the resistance of a person under fault conditions, allowing the circuit to react appropriately to real-world scenarios.
The circuit operates under the principle of differential current sensing, where the current flowing through the live and neutral wires is continuously monitored. If a difference in current is detected, indicative of leakage, the trip coil is energized, causing the relay to open and disconnect the load. This design emphasizes reliability and safety, making it suitable for various applications in residential and commercial electrical systems. Regular testing via the test button is essential to maintain the integrity of the leakage protection mechanism. CB85-10 leakage protection circuit diagram, T for the trip coil, SB is the test button, Ri is simulated human resistance
The CB85-10 leakage protection circuit is designed to enhance safety by detecting leakage currents and disconnecting the electrical supply to prevent electric shocks. The circuit includes a trip coil (T), which is the actuator responsible for opening the circuit when a leakage is detected. The test button (SB) allows users to simulate a fault condition to verify the functionality of the protection circuit. The simulated human resistance (Ri) represents the resistance of a human body, which is critical for determining the threshold at which the circuit will activate.
In this schematic, the trip coil is connected to a relay that interrupts the power supply when a leakage current exceeds a predetermined level. The test button is strategically placed in the circuit to facilitate routine testing, ensuring that the leakage protection system is operational. The simulated human resistance is typically set to approximate the resistance of a person under fault conditions, allowing the circuit to react appropriately to real-world scenarios.
The circuit operates under the principle of differential current sensing, where the current flowing through the live and neutral wires is continuously monitored. If a difference in current is detected, indicative of leakage, the trip coil is energized, causing the relay to open and disconnect the load. This design emphasizes reliability and safety, making it suitable for various applications in residential and commercial electrical systems. Regular testing via the test button is essential to maintain the integrity of the leakage protection mechanism. CB85-10 leakage protection circuit diagram, T for the trip coil, SB is the test button, Ri is simulated human resistance