charger for all battery types

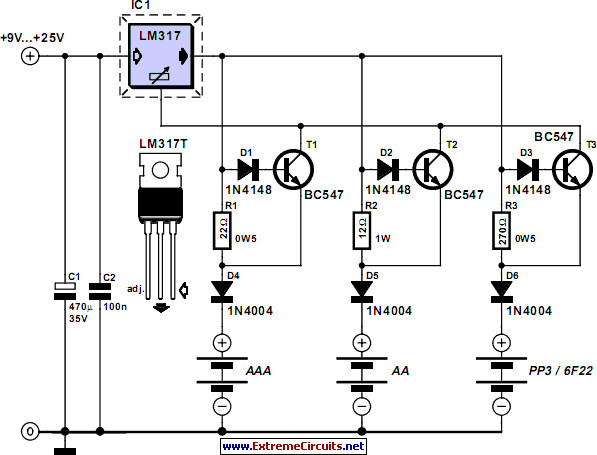
Charger for all battery types power supply. This lithium battery charger circuit is dedicated to charging lithium batteries. It uses two chips: the voltage regulator LM317T and ICL7665, which warns microprocessors of overvoltage and undervoltage conditions. Charging is completed with a constant current of 60 mA for AA cells to a cutoff voltage of 2.4 V per cell, at which point the charge should be terminated.
The charger circuit described is designed to accommodate various battery types, with a specific focus on lithium batteries. The core components include the LM317T voltage regulator, which is utilized for its ability to provide a stable output voltage necessary for charging lithium cells. The ICL7665 integrated circuit serves as a supervisory device, monitoring the voltage levels to prevent overvoltage and undervoltage conditions that could potentially damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
The charging process is initiated with a constant current of 60 mA, which is optimal for AA lithium cells. This current ensures that the batteries are charged efficiently without overheating. The circuit is designed to automatically terminate the charging process once the cells reach a cutoff voltage of 2.4 V. This cutoff is critical, as exceeding this voltage can lead to safety hazards, including battery swelling or leakage.
In terms of the schematic design, the LM317T is configured in a standard voltage regulator setup, with resistors determining the output voltage. The ICL7665 is integrated into the circuit to provide feedback to the microprocessor, allowing for real-time monitoring of the battery's voltage status. The microprocessor can then control the charging process, ensuring that the current remains constant until the cutoff voltage is achieved.
Additional components may include capacitors for filtering and stabilization, as well as protection diodes to prevent reverse polarity connections. The overall design emphasizes safety, efficiency, and adaptability, making it suitable for a wide range of lithium battery charging applications.Charger for All Battery Types power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. This Lithium batterychargercircuitis dedicatedto chargelithiumbatteries. Ituses 2chips, voltage regulatorLM317TandICL7665warnsmicroprocessors( Ps)ofovervoltageand undervolta geconditions. Charging is completed with a constant current of 60 ma for Aa cells to a cutoff voltage of 2. 4 V per cell, at which point the charge should be terminated. The. 🔗 External reference
The charger circuit described is designed to accommodate various battery types, with a specific focus on lithium batteries. The core components include the LM317T voltage regulator, which is utilized for its ability to provide a stable output voltage necessary for charging lithium cells. The ICL7665 integrated circuit serves as a supervisory device, monitoring the voltage levels to prevent overvoltage and undervoltage conditions that could potentially damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
The charging process is initiated with a constant current of 60 mA, which is optimal for AA lithium cells. This current ensures that the batteries are charged efficiently without overheating. The circuit is designed to automatically terminate the charging process once the cells reach a cutoff voltage of 2.4 V. This cutoff is critical, as exceeding this voltage can lead to safety hazards, including battery swelling or leakage.
In terms of the schematic design, the LM317T is configured in a standard voltage regulator setup, with resistors determining the output voltage. The ICL7665 is integrated into the circuit to provide feedback to the microprocessor, allowing for real-time monitoring of the battery's voltage status. The microprocessor can then control the charging process, ensuring that the current remains constant until the cutoff voltage is achieved.
Additional components may include capacitors for filtering and stabilization, as well as protection diodes to prevent reverse polarity connections. The overall design emphasizes safety, efficiency, and adaptability, making it suitable for a wide range of lithium battery charging applications.Charger for All Battery Types power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. This Lithium batterychargercircuitis dedicatedto chargelithiumbatteries. Ituses 2chips, voltage regulatorLM317TandICL7665warnsmicroprocessors( Ps)ofovervoltageand undervolta geconditions. Charging is completed with a constant current of 60 ma for Aa cells to a cutoff voltage of 2. 4 V per cell, at which point the charge should be terminated. The. 🔗 External reference