NE602 INPUT CIRCUITS
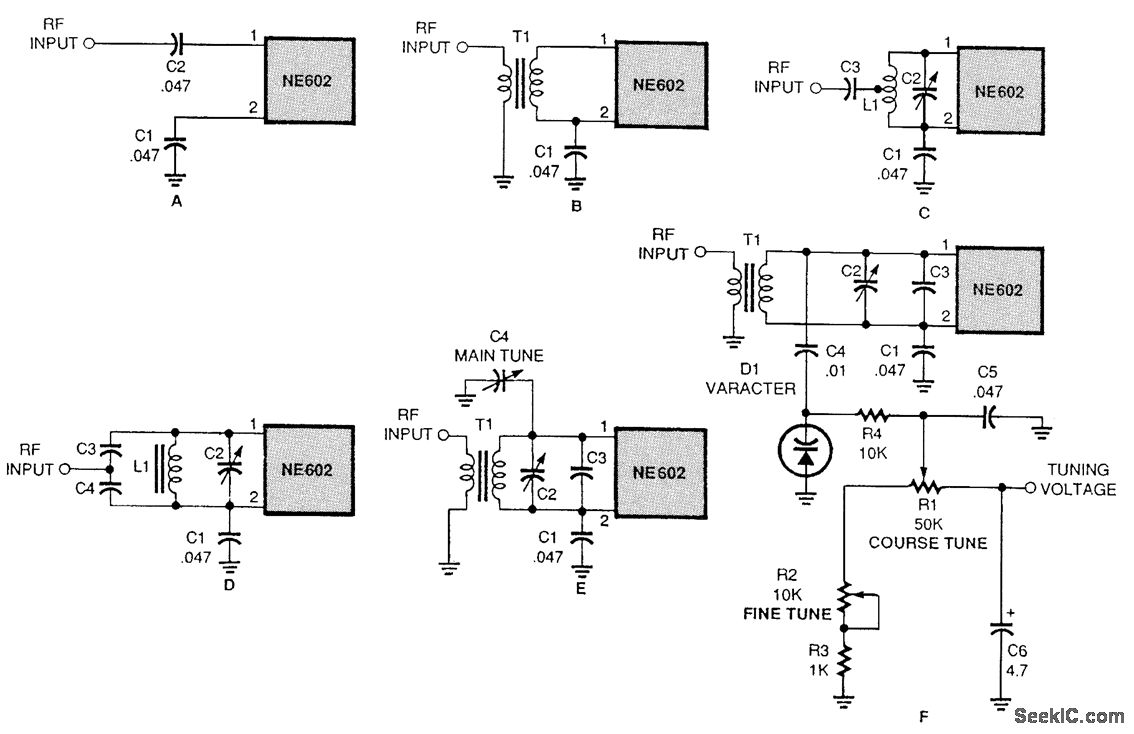
There are several methods to input a signal into the NE602. Simple untuned approaches (a and b) are viable. For tuning to a specific frequency, an LC resonant circuit with ungrounded trimmer capacitors (c and d) or grounded variable capacitors (e) can be utilized. Additionally, a tuning voltage can be applied in conjunction with a varactor (f).
The NE602 is a popular dual balanced mixer often used in radio frequency applications. Signal input can be achieved through various methods, each tailored to specific requirements. The untuned methods (a and b) are straightforward and do not require precise frequency adjustments, making them suitable for applications where simplicity is preferred.
For applications that necessitate tuning to a specific frequency, the use of an LC resonant circuit is recommended. This circuit can be constructed using ungrounded trimmer capacitors (c and d), which allow for fine-tuning of the resonant frequency. The trimmer capacitors can be adjusted to achieve the desired frequency response, providing flexibility in signal input.
Alternatively, grounded variable capacitors (e) can also be employed in the resonant circuit. These components offer a more stable tuning mechanism, as they are less susceptible to noise and interference. The grounded configuration helps maintain consistent performance over a range of frequencies.
A more advanced approach involves the use of a varactor (f), which is a voltage-controlled capacitor. By applying a tuning voltage to the varactor, the capacitance can be dynamically adjusted, allowing for real-time tuning of the input signal frequency. This method is particularly useful in applications requiring rapid frequency changes or in situations where space is limited, as it eliminates the need for bulky tuning components.
In summary, the NE602 provides flexibility in signal input through various methods, from simple untuned approaches to sophisticated tuned circuits using trimmer capacitors, grounded variable capacitors, or varactors, each suited to different application needs.A few of the many ways to input a signal into the NE602. Simple untuned methods (a and b) are acceptable. If you need to tune to a specific frequency, you can use an LC resonant circuit with un-grounded trimmer capacitors (c and d) or with grounded variable capacitors (e). You can even use a tuning voltage in connection with a varactor (f). 🔗 External reference
The NE602 is a popular dual balanced mixer often used in radio frequency applications. Signal input can be achieved through various methods, each tailored to specific requirements. The untuned methods (a and b) are straightforward and do not require precise frequency adjustments, making them suitable for applications where simplicity is preferred.
For applications that necessitate tuning to a specific frequency, the use of an LC resonant circuit is recommended. This circuit can be constructed using ungrounded trimmer capacitors (c and d), which allow for fine-tuning of the resonant frequency. The trimmer capacitors can be adjusted to achieve the desired frequency response, providing flexibility in signal input.
Alternatively, grounded variable capacitors (e) can also be employed in the resonant circuit. These components offer a more stable tuning mechanism, as they are less susceptible to noise and interference. The grounded configuration helps maintain consistent performance over a range of frequencies.
A more advanced approach involves the use of a varactor (f), which is a voltage-controlled capacitor. By applying a tuning voltage to the varactor, the capacitance can be dynamically adjusted, allowing for real-time tuning of the input signal frequency. This method is particularly useful in applications requiring rapid frequency changes or in situations where space is limited, as it eliminates the need for bulky tuning components.
In summary, the NE602 provides flexibility in signal input through various methods, from simple untuned approaches to sophisticated tuned circuits using trimmer capacitors, grounded variable capacitors, or varactors, each suited to different application needs.A few of the many ways to input a signal into the NE602. Simple untuned methods (a and b) are acceptable. If you need to tune to a specific frequency, you can use an LC resonant circuit with un-grounded trimmer capacitors (c and d) or with grounded variable capacitors (e). You can even use a tuning voltage in connection with a varactor (f). 🔗 External reference