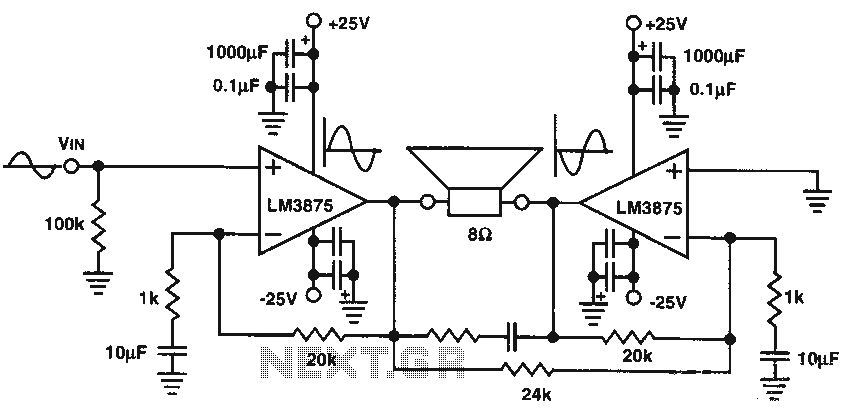
Pure Class-A Headphone Amplifier Schematic
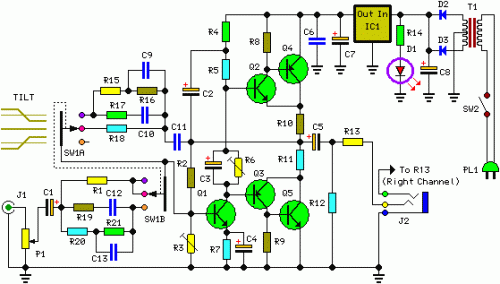
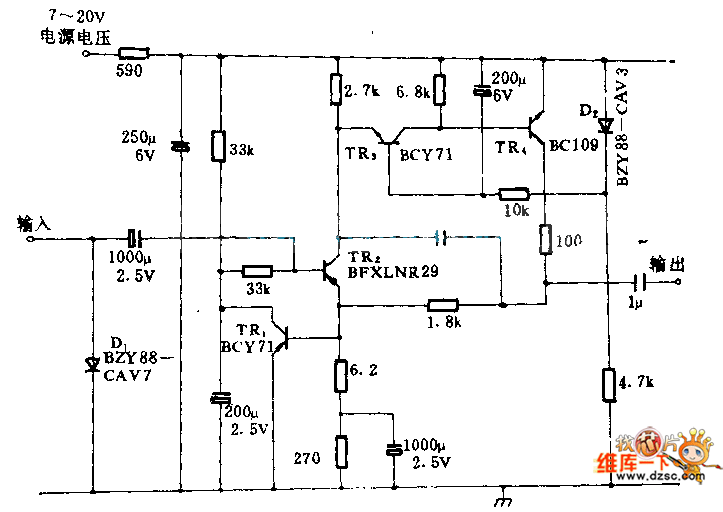
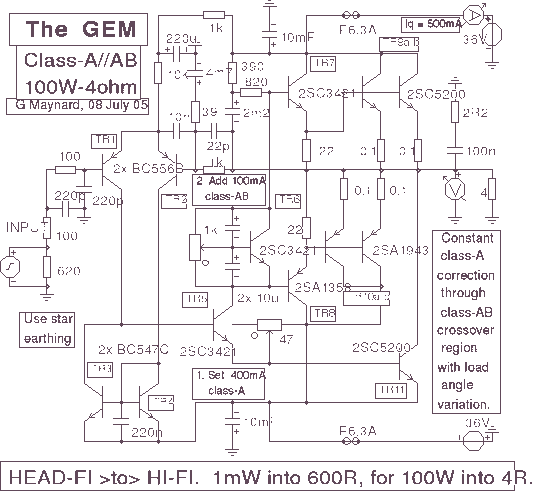
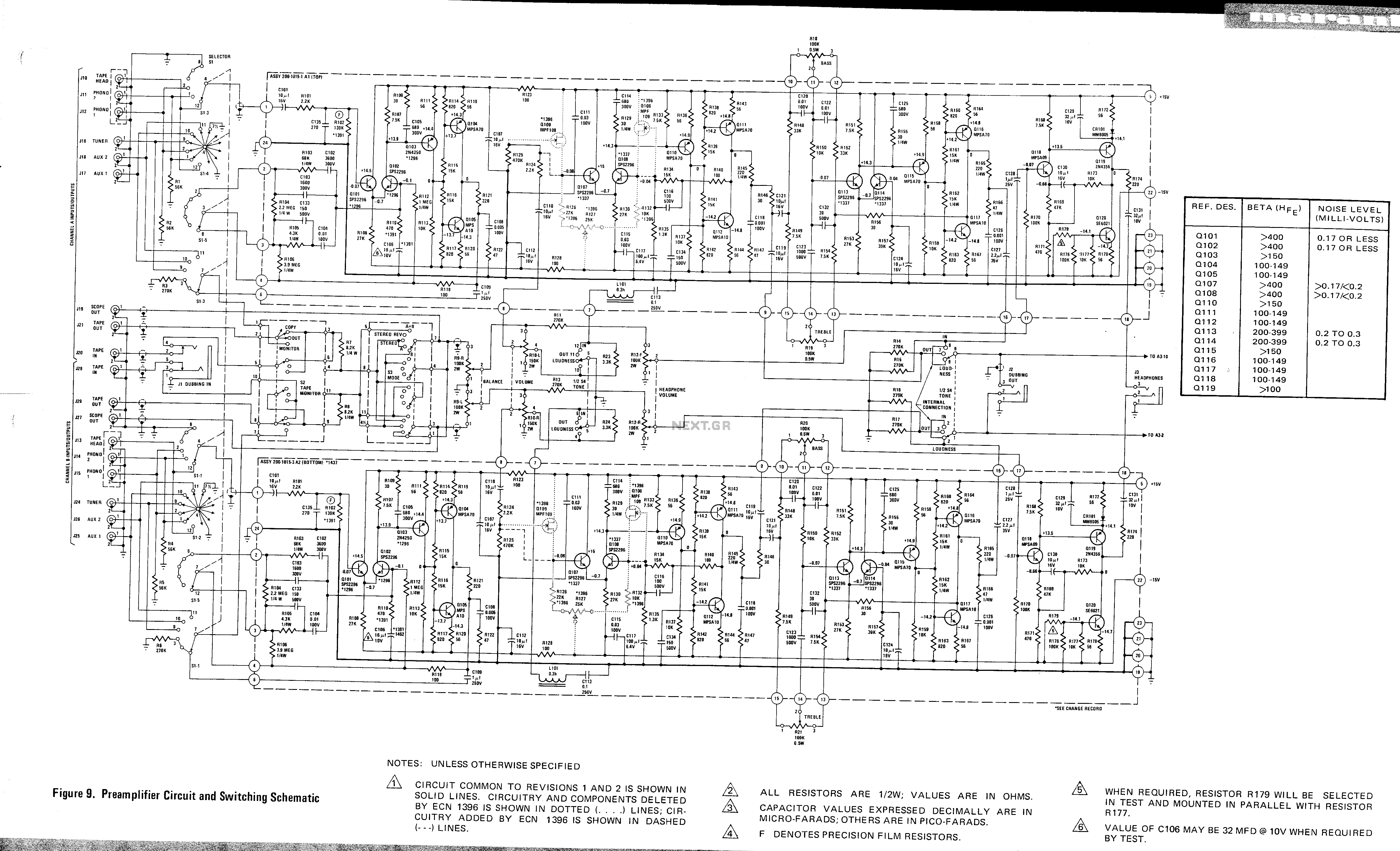
The described shunt-feedback configuration facilitates the straightforward integration of frequency-dependent networks to achieve a functional and discreet switchable tilt control (optional). When SW1 is in the first position, a gentle shelving bass boost and treble reduction is achieved. The central position of SW1 provides a flat frequency response, while the third position of this switch allows for a shelving treble boost and bass reduction.
The shunt-feedback configuration is a versatile circuit design commonly used in audio applications to manipulate the frequency response of an audio signal. This configuration utilizes feedback to stabilize the gain and enhance the performance of the circuit. The integration of frequency-dependent networks enables the implementation of tilt control, which is a valuable feature for adjusting the tonal balance of audio signals.
The switch SW1 offers three distinct positions, each corresponding to a different frequency response characteristic. In the first position, the circuit applies a shelving bass lift while simultaneously reducing the treble frequencies. This can be particularly useful in situations where low-frequency enhancement is desired, such as in bass-heavy music genres or environments where low-end presence is critical.
The central position of SW1 provides a flat frequency response, ensuring that the audio signal is reproduced without any coloration or alteration. This is essential for applications requiring accurate sound reproduction, such as studio monitoring or critical listening environments.
In the third position, SW1 activates a shelving treble lift and a bass cut, allowing for a brighter sound profile. This setting can be advantageous in scenarios where clarity and articulation of higher frequencies are paramount, such as in vocal performances or high-frequency instrument playback.
Overall, the shunt-feedback configuration with the optional tilt control provides a flexible solution for tailoring audio signals to meet specific requirements, enhancing the listening experience while maintaining the integrity of the original sound. The design's ability to incorporate frequency-dependent networks further expands its utility in various audio applications.The mentioned shunt-feedback configuration also allows the easy addition of frequency dependent networks in order to obtain an useful, unobtrusive, switchable Tilt control (optional). When SW1 is set in the first position a gentle, shelving bass lift and treble cut is obtained. The central position of SW1 allows a flat frequency response, whereas the third position of this switch enables a shelving treble lift and bass cut
🔗 External reference
The shunt-feedback configuration is a versatile circuit design commonly used in audio applications to manipulate the frequency response of an audio signal. This configuration utilizes feedback to stabilize the gain and enhance the performance of the circuit. The integration of frequency-dependent networks enables the implementation of tilt control, which is a valuable feature for adjusting the tonal balance of audio signals.
The switch SW1 offers three distinct positions, each corresponding to a different frequency response characteristic. In the first position, the circuit applies a shelving bass lift while simultaneously reducing the treble frequencies. This can be particularly useful in situations where low-frequency enhancement is desired, such as in bass-heavy music genres or environments where low-end presence is critical.
The central position of SW1 provides a flat frequency response, ensuring that the audio signal is reproduced without any coloration or alteration. This is essential for applications requiring accurate sound reproduction, such as studio monitoring or critical listening environments.
In the third position, SW1 activates a shelving treble lift and a bass cut, allowing for a brighter sound profile. This setting can be advantageous in scenarios where clarity and articulation of higher frequencies are paramount, such as in vocal performances or high-frequency instrument playback.
Overall, the shunt-feedback configuration with the optional tilt control provides a flexible solution for tailoring audio signals to meet specific requirements, enhancing the listening experience while maintaining the integrity of the original sound. The design's ability to incorporate frequency-dependent networks further expands its utility in various audio applications.The mentioned shunt-feedback configuration also allows the easy addition of frequency dependent networks in order to obtain an useful, unobtrusive, switchable Tilt control (optional). When SW1 is set in the first position a gentle, shelving bass lift and treble cut is obtained. The central position of SW1 allows a flat frequency response, whereas the third position of this switch enables a shelving treble lift and bass cut
🔗 External reference