Code practice oscillator
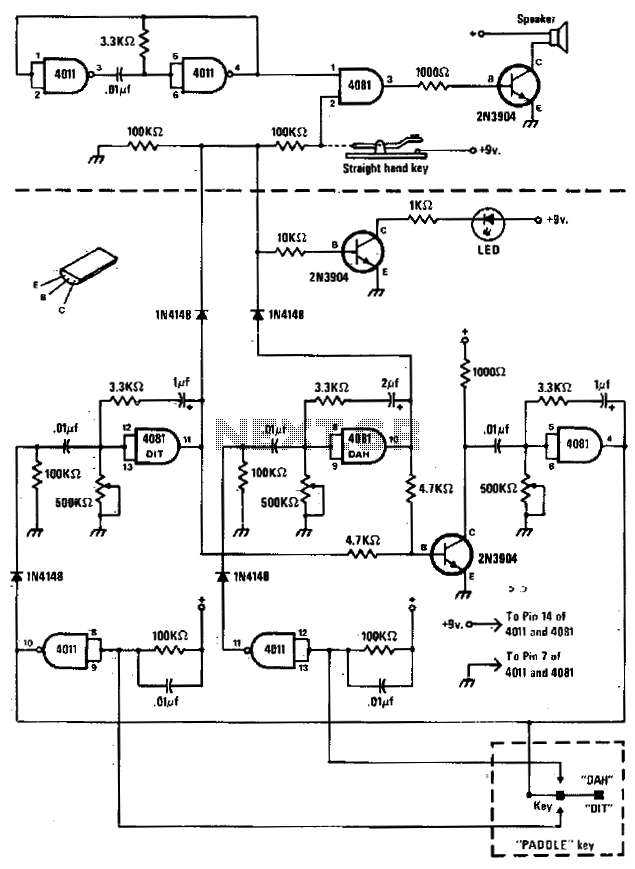
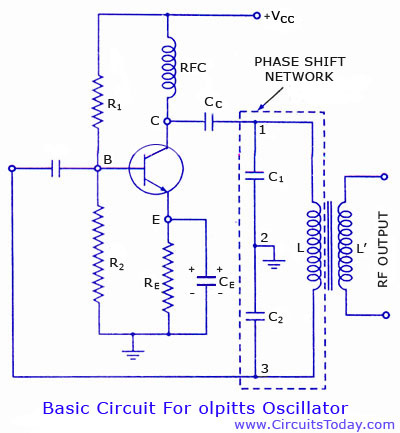
The circuit comprises a basic oscillator (above the dashed line) and an automatic keyer (below the dashed line). The unit can be utilized with either a straight hand key or a paddle key for automatic operation.
The described circuit integrates two primary components: a basic oscillator and an automatic keyer, each serving distinct functions within the overall design. The basic oscillator is responsible for generating a consistent frequency output, which is essential for various applications, including signal transmission in communication devices. This oscillator typically employs a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) or LC (inductor-capacitor) network to establish its oscillation frequency, ensuring stable and reliable performance.
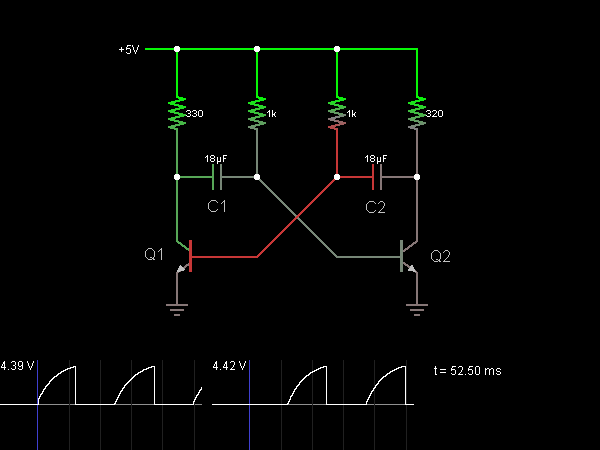
The automatic keyer, situated below the dashed line, is designed to facilitate automated Morse code transmission. This component can interpret input from two types of keys: a straight hand key, which is a simple mechanical switch, and a paddle key, which allows for more nuanced control over the timing and spacing of the Morse code signals. The automatic keyer processes the input from these keys to produce a series of on-off signals that correspond to the Morse code characters being transmitted.
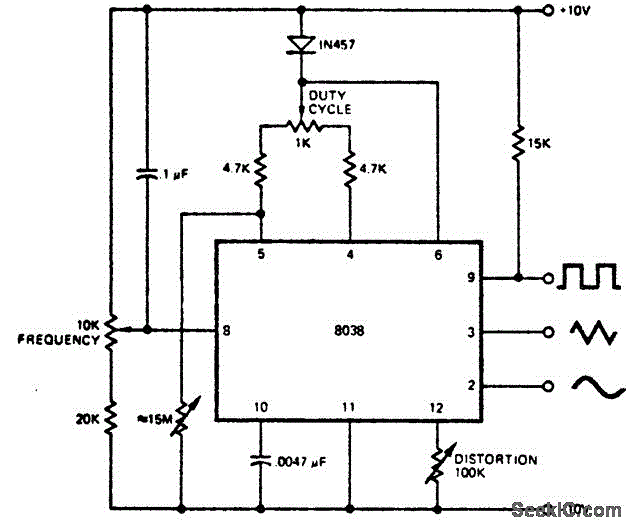
The integration of both the oscillator and the automatic keyer allows for efficient operation in transmitting Morse code without the need for continuous manual input. This design is particularly beneficial for amateur radio operators and other communication enthusiasts who require reliable and automated communication capabilities. The circuit can be further enhanced with additional features such as adjustable speed control for the keyer, allowing operators to customize the transmission speed to their preference.The circuit consists of a basic oscillator (above dashed line) and an automatic keyer (below dashed line) The unit can be used with a straight hand key or a paddle key for automatic operation. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit integrates two primary components: a basic oscillator and an automatic keyer, each serving distinct functions within the overall design. The basic oscillator is responsible for generating a consistent frequency output, which is essential for various applications, including signal transmission in communication devices. This oscillator typically employs a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) or LC (inductor-capacitor) network to establish its oscillation frequency, ensuring stable and reliable performance.
The automatic keyer, situated below the dashed line, is designed to facilitate automated Morse code transmission. This component can interpret input from two types of keys: a straight hand key, which is a simple mechanical switch, and a paddle key, which allows for more nuanced control over the timing and spacing of the Morse code signals. The automatic keyer processes the input from these keys to produce a series of on-off signals that correspond to the Morse code characters being transmitted.
The integration of both the oscillator and the automatic keyer allows for efficient operation in transmitting Morse code without the need for continuous manual input. This design is particularly beneficial for amateur radio operators and other communication enthusiasts who require reliable and automated communication capabilities. The circuit can be further enhanced with additional features such as adjustable speed control for the keyer, allowing operators to customize the transmission speed to their preference.The circuit consists of a basic oscillator (above dashed line) and an automatic keyer (below dashed line) The unit can be used with a straight hand key or a paddle key for automatic operation. 🔗 External reference