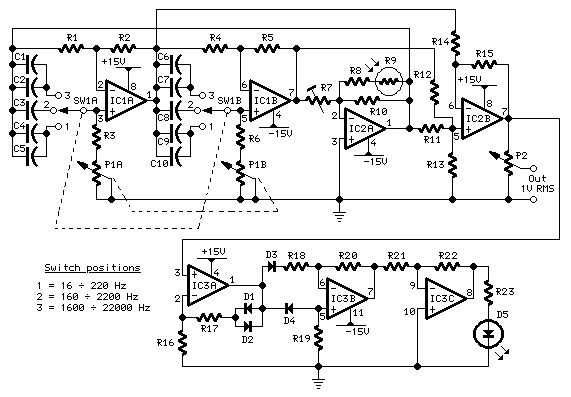
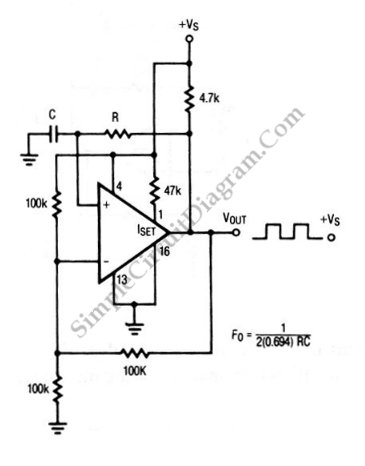
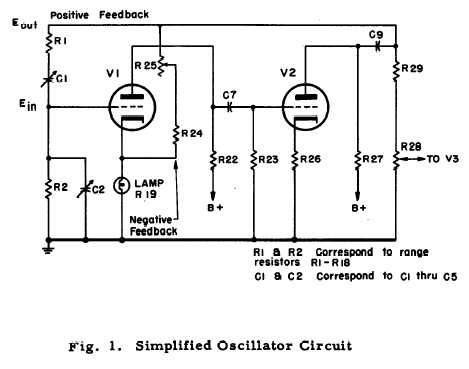
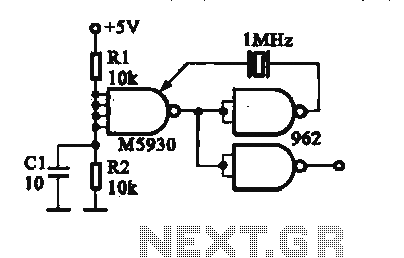
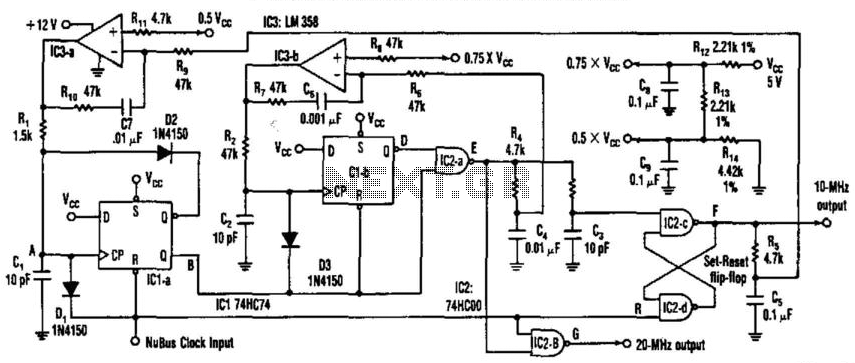
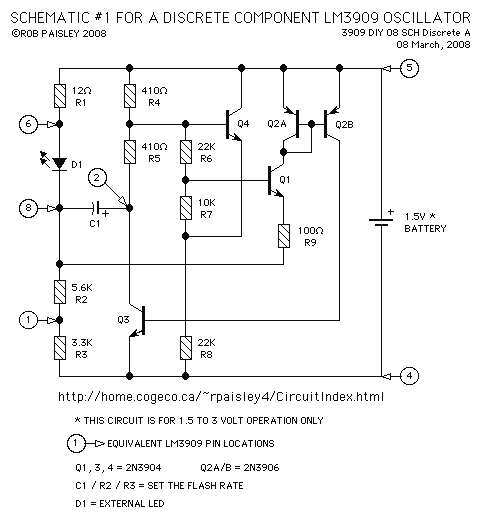
colpitts oscillator

A simulation of a Colpitts Oscillator circuit using an NPN transistor and other components available in SimElectronics is presented. The feedback ratio is determined by the relative values of the capacitors C1 and C2. The frequency of oscillation is given by the formula f = 1/(2*pi*sqrt(L*CT)), where CT = (C1*C2)/(C1+C2).
The Colpitts Oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that utilizes a combination of an inductor (L) and two capacitors (C1 and C2) to produce an oscillating signal. The configuration typically involves an NPN transistor, which serves as the active device to amplify the signal. The feedback network, composed of capacitors C1 and C2, is critical for determining the oscillation frequency and stability of the circuit.
In this circuit, the capacitors C1 and C2 are connected in series, and their combined capacitance (CT) is calculated using the formula CT = (C1*C2)/(C1+C2). This relationship affects the overall feedback ratio, which is essential for sustaining oscillations. The inductor L is also a key component, as it, along with CT, defines the oscillation frequency through the equation f = 1/(2*pi*sqrt(L*CT)).
The design of the Colpitts Oscillator allows for the generation of sine wave signals, making it suitable for various applications, including signal generation and frequency synthesis. The choice of component values directly influences the performance characteristics, such as frequency stability, output amplitude, and phase noise. Proper simulation in environments like SimElectronics aids in optimizing these parameters before physical implementation.Simulation of Colpitts Oscillator circuit using npn transistor and other components available in SimElectronics is shown. The feedback ratio is determined by the relative values of the Capacitors C1 and C2. Frequency of oscillation is given by f = 1/(2*pi*sqrt(L*CT) where CT = (C1*C2)/(C1+C2) 🔗 External reference
The Colpitts Oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that utilizes a combination of an inductor (L) and two capacitors (C1 and C2) to produce an oscillating signal. The configuration typically involves an NPN transistor, which serves as the active device to amplify the signal. The feedback network, composed of capacitors C1 and C2, is critical for determining the oscillation frequency and stability of the circuit.
In this circuit, the capacitors C1 and C2 are connected in series, and their combined capacitance (CT) is calculated using the formula CT = (C1*C2)/(C1+C2). This relationship affects the overall feedback ratio, which is essential for sustaining oscillations. The inductor L is also a key component, as it, along with CT, defines the oscillation frequency through the equation f = 1/(2*pi*sqrt(L*CT)).
The design of the Colpitts Oscillator allows for the generation of sine wave signals, making it suitable for various applications, including signal generation and frequency synthesis. The choice of component values directly influences the performance characteristics, such as frequency stability, output amplitude, and phase noise. Proper simulation in environments like SimElectronics aids in optimizing these parameters before physical implementation.Simulation of Colpitts Oscillator circuit using npn transistor and other components available in SimElectronics is shown. The feedback ratio is determined by the relative values of the Capacitors C1 and C2. Frequency of oscillation is given by f = 1/(2*pi*sqrt(L*CT) where CT = (C1*C2)/(C1+C2) 🔗 External reference