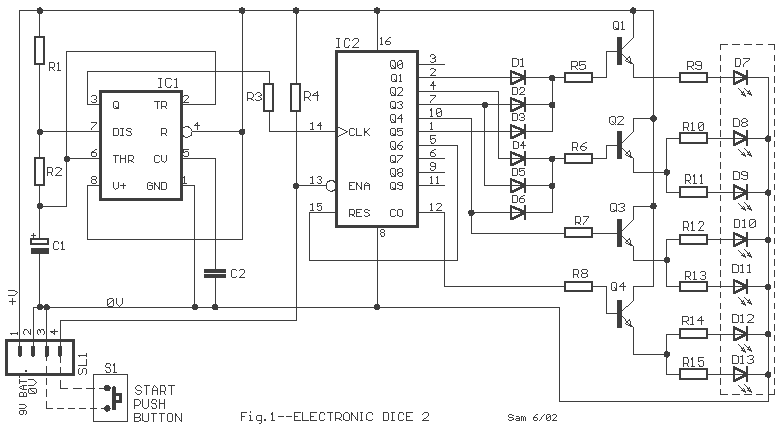
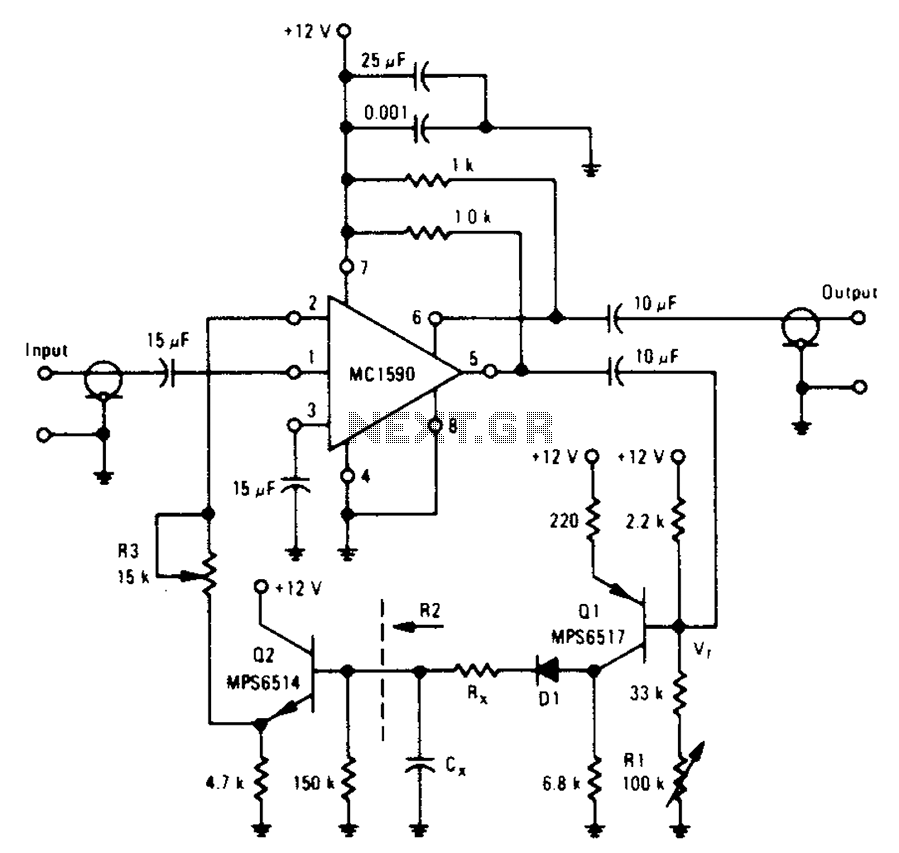
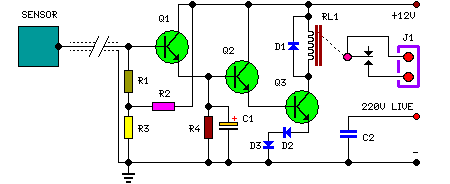
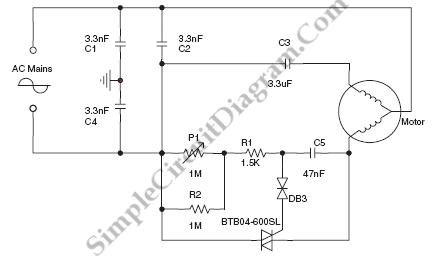
Control circuit of automatic water
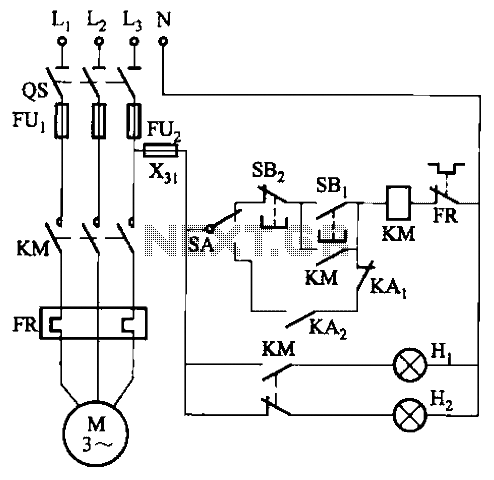
In certain locations near the reservoir or well, when the water level is constrained by the water towers, there is a need for simultaneous monitoring of the water towers and reservoirs as part of an automatic water control system. This system is designed to manage the water level in Sheung Shui, while also controlling the water tank level to prevent situations where the water or reservoir level becomes too low, potentially leading to pump idling and accidents. The circuit design is based on two conditions: the pump starts automatically when the water levels in both the water tower and reservoir drop below a specified threshold (i.e., the water level is above the lower limit); the pump stops when the water level in the tower rises or when the reservoir water level reaches the next designated level.
The automatic water control system incorporates a dual-level sensing mechanism to ensure efficient operation of the water supply infrastructure. The circuit utilizes float switches or pressure sensors placed at strategic locations within the water tower and reservoir to monitor the water levels continuously. These sensors are connected to a microcontroller or a relay-based control circuit that processes the input signals from the sensors.
When the water level in the reservoir or the water tower drops below a predetermined threshold, the sensors trigger the control circuit to activate the pump. The pump will continue to operate until the water levels in either the tower or the reservoir reach their respective upper limits. This configuration not only prevents the pump from running dry, which could cause damage, but also ensures that the water supply is maintained at optimal levels.
Additionally, the control circuit may include visual and audible indicators to alert operators of the system status, such as low water levels or pump operation. The use of timers and delays can be implemented to prevent rapid cycling of the pump, thereby enhancing the longevity of the equipment. Overall, this circuit design emphasizes reliability and efficiency, contributing to the effective management of water resources in the monitored area.In some places by the reservoir (or well) when the water level constraints to water towers, need to have with simultaneous monitoring of water towers and reservoirs (or well) of automatic water control system. That is when the water level in Sheung Shui being subject to control, but also at the same time by the water tank level control, in order to avoid water or reservoir water level is too low, the pump burned idling pumps cause accidents. Circuit design is based on: O pump starts automatically to meet two conditions, namely water tower and reservoir water level dropped to under water (ie water level above the lower bits); pump stops to draw with the proviso that the water level rise tower or supreme water reservoir water level dropped to the next level.
The automatic water control system incorporates a dual-level sensing mechanism to ensure efficient operation of the water supply infrastructure. The circuit utilizes float switches or pressure sensors placed at strategic locations within the water tower and reservoir to monitor the water levels continuously. These sensors are connected to a microcontroller or a relay-based control circuit that processes the input signals from the sensors.
When the water level in the reservoir or the water tower drops below a predetermined threshold, the sensors trigger the control circuit to activate the pump. The pump will continue to operate until the water levels in either the tower or the reservoir reach their respective upper limits. This configuration not only prevents the pump from running dry, which could cause damage, but also ensures that the water supply is maintained at optimal levels.
Additionally, the control circuit may include visual and audible indicators to alert operators of the system status, such as low water levels or pump operation. The use of timers and delays can be implemented to prevent rapid cycling of the pump, thereby enhancing the longevity of the equipment. Overall, this circuit design emphasizes reliability and efficiency, contributing to the effective management of water resources in the monitored area.In some places by the reservoir (or well) when the water level constraints to water towers, need to have with simultaneous monitoring of water towers and reservoirs (or well) of automatic water control system. That is when the water level in Sheung Shui being subject to control, but also at the same time by the water tank level control, in order to avoid water or reservoir water level is too low, the pump burned idling pumps cause accidents. Circuit design is based on: O pump starts automatically to meet two conditions, namely water tower and reservoir water level dropped to under water (ie water level above the lower bits); pump stops to draw with the proviso that the water level rise tower or supreme water reservoir water level dropped to the next level.