Corridor counter delay circuit for controlling lights
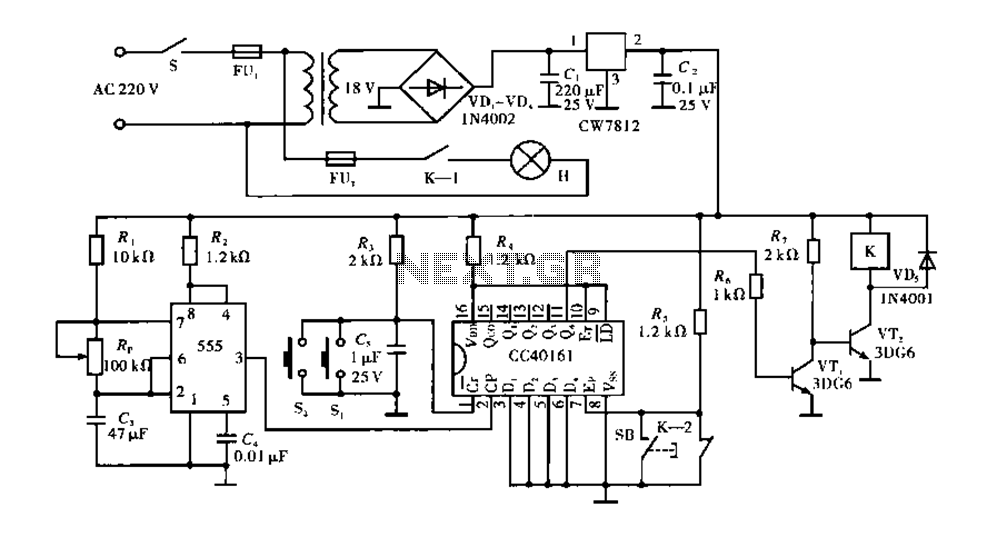
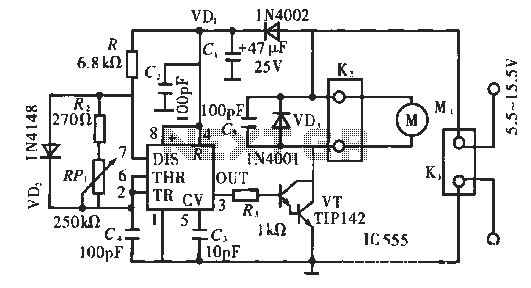
Corridor counter delay circuit for controlling lights. This circuit is tested and functional. When the circuit is energized, the 555 oscillator starts to oscillate. The CC40161 is cleared, and an integrating circuit composed of R3 and C5 transitions the state into the count. Relay K is energized, closing K-1, which lights the lights H, while K-2, the normally closed contacts, disconnects. The output of CC40161 goes high.
The corridor counter delay circuit is designed to manage lighting in corridor areas efficiently. The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a pulse-width modulation signal, which controls the timing of the relay operation. The CC40161 is a binary counter that keeps track of the number of oscillations produced by the 555 timer, allowing for the integration of time delays before activating the relay.
Upon energizing the circuit, the 555 timer initiates oscillation, producing a square wave output. This output is fed into the CC40161, which counts the pulses. The R3 and C5 components form an RC time constant that determines the integration time, effectively controlling how long the circuit will wait before responding to the count.
When the binary count reaches a predetermined value, the CC40161 activates the relay K. This relay has two sets of contacts: K-1, which is normally open, closes to power the lights (H), and K-2, which is normally closed, opens to disconnect the circuit from the power source, ensuring that the lights are only on for the required duration. The output of the CC40161 going high signals that the counting process is complete, allowing for a controlled and efficient lighting solution in corridor settings.
This design minimizes energy consumption by ensuring that lights are only activated when necessary, thus providing both functionality and efficiency in corridor lighting management.Corridor counter delay circuit for controlling lights This circuit is tested and functionable. When the circuit is energized, the 555 oscillator starts to oscillate, CC40161 is cleared R3, C5 integrating circuit composed of the state and into the count. Relay K to be energized, K-1 is closed, lights H lit, while K-2 normally closed contacts disconnect, C C40161 of E, goes high.
The corridor counter delay circuit is designed to manage lighting in corridor areas efficiently. The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a pulse-width modulation signal, which controls the timing of the relay operation. The CC40161 is a binary counter that keeps track of the number of oscillations produced by the 555 timer, allowing for the integration of time delays before activating the relay.
Upon energizing the circuit, the 555 timer initiates oscillation, producing a square wave output. This output is fed into the CC40161, which counts the pulses. The R3 and C5 components form an RC time constant that determines the integration time, effectively controlling how long the circuit will wait before responding to the count.
When the binary count reaches a predetermined value, the CC40161 activates the relay K. This relay has two sets of contacts: K-1, which is normally open, closes to power the lights (H), and K-2, which is normally closed, opens to disconnect the circuit from the power source, ensuring that the lights are only on for the required duration. The output of the CC40161 going high signals that the counting process is complete, allowing for a controlled and efficient lighting solution in corridor settings.
This design minimizes energy consumption by ensuring that lights are only activated when necessary, thus providing both functionality and efficiency in corridor lighting management.Corridor counter delay circuit for controlling lights This circuit is tested and functionable. When the circuit is energized, the 555 oscillator starts to oscillate, CC40161 is cleared R3, C5 integrating circuit composed of the state and into the count. Relay K to be energized, K-1 is closed, lights H lit, while K-2 normally closed contacts disconnect, C C40161 of E, goes high.