Current three-phase motor phase protection circuit diagram
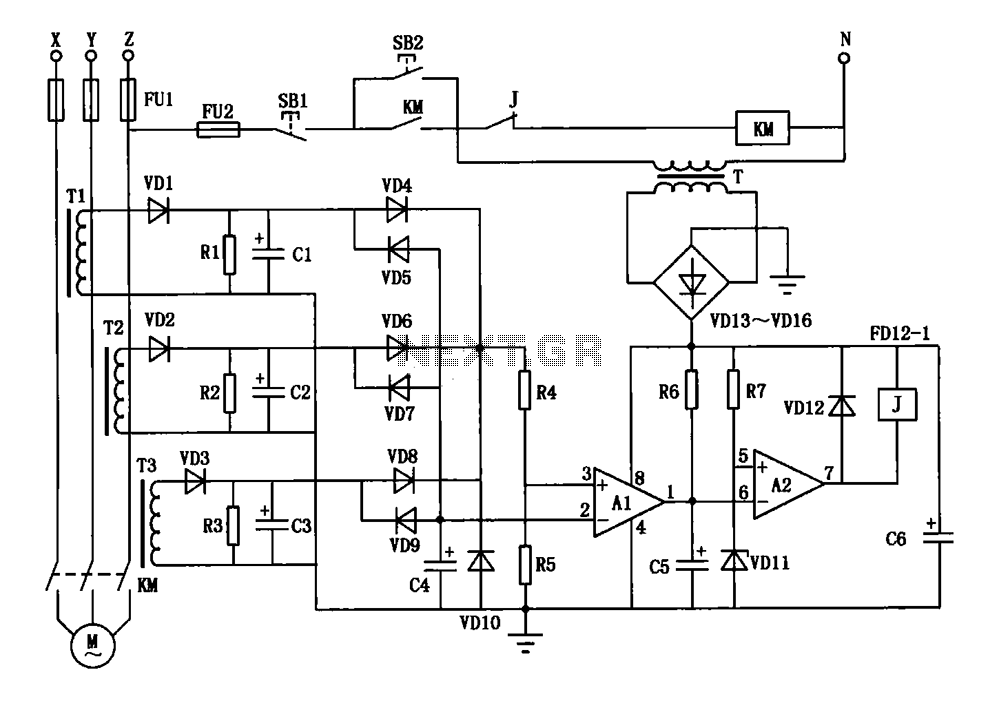
A current three-phase motor phase protection circuit is designed to detect three-phase current using homemade small current transformers T1, T2, and T3. The current signals are collected by rectifiers VD1, VD2, and VD3, while capacitors C1, C2, and C3 serve to filter the signals. The OR gate circuit is formed by resistors R4 and R5, which provide a partial voltage to the inverting terminal of comparator A1. The output circuit identifies the presence or absence of current through diodes VD5, VD7, and VD9, which are connected to the non-inverting terminal of comparator A1. Transformers T1 to T3 are commercially available toroidal ferrite cores, wound with high-strength wire in the range of 150 to 250 turns, depending on the motor's power. The primary winding is created by passing the power cord through the toroidal core. Capacitors C1 to C3 are electrolytic capacitors rated at 10 µF/25V, while C4 is a ceramic capacitor rated at 0.1 µF/63V. Capacitor C6 is an electrolytic capacitor rated at 470 µF/25V. Capacitor C5 is used for interference absorption, with its capacitance value adjustable between 4.7 µF and 33 µF/25V based on sensitivity requirements. Resistors R1 and R2 are 1.2 kΩ, R4 is 390 kΩ, R5 is 680 kΩ, R6 is 15 kΩ, and R7 is 2 kΩ, all with a power rating of 1/8W. The Zener diode VD11 regulates the voltage to approximately 8V, while the other diodes used are 1N4004.
The current three-phase motor phase protection circuit is structured to ensure reliable operation of three-phase motors by monitoring the current flow through each phase. The use of small current transformers (T1, T2, T3) allows for accurate detection of the motor's current without direct electrical connections, thereby enhancing safety and reducing wear on components.
The rectification process, facilitated by diodes VD1, VD2, and VD3, converts the AC signals from the transformers into DC signals, which are then filtered by capacitors C1, C2, and C3 to remove any ripple, ensuring a stable voltage for the subsequent processing stages. The OR gate circuit, composed of resistors R4 and R5, is critical for voltage level adjustment, allowing the comparator A1 to receive a suitable input for accurate monitoring.
Comparator A1 plays a pivotal role in determining the operational status of the motor. It compares the voltage from the OR gate circuit and the input from the diodes VD5, VD7, and VD9, which are configured to detect current presence or absence. This dual comparison ensures that any phase loss or imbalance triggers appropriate protective measures, preventing potential motor damage.
Transformers T1 to T3 are designed using toroidal ferrite cores, known for their efficiency in reducing electromagnetic interference. The winding specifications (150 to 250 turns) are tailored to the motor's power requirements, allowing for flexibility in application. The primary winding is ingeniously created by routing the power cord through the toroidal core, optimizing space and minimizing installation complexity.
Capacitors C1 to C3, with their specified ratings, are integral to the circuit's performance, providing necessary filtering and stabilization. Capacitor C5, which serves as an interference absorption component, can be fine-tuned to adjust the circuit's sensitivity, allowing for customization based on the specific operational environment.
The resistors in the circuit are carefully selected for their values and power ratings, ensuring that they can handle the expected current without overheating. The inclusion of a Zener diode (VD11) for voltage regulation adds an additional layer of protection, maintaining stable operation across varying input conditions.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an effective approach to three-phase motor protection, combining reliable detection, filtering, and voltage regulation to enhance motor longevity and performance.Current three-phase motor phase protection circuit, as shown in FIG. 3 homemade small current transformers Tl, T2 and T3 on the motor is running three-phase current detection s ignals are collected by the VDl, VD2 and VD3 rectifier, Cl, C2 and C3 filter by VD4, VD6 and VD8 oR gate circuit is composed of R4, R5 partial pressure of the supplied voltage comparator Al-inverting terminal; the gate as a three-phase current output circuit to identify the presence or absence VD5, VD7, VD9 composed of input voltage comparator Al counter phase terminal.Transformer Tl ~ T3 making available on the market Tesco toroidal ferrite core with µ0.25mm high-strength wire, winding 150 to 250 turns. The number of turns is determined by the power of the motor, motor power small can around more. Through the power cord from the ring, as the primary winding. Capacitor C1 ~ C3 electrolytic capacitor 10 F/25V of; C4 use 0.1 F/63V ceramic capacitors; C6 electrolytic capacitor 470 F/25V is; C5 is interference absorption capacitor, to increase the capacitance value C5 when the action is too sensitive, Conversely reduce the value of C5, which is in the range of 4.7 ~ 33 F/25V.
Resistance Rl R2 l.2k, R4 390k, R5 680k, R6 15k, R7 2k, nominal power are RJ resistance 1/8W of. Zener diode VD11, which the regulator is about 8V. Other diodes with 1N4004.
The current three-phase motor phase protection circuit is structured to ensure reliable operation of three-phase motors by monitoring the current flow through each phase. The use of small current transformers (T1, T2, T3) allows for accurate detection of the motor's current without direct electrical connections, thereby enhancing safety and reducing wear on components.
The rectification process, facilitated by diodes VD1, VD2, and VD3, converts the AC signals from the transformers into DC signals, which are then filtered by capacitors C1, C2, and C3 to remove any ripple, ensuring a stable voltage for the subsequent processing stages. The OR gate circuit, composed of resistors R4 and R5, is critical for voltage level adjustment, allowing the comparator A1 to receive a suitable input for accurate monitoring.
Comparator A1 plays a pivotal role in determining the operational status of the motor. It compares the voltage from the OR gate circuit and the input from the diodes VD5, VD7, and VD9, which are configured to detect current presence or absence. This dual comparison ensures that any phase loss or imbalance triggers appropriate protective measures, preventing potential motor damage.
Transformers T1 to T3 are designed using toroidal ferrite cores, known for their efficiency in reducing electromagnetic interference. The winding specifications (150 to 250 turns) are tailored to the motor's power requirements, allowing for flexibility in application. The primary winding is ingeniously created by routing the power cord through the toroidal core, optimizing space and minimizing installation complexity.
Capacitors C1 to C3, with their specified ratings, are integral to the circuit's performance, providing necessary filtering and stabilization. Capacitor C5, which serves as an interference absorption component, can be fine-tuned to adjust the circuit's sensitivity, allowing for customization based on the specific operational environment.
The resistors in the circuit are carefully selected for their values and power ratings, ensuring that they can handle the expected current without overheating. The inclusion of a Zener diode (VD11) for voltage regulation adds an additional layer of protection, maintaining stable operation across varying input conditions.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an effective approach to three-phase motor protection, combining reliable detection, filtering, and voltage regulation to enhance motor longevity and performance.Current three-phase motor phase protection circuit, as shown in FIG. 3 homemade small current transformers Tl, T2 and T3 on the motor is running three-phase current detection s ignals are collected by the VDl, VD2 and VD3 rectifier, Cl, C2 and C3 filter by VD4, VD6 and VD8 oR gate circuit is composed of R4, R5 partial pressure of the supplied voltage comparator Al-inverting terminal; the gate as a three-phase current output circuit to identify the presence or absence VD5, VD7, VD9 composed of input voltage comparator Al counter phase terminal.Transformer Tl ~ T3 making available on the market Tesco toroidal ferrite core with µ0.25mm high-strength wire, winding 150 to 250 turns. The number of turns is determined by the power of the motor, motor power small can around more. Through the power cord from the ring, as the primary winding. Capacitor C1 ~ C3 electrolytic capacitor 10 F/25V of; C4 use 0.1 F/63V ceramic capacitors; C6 electrolytic capacitor 470 F/25V is; C5 is interference absorption capacitor, to increase the capacitance value C5 when the action is too sensitive, Conversely reduce the value of C5, which is in the range of 4.7 ~ 33 F/25V.
Resistance Rl R2 l.2k, R4 390k, R5 680k, R6 15k, R7 2k, nominal power are RJ resistance 1/8W of. Zener diode VD11, which the regulator is about 8V. Other diodes with 1N4004.