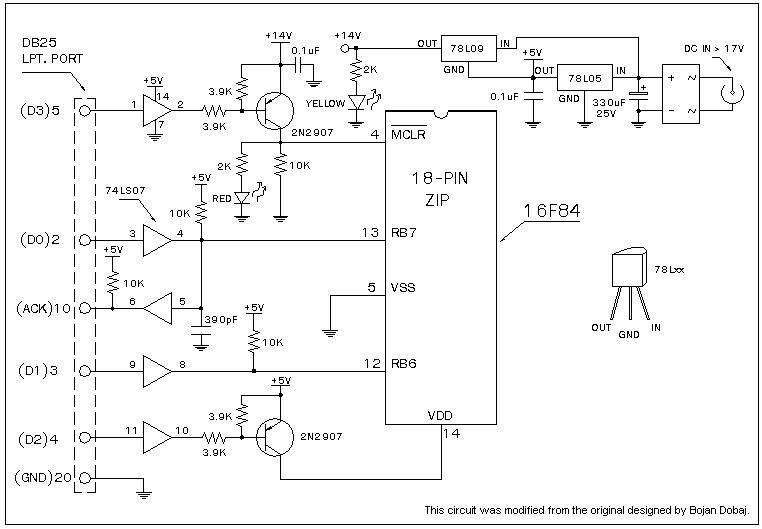
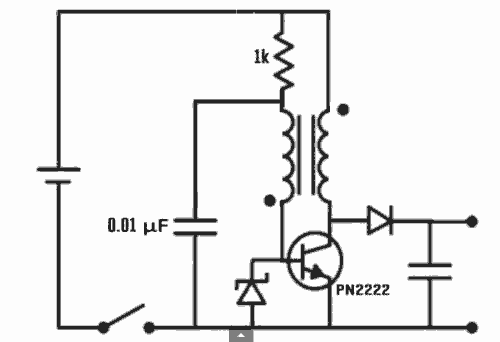
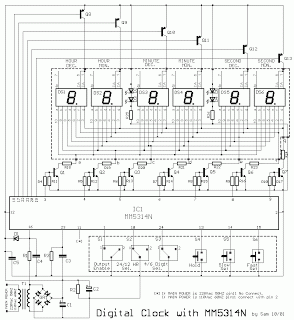
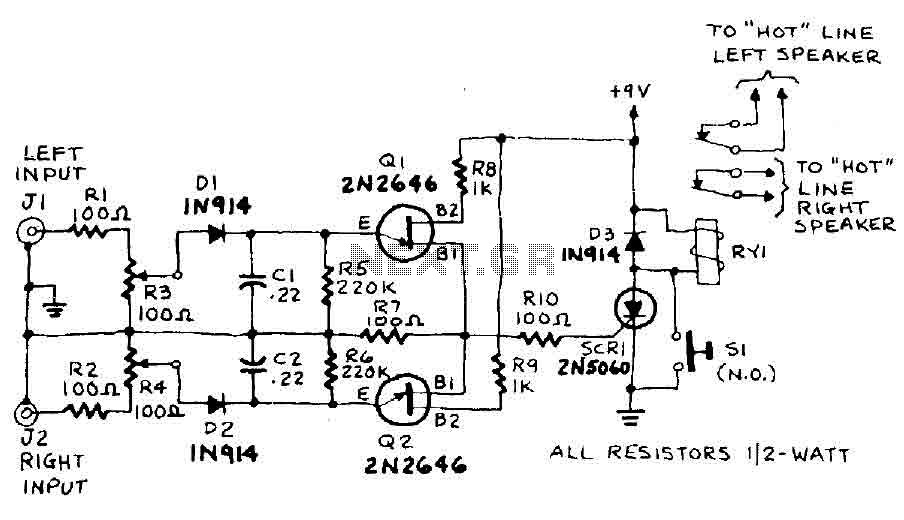
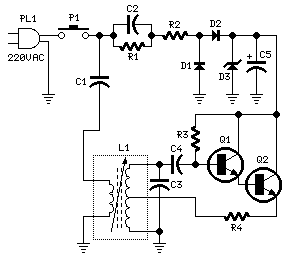
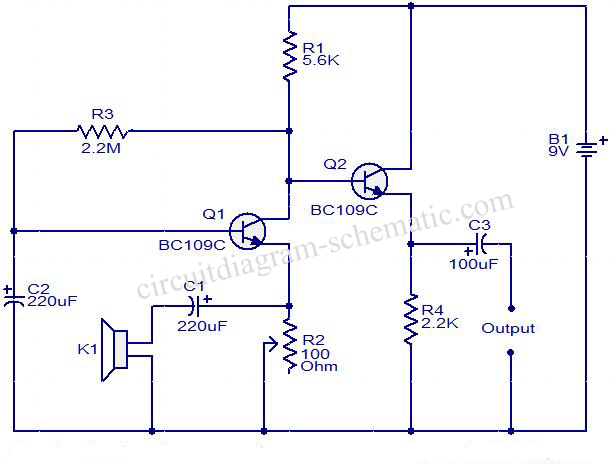
DC-coupled multi-stage amplifier circuit a
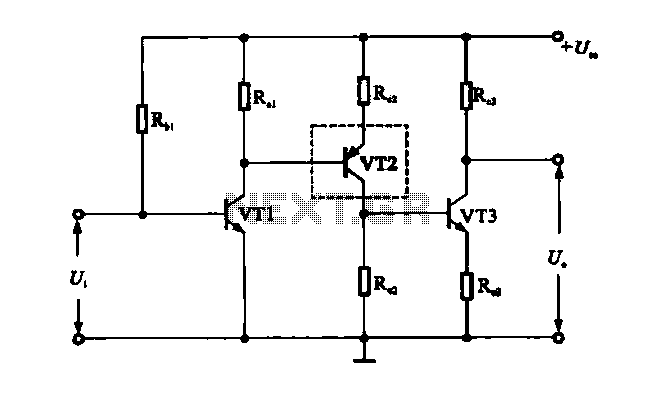
A multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier circuit utilizes NPN type transistors. Each stage is designed to achieve an appropriate operating point at the base, resulting in a stepwise increase in collector potential, which subsequently reduces the final output voltage range. To address this issue, a combination of NPN and PNP transistors can be employed to lower the DC potential of the post-stage. For example, an NPN transistor (VT1) and a PNP transistor (VT2) can be used to decrease the potential of the following stage (VT3). Alternatively, an emitter follower stage can be utilized to amplify voltage while reducing the DC potential of the circuit.
The multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier circuit is designed to provide significant amplification while maintaining stability and linearity across its operational range. The use of NPN transistors in the initial stages allows for efficient amplification of the input signal. Each stage is configured to ensure that the biasing conditions are optimized, allowing the amplifier to operate effectively without distortion.
As the signal progresses through each stage, the collector potential incrementally rises. However, this increase in potential can lead to a reduction in the overall output voltage range, which may limit the circuit's performance in certain applications. To mitigate this effect, the implementation of PNP transistors in conjunction with NPN transistors is a common practice. The PNP transistor (VT2) can effectively lower the DC potential of the subsequent stage (VT3), allowing for a more manageable output voltage range.
In addition to using complementary transistor configurations, the circuit can also incorporate an emitter follower stage. This configuration serves as a buffer that provides voltage gain while simultaneously reducing the DC potential seen by the following stages. The emitter follower is characterized by its high input impedance and low output impedance, making it an ideal choice for interfacing between stages of an amplifier.
In summary, the multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier circuit leverages the properties of both NPN and PNP transistors to achieve a robust amplification solution, while the inclusion of emitter follower stages enhances the circuit's overall performance by managing DC levels effectively.DC-coupled multi-stage amplifier circuit a (3) multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier in DC-coupled by a multi-stage amplifier circuit amplifying circuit, if used NPN type transistor of each stage, in order to fit all levels have appropriate operating point of stage base, Step by step the collector potential increases, so reducing the final output voltage range. In order to solve this problem, in practice, it can be used in conjunction with NPN and PNP transistor to reduce the post-stage DC potential, as shown in FIG.
Figure (8) shows an NPN cvri) and PNP transistor (VT2) wish, is used to reduce the subsequent stage (VT3) potential. Alternatively, you can use emitter follower, stage amplified voltage diode to reduce a DC potential of the circuit.
Figure l-43 (b) shows the use of emitter cvn) is used to reduce the subsequent stage (, rr3) potential.
The multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier circuit is designed to provide significant amplification while maintaining stability and linearity across its operational range. The use of NPN transistors in the initial stages allows for efficient amplification of the input signal. Each stage is configured to ensure that the biasing conditions are optimized, allowing the amplifier to operate effectively without distortion.
As the signal progresses through each stage, the collector potential incrementally rises. However, this increase in potential can lead to a reduction in the overall output voltage range, which may limit the circuit's performance in certain applications. To mitigate this effect, the implementation of PNP transistors in conjunction with NPN transistors is a common practice. The PNP transistor (VT2) can effectively lower the DC potential of the subsequent stage (VT3), allowing for a more manageable output voltage range.
In addition to using complementary transistor configurations, the circuit can also incorporate an emitter follower stage. This configuration serves as a buffer that provides voltage gain while simultaneously reducing the DC potential seen by the following stages. The emitter follower is characterized by its high input impedance and low output impedance, making it an ideal choice for interfacing between stages of an amplifier.
In summary, the multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier circuit leverages the properties of both NPN and PNP transistors to achieve a robust amplification solution, while the inclusion of emitter follower stages enhances the circuit's overall performance by managing DC levels effectively.DC-coupled multi-stage amplifier circuit a (3) multi-stage DC-coupled amplifier in DC-coupled by a multi-stage amplifier circuit amplifying circuit, if used NPN type transistor of each stage, in order to fit all levels have appropriate operating point of stage base, Step by step the collector potential increases, so reducing the final output voltage range. In order to solve this problem, in practice, it can be used in conjunction with NPN and PNP transistor to reduce the post-stage DC potential, as shown in FIG.
Figure (8) shows an NPN cvri) and PNP transistor (VT2) wish, is used to reduce the subsequent stage (VT3) potential. Alternatively, you can use emitter follower, stage amplified voltage diode to reduce a DC potential of the circuit.
Figure l-43 (b) shows the use of emitter cvn) is used to reduce the subsequent stage (, rr3) potential.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713