DC-DC regulating converter
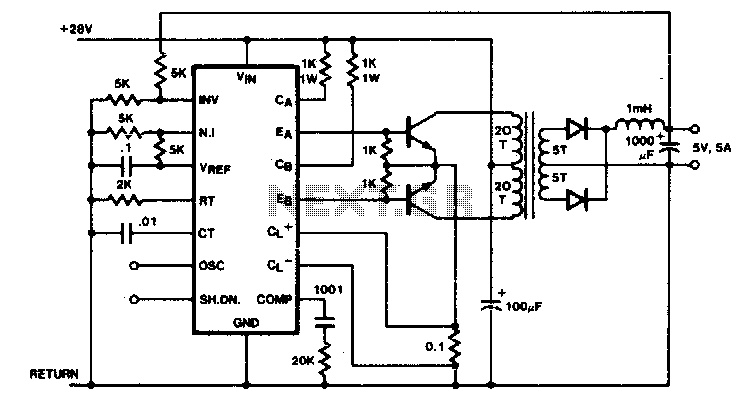
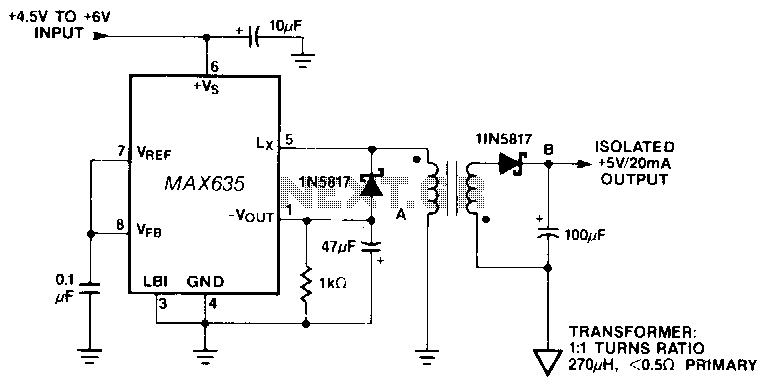
Push-pull outputs are utilized in this transformer-coupled DC-DC regulating converter. It is important to note that the oscillator must be configured to operate at twice the desired output frequency, as the SGI 524's internal flip-flop divides the frequency by two when switching the PWM signal between outputs. Current limiting is implemented in the primary circuit to reduce the pulse width in the event of transformer saturation.
In this transformer-coupled DC-DC regulating converter, the push-pull topology is employed to effectively manage power conversion and regulation. The configuration utilizes two transistors that alternately switch on and off, allowing for efficient energy transfer from the primary winding of the transformer to the secondary winding. The SGI 524 integrated circuit plays a critical role in this design by generating the necessary PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control signals. The oscillator frequency must be set to twice the target output frequency to compensate for the internal frequency division performed by the flip-flop within the SGI 524. This ensures that the output frequency remains stable and adheres to the design specifications.
Additionally, the current limiting feature is crucial for protecting the circuit from potential damage due to transformer saturation. In the primary side of the converter, a current sensing mechanism monitors the flow of current through the transformer. When the current exceeds a predefined threshold, the pulse width of the PWM signal is automatically reduced. This action limits the energy delivered to the transformer, preventing saturation and ensuring that the system operates within safe parameters. The combination of push-pull outputs, precise frequency control, and current limiting mechanisms contributes to the overall reliability and efficiency of the DC-DC converter circuit.Push-pull outputs are used in this transformer-coupled dc-dc regulating converter. Note that the oscillator must be set at twice the desired output frequency as the SGI 524"s internal flip-flop divides the frequency by 2 as it switches the PWM signal from one output to the other Current limiting is done here in the primary so that the pulse width will be reduced should transformer saturation occur. 🔗 External reference
In this transformer-coupled DC-DC regulating converter, the push-pull topology is employed to effectively manage power conversion and regulation. The configuration utilizes two transistors that alternately switch on and off, allowing for efficient energy transfer from the primary winding of the transformer to the secondary winding. The SGI 524 integrated circuit plays a critical role in this design by generating the necessary PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control signals. The oscillator frequency must be set to twice the target output frequency to compensate for the internal frequency division performed by the flip-flop within the SGI 524. This ensures that the output frequency remains stable and adheres to the design specifications.
Additionally, the current limiting feature is crucial for protecting the circuit from potential damage due to transformer saturation. In the primary side of the converter, a current sensing mechanism monitors the flow of current through the transformer. When the current exceeds a predefined threshold, the pulse width of the PWM signal is automatically reduced. This action limits the energy delivered to the transformer, preventing saturation and ensuring that the system operates within safe parameters. The combination of push-pull outputs, precise frequency control, and current limiting mechanisms contributes to the overall reliability and efficiency of the DC-DC converter circuit.Push-pull outputs are used in this transformer-coupled dc-dc regulating converter. Note that the oscillator must be set at twice the desired output frequency as the SGI 524"s internal flip-flop divides the frequency by 2 as it switches the PWM signal from one output to the other Current limiting is done here in the primary so that the pulse width will be reduced should transformer saturation occur. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713