TPS54618 6-A Step-Down SWIFT DC/DC Converter
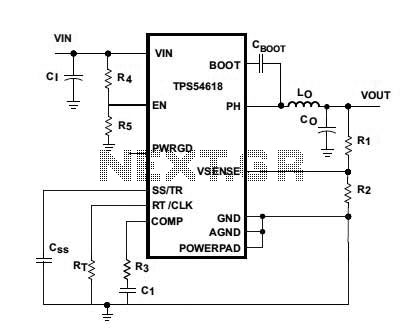
Texas Instruments introduced the TPS54618, a 6-A step-down SWIFT DC/DC converter. The new TPS54618 is a monolithic synchronous switcher featuring two integrated 12-milliohm MOSFETs.
The TPS54618 is designed to provide high efficiency and compact solutions for powering a variety of applications, including point-of-load converters in distributed power architectures. It operates with a wide input voltage range, typically from 4.5 V to 17 V, making it suitable for various power supply designs. The device is capable of delivering up to 6 A of continuous output current while maintaining a low output voltage ripple.
This converter utilizes a synchronous rectification technique, which enhances efficiency by minimizing conduction losses. The integrated MOSFETs, with their low on-resistance of 12 milliohms, contribute to improved thermal performance and reduced power dissipation. The TPS54618 also features a current mode control architecture, allowing for fast transient response and stable operation across varying load conditions.
To ensure robust operation, the TPS54618 incorporates several protection features, including over-current protection, thermal shutdown, and under-voltage lockout. These features safeguard the device and the connected load from adverse operating conditions, enhancing reliability in end applications.
The device supports various output voltage configurations through an external resistor divider, enabling designers to tailor the output voltage to specific requirements. Additionally, the TPS54618 can be easily synchronized with external clock signals, facilitating the design of multi-phase systems for higher output power needs.
Overall, the TPS54618 is a versatile solution for efficient DC/DC conversion, offering a combination of high performance, reliability, and ease of use for modern electronic designs.Texas Instruments introduced TPS54618, 6-A step-down SWIFT DC/DC converter. The new TPS54618 monolithic synchronous switcher with two integrated 12-milliohm.. 🔗 External reference
The TPS54618 is designed to provide high efficiency and compact solutions for powering a variety of applications, including point-of-load converters in distributed power architectures. It operates with a wide input voltage range, typically from 4.5 V to 17 V, making it suitable for various power supply designs. The device is capable of delivering up to 6 A of continuous output current while maintaining a low output voltage ripple.
This converter utilizes a synchronous rectification technique, which enhances efficiency by minimizing conduction losses. The integrated MOSFETs, with their low on-resistance of 12 milliohms, contribute to improved thermal performance and reduced power dissipation. The TPS54618 also features a current mode control architecture, allowing for fast transient response and stable operation across varying load conditions.
To ensure robust operation, the TPS54618 incorporates several protection features, including over-current protection, thermal shutdown, and under-voltage lockout. These features safeguard the device and the connected load from adverse operating conditions, enhancing reliability in end applications.
The device supports various output voltage configurations through an external resistor divider, enabling designers to tailor the output voltage to specific requirements. Additionally, the TPS54618 can be easily synchronized with external clock signals, facilitating the design of multi-phase systems for higher output power needs.
Overall, the TPS54618 is a versatile solution for efficient DC/DC conversion, offering a combination of high performance, reliability, and ease of use for modern electronic designs.Texas Instruments introduced TPS54618, 6-A step-down SWIFT DC/DC converter. The new TPS54618 monolithic synchronous switcher with two integrated 12-milliohm.. 🔗 External reference