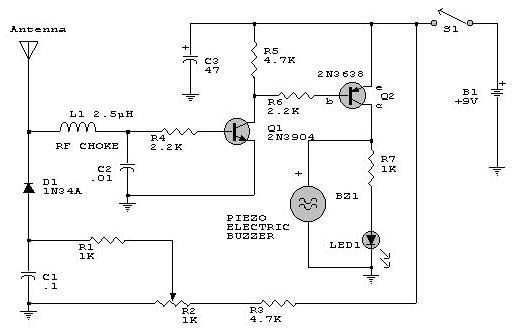
DC relay circuit to accelerate the release
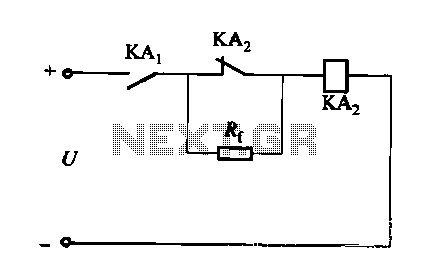
A DC relay or contactor is utilized to enhance the excitation pull-in and release mechanisms in a circuit. The relay circuit, as depicted in Figure 6-28, facilitates improved return line efficiency. When the control relay KAi is activated, its normally closed contact is initially engaged. This energizes the KAz coil, preventing a return path through the coil. Consequently, when KAi is deactivated, KAz aids in accelerating the release process. The additional value can be adjusted to modify the wind resistance of the relay return coefficient, Rf, which should not exceed 1 to 2 times the relay coil resistance, RL.
The described circuit employs a DC relay or contactor to optimize the operation of the relay system. The relay, designated as KAi, serves as the primary control element, engaging its normally closed contact at the moment of activation. This engagement allows for the energization of a secondary relay, KAz, which plays a crucial role in the release phase of the circuit operation.
Upon activation of KAi, the circuit configuration ensures that the KAz coil is energized without creating a return path through KAi. This design prevents any undesirable feedback that could hinder performance. The acceleration of the release process is achieved through the interaction between KAi and KAz, where KAz is specifically designed to assist in quickly disengaging the load once KAi is turned off.
The adjustment of the return coefficient, Rf, is critical to the overall performance of the relay circuit. By fine-tuning Rf, the wind resistance of the relay can be optimized, enhancing the speed and efficiency of the release mechanism. It is important to maintain Rf within a specified range, ideally between 1 to 2 times the resistance of the relay coil, RL, to ensure reliable operation without overloading the circuit.
This configuration not only improves the efficiency of the relay operation but also minimizes wear and tear on the mechanical components by providing a more controlled release action. The resulting system is more responsive and reliable, suitable for applications where quick actuation and release are essential.DC relay or contactor in addition to using strong excitation pull way accelerate, accelerate the release, but also the following circuit to achieve the purpose of accelerating the release. Circuit shown in Figure 6-28. The relay circuit can improve the return line number. When the control relay KAi (not shown) pulls in, the result of K normally closed contact initially closed. KAz coil is energized, people avoid string coil back road, so when KAi release, KAz will accelerate the release.
Additional value can be adjusted to change the wind resistance of the relay returns coefficient, Rf but not too large, about 1 to 2 times the relay coil resistance RL.
The described circuit employs a DC relay or contactor to optimize the operation of the relay system. The relay, designated as KAi, serves as the primary control element, engaging its normally closed contact at the moment of activation. This engagement allows for the energization of a secondary relay, KAz, which plays a crucial role in the release phase of the circuit operation.
Upon activation of KAi, the circuit configuration ensures that the KAz coil is energized without creating a return path through KAi. This design prevents any undesirable feedback that could hinder performance. The acceleration of the release process is achieved through the interaction between KAi and KAz, where KAz is specifically designed to assist in quickly disengaging the load once KAi is turned off.
The adjustment of the return coefficient, Rf, is critical to the overall performance of the relay circuit. By fine-tuning Rf, the wind resistance of the relay can be optimized, enhancing the speed and efficiency of the release mechanism. It is important to maintain Rf within a specified range, ideally between 1 to 2 times the resistance of the relay coil, RL, to ensure reliable operation without overloading the circuit.
This configuration not only improves the efficiency of the relay operation but also minimizes wear and tear on the mechanical components by providing a more controlled release action. The resulting system is more responsive and reliable, suitable for applications where quick actuation and release are essential.DC relay or contactor in addition to using strong excitation pull way accelerate, accelerate the release, but also the following circuit to achieve the purpose of accelerating the release. Circuit shown in Figure 6-28. The relay circuit can improve the return line number. When the control relay KAi (not shown) pulls in, the result of K normally closed contact initially closed. KAz coil is energized, people avoid string coil back road, so when KAi release, KAz will accelerate the release.
Additional value can be adjusted to change the wind resistance of the relay returns coefficient, Rf but not too large, about 1 to 2 times the relay coil resistance RL.