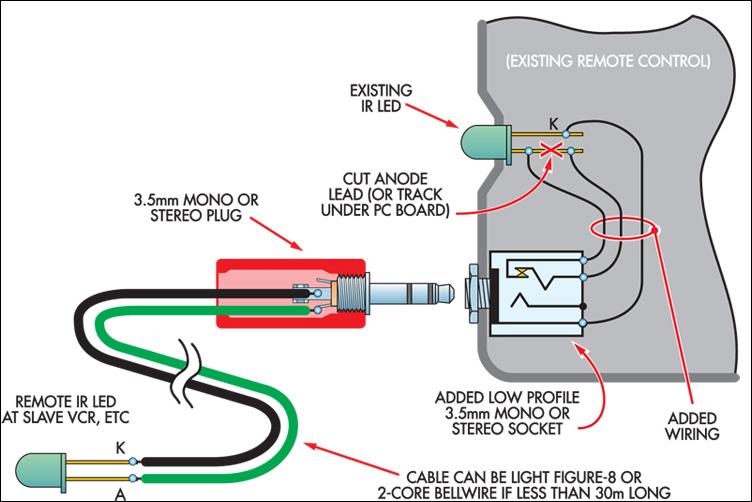
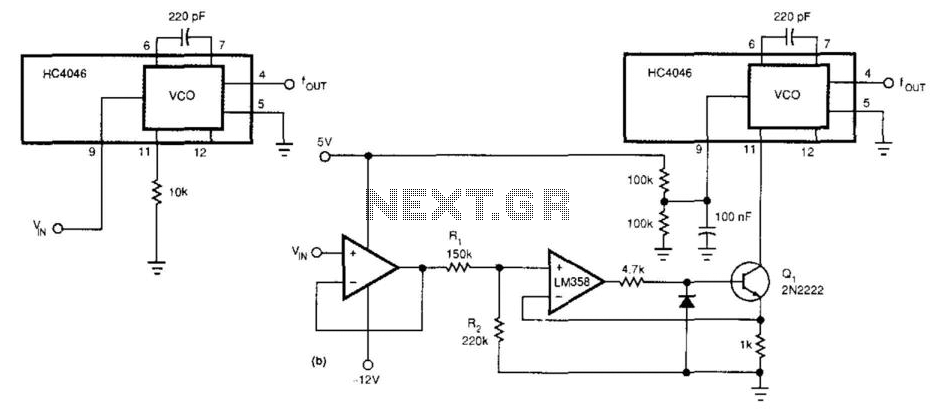
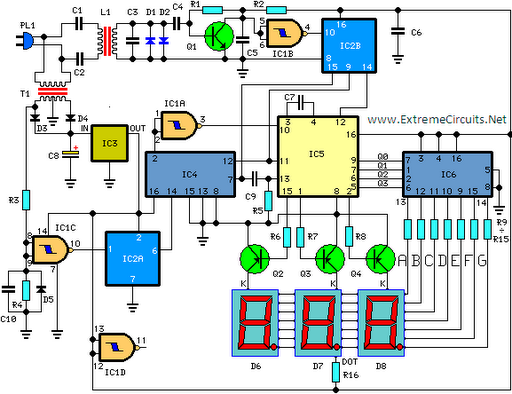
device Cheapest way to build or buy a remote controlled sound maker
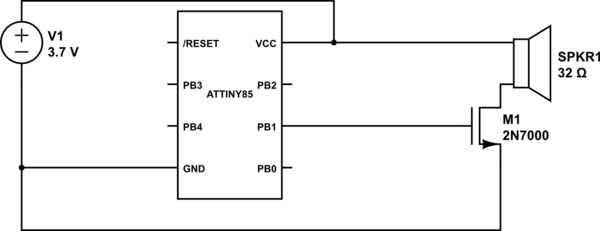
A more affordable method to create or purchase a device that offers similar functionality. It does not necessarily need to be remote-controlled if it can be programmed to activate at specific times.
This description suggests the development of a cost-effective electronic device that can perform tasks typically associated with more expensive alternatives. The device's functionality may include automation features, allowing it to operate independently based on pre-set schedules rather than requiring remote control.
For example, consider a programmable timer circuit that can control various appliances or systems. The circuit could incorporate a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or a PIC, which would allow users to input specific time settings for activation. The microcontroller can drive a relay module to handle higher voltage appliances, making it suitable for a range of applications, from turning lights on and off to controlling small motors.
The schematic for such a device would include the following components:
1. **Microcontroller**: The central unit that executes programmed instructions. It should be selected based on the required input/output pins and processing power.
2. **Real-Time Clock (RTC)**: This component keeps track of the current time, allowing the microcontroller to trigger actions at the specified times. Modules like the DS3231 can provide high accuracy.
3. **Relay Module**: Used to switch high voltage loads. The relay can be controlled by the microcontroller, allowing it to turn devices on or off based on the programmed schedule.
4. **Power Supply**: Ensures that the microcontroller and other components receive the necessary voltage and current. A regulated power supply would be essential for consistent operation.
5. **User Interface**: This could be a simple keypad and LCD display that allows users to set the time and configure other settings easily.
6. **Protection Components**: Diodes for flyback protection across the relay coils, fuses for overcurrent protection, and capacitors for voltage smoothing.
The overall design should prioritize safety, especially when dealing with high voltage circuits, and ensure that the user interface is intuitive for ease of programming. This approach not only reduces costs but also provides flexibility in functionality, catering to various user needs without the complexities associated with remote-controlled devices.A cheaper way to build or buy something with similar functionality It doesn`t necessarily even need to be remote controlled if it could be programmed to go off at certain times. 🔗 External reference
This description suggests the development of a cost-effective electronic device that can perform tasks typically associated with more expensive alternatives. The device's functionality may include automation features, allowing it to operate independently based on pre-set schedules rather than requiring remote control.
For example, consider a programmable timer circuit that can control various appliances or systems. The circuit could incorporate a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or a PIC, which would allow users to input specific time settings for activation. The microcontroller can drive a relay module to handle higher voltage appliances, making it suitable for a range of applications, from turning lights on and off to controlling small motors.
The schematic for such a device would include the following components:
1. **Microcontroller**: The central unit that executes programmed instructions. It should be selected based on the required input/output pins and processing power.
2. **Real-Time Clock (RTC)**: This component keeps track of the current time, allowing the microcontroller to trigger actions at the specified times. Modules like the DS3231 can provide high accuracy.
3. **Relay Module**: Used to switch high voltage loads. The relay can be controlled by the microcontroller, allowing it to turn devices on or off based on the programmed schedule.
4. **Power Supply**: Ensures that the microcontroller and other components receive the necessary voltage and current. A regulated power supply would be essential for consistent operation.
5. **User Interface**: This could be a simple keypad and LCD display that allows users to set the time and configure other settings easily.
6. **Protection Components**: Diodes for flyback protection across the relay coils, fuses for overcurrent protection, and capacitors for voltage smoothing.
The overall design should prioritize safety, especially when dealing with high voltage circuits, and ensure that the user interface is intuitive for ease of programming. This approach not only reduces costs but also provides flexibility in functionality, catering to various user needs without the complexities associated with remote-controlled devices.A cheaper way to build or buy something with similar functionality It doesn`t necessarily even need to be remote controlled if it could be programmed to go off at certain times. 🔗 External reference