DIAC Basic Operation
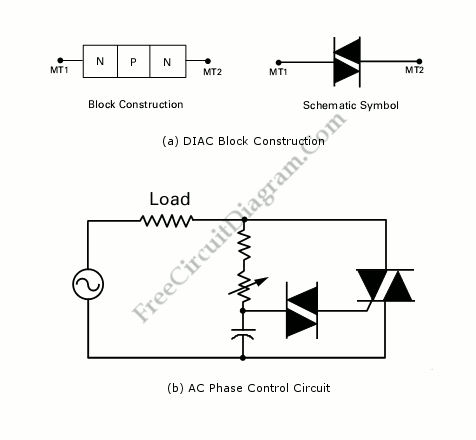
A diode for alternating current is a trigger diode that conducts current only after the DIAC reaches the breakdown voltage. The breakdown voltage of the DIAC is 30 V.
A DIAC, or Diode for Alternating Current, is a semiconductor device that operates in a unique manner compared to standard diodes. It is designed to remain in a non-conductive state until a specific breakdown voltage is applied across its terminals, at which point it becomes conductive. This characteristic makes it particularly useful in applications requiring control of AC signals.
In this case, the DIAC has a breakdown voltage of 30 V. When the voltage across the DIAC reaches this threshold, the device transitions from a non-conductive to a conductive state, allowing current to flow. This behavior is essential in various applications, including phase control in light dimmers, motor speed controls, and over-voltage protection circuits.
The operation of a DIAC can be visualized in an electronic schematic as follows: the DIAC is typically placed in series with a load and a triggering circuit. The triggering circuit may consist of a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that charges until the voltage reaches the breakdown level of the DIAC. Once triggered, the DIAC will conduct until the current through it drops below a certain level, at which point it will turn off, returning to its non-conductive state.
The use of a DIAC in a circuit allows for precise control of AC signals and is a key component in creating efficient and reliable electronic systems. It is important to consider the power ratings and thermal characteristics of the DIAC to ensure proper operation within the intended application.Diode for alternating current is a trigger diode which conducts current only after the DIAC reach the breakdown voltage. The breakdown voltage of DIAC is 30 V 🔗 External reference
A DIAC, or Diode for Alternating Current, is a semiconductor device that operates in a unique manner compared to standard diodes. It is designed to remain in a non-conductive state until a specific breakdown voltage is applied across its terminals, at which point it becomes conductive. This characteristic makes it particularly useful in applications requiring control of AC signals.
In this case, the DIAC has a breakdown voltage of 30 V. When the voltage across the DIAC reaches this threshold, the device transitions from a non-conductive to a conductive state, allowing current to flow. This behavior is essential in various applications, including phase control in light dimmers, motor speed controls, and over-voltage protection circuits.
The operation of a DIAC can be visualized in an electronic schematic as follows: the DIAC is typically placed in series with a load and a triggering circuit. The triggering circuit may consist of a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that charges until the voltage reaches the breakdown level of the DIAC. Once triggered, the DIAC will conduct until the current through it drops below a certain level, at which point it will turn off, returning to its non-conductive state.
The use of a DIAC in a circuit allows for precise control of AC signals and is a key component in creating efficient and reliable electronic systems. It is important to consider the power ratings and thermal characteristics of the DIAC to ensure proper operation within the intended application.Diode for alternating current is a trigger diode which conducts current only after the DIAC reach the breakdown voltage. The breakdown voltage of DIAC is 30 V 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713