Digital Compass for PC
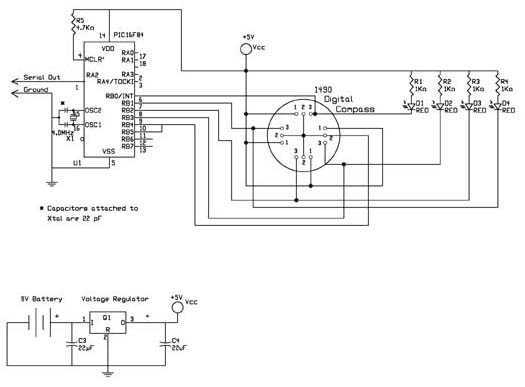
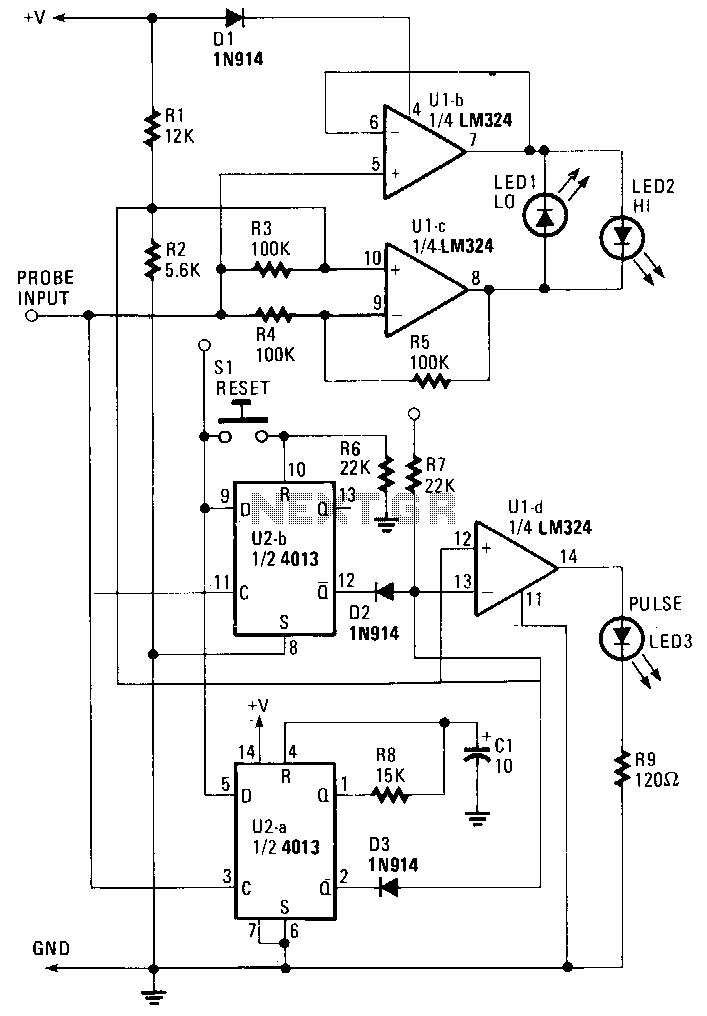
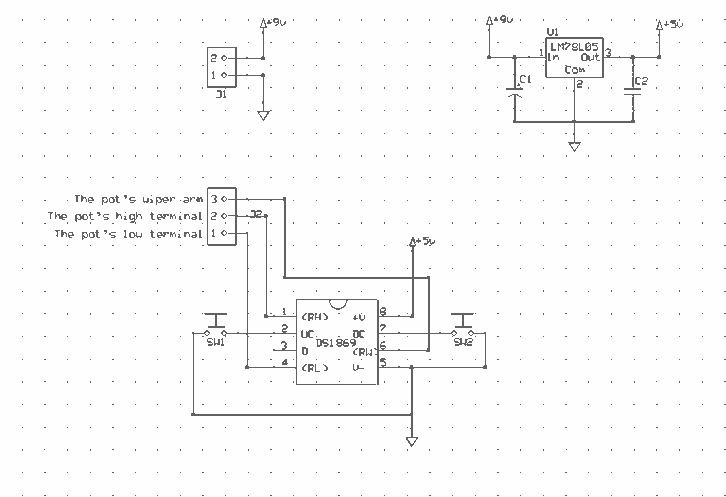
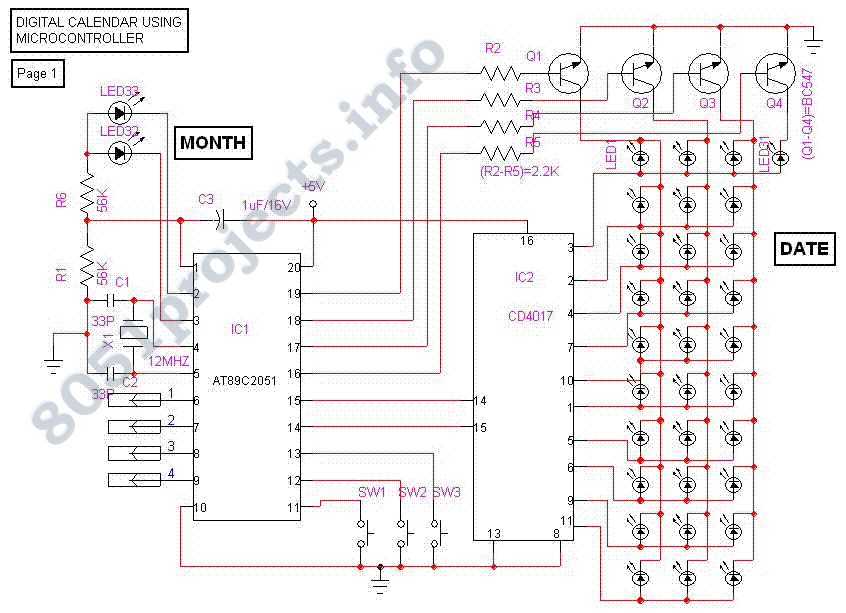
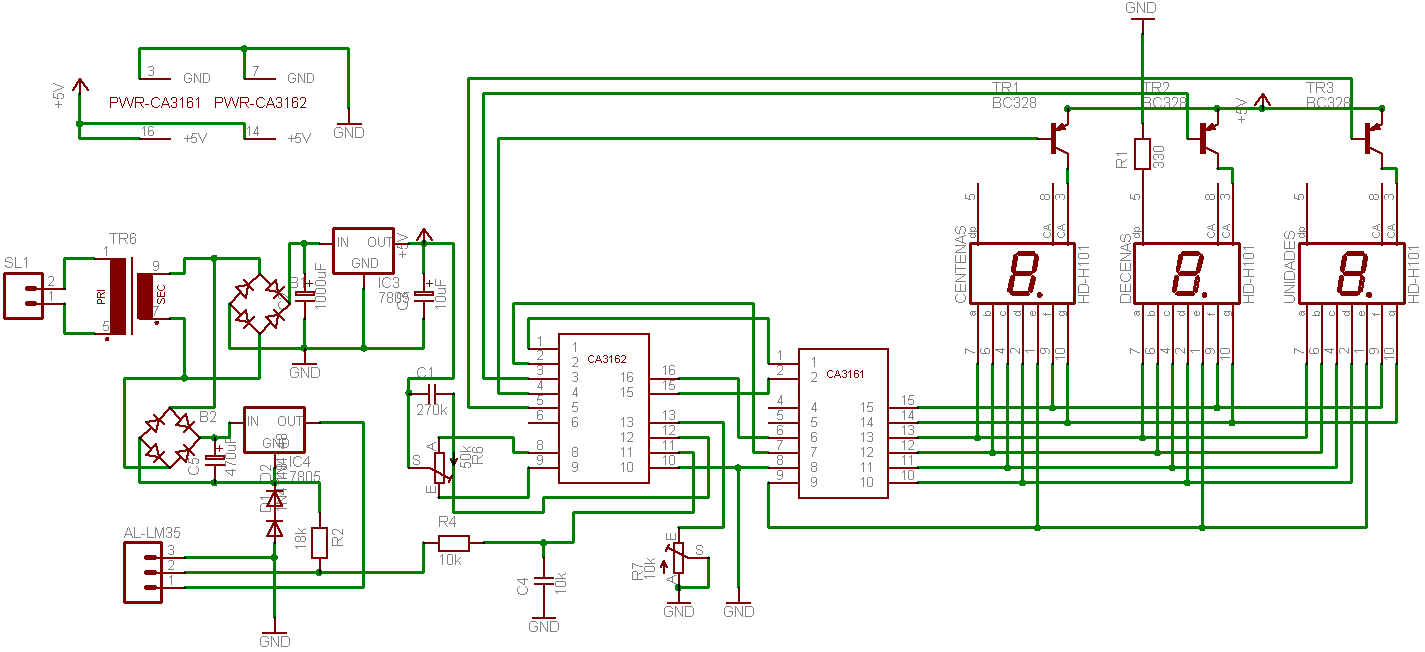
The digital navigation PC board may be configured for a number of navigation functions. It may be made into a simple visual digital compass, or a microcontroller based compass. The microcontroller based compass can be used for mobile robotics or a PC based compass. The sensor used on the PC Board is the 1490 digital compass manufactured by Robson Company. This sensor is a solid-state Hall effect device. It is sensitive enough to detect the Earth's weak magnetic field. When rotated it can display the position of the four cardinal points on a compass: North (N), South (S), East (E), and West (W), as well as the intermediate directions: North East (NE), North West (NW), South East (SE), and South West (SW). The sensor is dampened to approximate the speed of a liquid filled compass. The dampening prevents over swinging the direction. In addition, the built-in hysteresis prevents flutter when near a switching direction. The 1490 device is sensitive to tilt, and any tilt greater than 12 degrees will create directional errors. The bottom of the device has 12 leads arranged in four groups of three leads. Looking at the device from the top, each group of leads are labeled 1, 2, and 3. The leads labeled 1 are connected to Vcc (+5V). Leads numbered 2 are connected to ground. The leads labeled 3 are the output leads. The output leads of the device are equivalent to an open collector of an NPN transistor. Each output is capable of sinking 20 mA continuously or up to 25 mA intermittently.
The digital navigation PC board serves as a versatile platform for various navigation applications, primarily utilizing the 1490 digital compass sensor from Robson Company. This solid-state Hall effect sensor is adept at detecting the Earth's magnetic field, making it suitable for both simple visual compasses and more complex microcontroller-based systems.
In operation, the sensor can accurately indicate the four cardinal directions (N, S, E, W) and the intermediate directions (NE, NW, SE, SW) when the board is rotated. This capability is enhanced by a dampening mechanism that mimics the response of a traditional liquid-filled compass, reducing overshooting and providing stable readings. The built-in hysteresis feature further stabilizes output by preventing fluctuations when the sensor is near a directional threshold.
The 1490 sensor's design includes a sensitivity to tilt, which is a critical consideration in applications where the device may not be perfectly level. Any tilt exceeding 12 degrees can introduce significant directional inaccuracies, thus the installation and orientation of the board must be carefully managed.
The sensor's lead configuration consists of 12 pins organized into four groups of three. The first group of leads (labeled 1) is connected to a power supply of +5V (Vcc), while the second group (labeled 2) is grounded. The third group (labeled 3) serves as the output leads, functioning similarly to an open collector output of an NPN transistor. Each output can handle a continuous current of 20 mA, with a maximum intermittent current of 25 mA, allowing for reliable interfacing with microcontrollers or other processing units.
This configuration makes the digital navigation PC board an effective tool for mobile robotics, PC-based compass applications, and other navigation functions, providing both flexibility and precision in directional sensing.The digital navigation PC board may be configured for a number of navigation functions, see figure 1. It may be made into a simple visual digital compass, or a microcontroller based compass. The microcontroller based compass can be used for mobile robotics or a PC based compass. The sensor used on the PC Board is the 1490 digital compass manufactured by Robson Company, see figure 2.
This sensor is a solid-state Hall effect device. It is sensitive enough to detect the Earth's weak magnetic field. When rotated it can display the position of the four cardinal points on a compass, North (N), South (S), East (E) and West (W). As well as the intermediate directions: North East (NE), North West (NW), South East (SE), and South West (SW), see figure 3.
The sensor is dampened to approximate the speed of a liquid filled compass. The dampening prevents over swinging the direction. In addition the built in hysteresis prevents flutter when near a switching direction. The 1490 device is sensitive to tilt. Any tilt greater than 12 degrees will create directional errors. The bottom of the device has 12 leads arranged in four groups of three leads. Looking at the device from the top each group of leads are labeled 1, 2 and 3. The leads labeled 1 are connected to Vcc (+5V). Leads numbered 2 are connected to ground. And the leads labeled 3 are our output leads. The output leads of the device are equivalent to an open collector of an NPN transistor, see figure 4. Each output is capable of sinking 20 mA continuously or up to 25 mA intermittently. 🔗 External reference
The digital navigation PC board serves as a versatile platform for various navigation applications, primarily utilizing the 1490 digital compass sensor from Robson Company. This solid-state Hall effect sensor is adept at detecting the Earth's magnetic field, making it suitable for both simple visual compasses and more complex microcontroller-based systems.
In operation, the sensor can accurately indicate the four cardinal directions (N, S, E, W) and the intermediate directions (NE, NW, SE, SW) when the board is rotated. This capability is enhanced by a dampening mechanism that mimics the response of a traditional liquid-filled compass, reducing overshooting and providing stable readings. The built-in hysteresis feature further stabilizes output by preventing fluctuations when the sensor is near a directional threshold.
The 1490 sensor's design includes a sensitivity to tilt, which is a critical consideration in applications where the device may not be perfectly level. Any tilt exceeding 12 degrees can introduce significant directional inaccuracies, thus the installation and orientation of the board must be carefully managed.
The sensor's lead configuration consists of 12 pins organized into four groups of three. The first group of leads (labeled 1) is connected to a power supply of +5V (Vcc), while the second group (labeled 2) is grounded. The third group (labeled 3) serves as the output leads, functioning similarly to an open collector output of an NPN transistor. Each output can handle a continuous current of 20 mA, with a maximum intermittent current of 25 mA, allowing for reliable interfacing with microcontrollers or other processing units.
This configuration makes the digital navigation PC board an effective tool for mobile robotics, PC-based compass applications, and other navigation functions, providing both flexibility and precision in directional sensing.The digital navigation PC board may be configured for a number of navigation functions, see figure 1. It may be made into a simple visual digital compass, or a microcontroller based compass. The microcontroller based compass can be used for mobile robotics or a PC based compass. The sensor used on the PC Board is the 1490 digital compass manufactured by Robson Company, see figure 2.
This sensor is a solid-state Hall effect device. It is sensitive enough to detect the Earth's weak magnetic field. When rotated it can display the position of the four cardinal points on a compass, North (N), South (S), East (E) and West (W). As well as the intermediate directions: North East (NE), North West (NW), South East (SE), and South West (SW), see figure 3.
The sensor is dampened to approximate the speed of a liquid filled compass. The dampening prevents over swinging the direction. In addition the built in hysteresis prevents flutter when near a switching direction. The 1490 device is sensitive to tilt. Any tilt greater than 12 degrees will create directional errors. The bottom of the device has 12 leads arranged in four groups of three leads. Looking at the device from the top each group of leads are labeled 1, 2 and 3. The leads labeled 1 are connected to Vcc (+5V). Leads numbered 2 are connected to ground. And the leads labeled 3 are our output leads. The output leads of the device are equivalent to an open collector of an NPN transistor, see figure 4. Each output is capable of sinking 20 mA continuously or up to 25 mA intermittently. 🔗 External reference