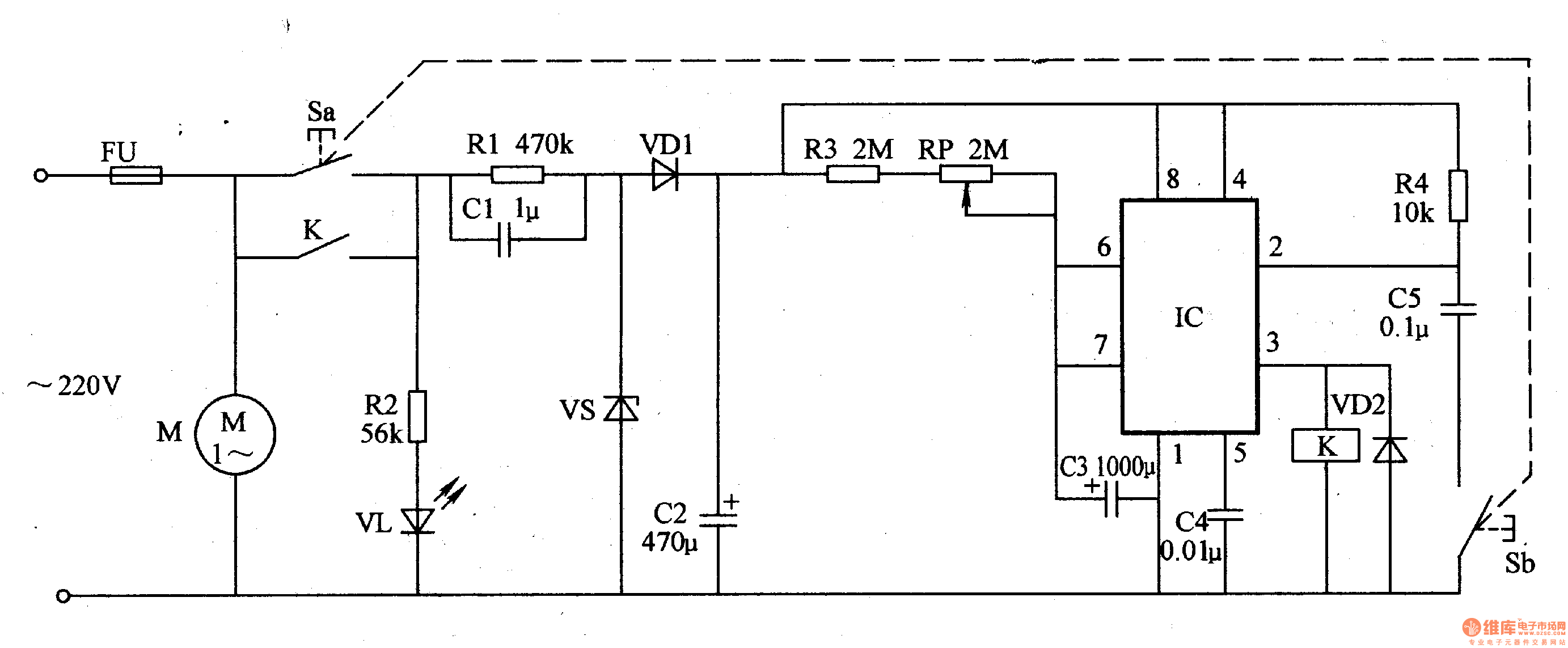
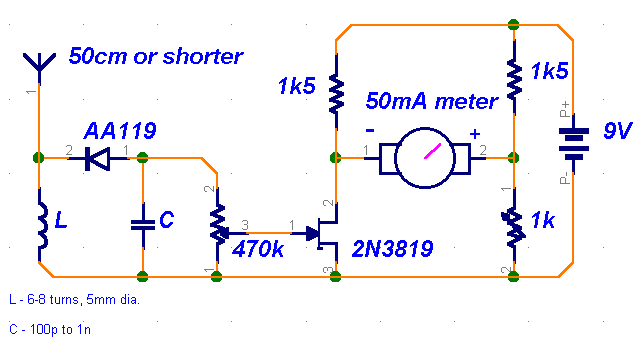
Digital Vom Phase Meter
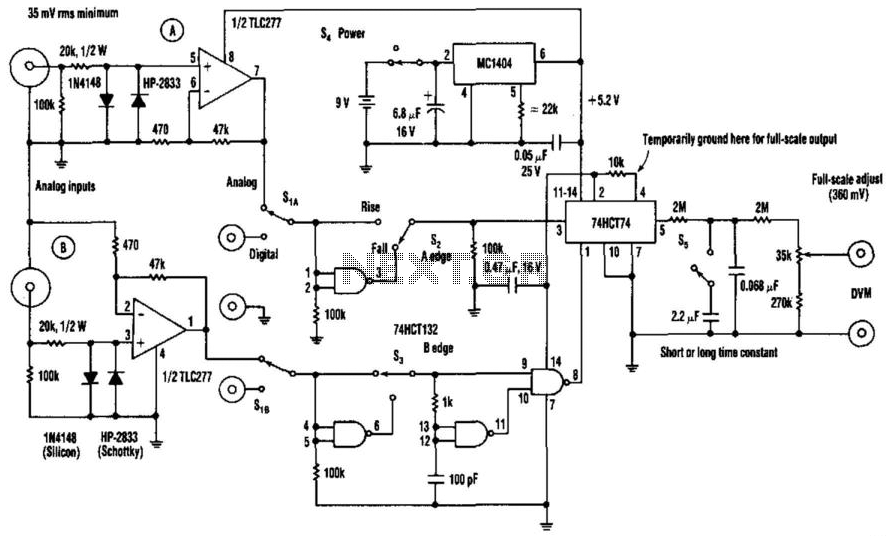
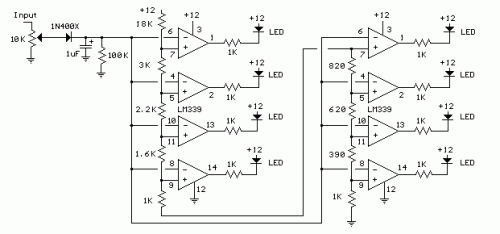
The phase-angle meter operates with both analog and digital inputs. A digital voltmeter (DVM) serves as the readout device. The output is 1 mV per degree, with a full-scale output of 360 mV corresponding to 360 degrees. The MC1404 precision regulator ensures calibration is maintained with a 9 V battery source.
The phase-angle meter is designed to measure the phase difference between two signals, which is essential in various applications such as power systems, audio electronics, and signal processing. The device accepts both analog and digital inputs, allowing for versatile integration into different systems.
The output of the phase-angle meter is configured to provide a linear response, where an output of 1 mV corresponds to a phase shift of 1 degree. Thus, the full-scale output is 360 mV, indicating a complete phase shift of 360 degrees. This linearity is crucial for accurate phase measurement and subsequent analysis.
To ensure the precision and reliability of the measurements, the MC1404 precision voltage regulator is employed. This component stabilizes the voltage supplied by a 9 V battery, which is vital for maintaining the calibration of the phase-angle meter. The use of a precision regulator helps minimize variations in output due to fluctuations in the supply voltage, thereby enhancing measurement accuracy.
In practical applications, the phase-angle meter can be utilized in conjunction with various signal sources, including sine waves and square waves. The output can be monitored using the DVM, which provides a clear digital readout of the phase angle, facilitating easy interpretation of the results. This setup is particularly advantageous in laboratory settings and field measurements where precise phase information is required.
Overall, the combination of analog and digital input compatibility, a linear output characteristic, and the use of a precision voltage regulator makes this phase-angle meter a reliable tool for engineers and technicians working with phase measurements in electronic circuits. The phase-angle meter will work with either analog or digital inputs. A DVM is used as a readout device. The output is 1 mV per degree (360 mV or degrees full-scale). The MC1404 precision regulator maintains calibration with a battery source (9 V). 🔗 External reference
The phase-angle meter is designed to measure the phase difference between two signals, which is essential in various applications such as power systems, audio electronics, and signal processing. The device accepts both analog and digital inputs, allowing for versatile integration into different systems.
The output of the phase-angle meter is configured to provide a linear response, where an output of 1 mV corresponds to a phase shift of 1 degree. Thus, the full-scale output is 360 mV, indicating a complete phase shift of 360 degrees. This linearity is crucial for accurate phase measurement and subsequent analysis.
To ensure the precision and reliability of the measurements, the MC1404 precision voltage regulator is employed. This component stabilizes the voltage supplied by a 9 V battery, which is vital for maintaining the calibration of the phase-angle meter. The use of a precision regulator helps minimize variations in output due to fluctuations in the supply voltage, thereby enhancing measurement accuracy.
In practical applications, the phase-angle meter can be utilized in conjunction with various signal sources, including sine waves and square waves. The output can be monitored using the DVM, which provides a clear digital readout of the phase angle, facilitating easy interpretation of the results. This setup is particularly advantageous in laboratory settings and field measurements where precise phase information is required.
Overall, the combination of analog and digital input compatibility, a linear output characteristic, and the use of a precision voltage regulator makes this phase-angle meter a reliable tool for engineers and technicians working with phase measurements in electronic circuits. The phase-angle meter will work with either analog or digital inputs. A DVM is used as a readout device. The output is 1 mV per degree (360 mV or degrees full-scale). The MC1404 precision regulator maintains calibration with a battery source (9 V). 🔗 External reference