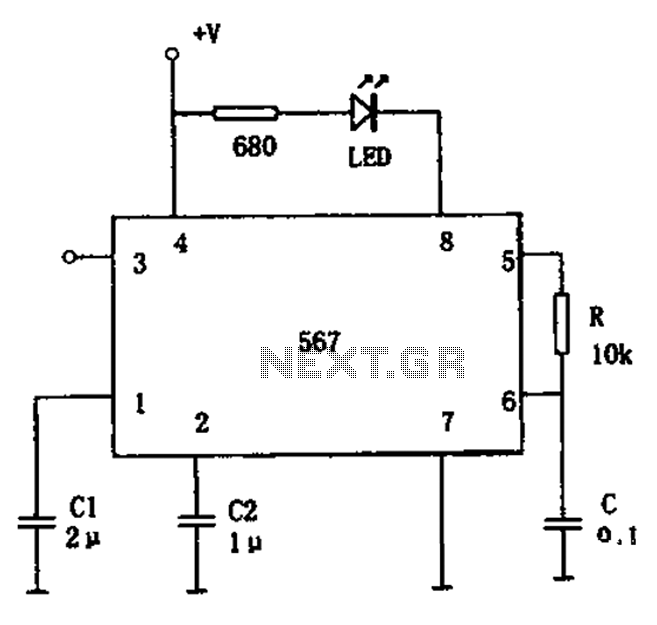
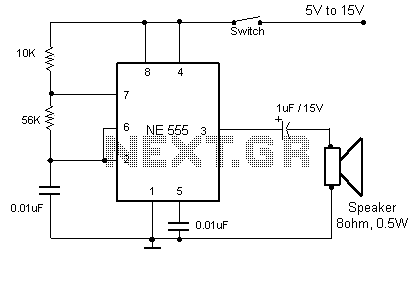
Discrete circuit elements constituting the ultrasonic transmitter
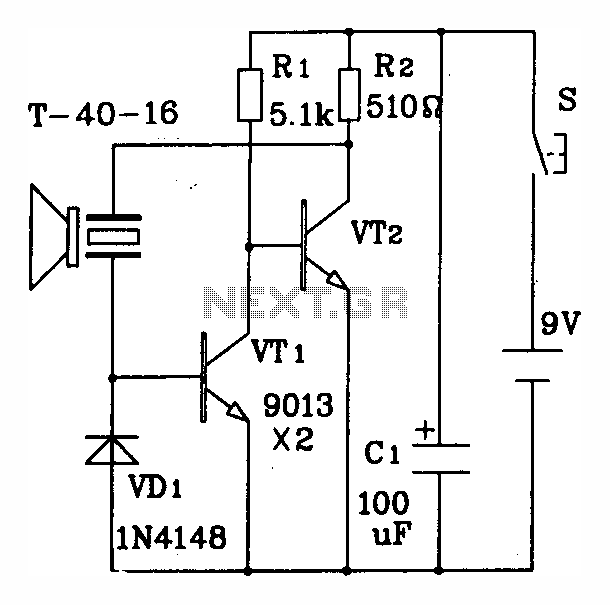
The discrete components ultrasonic transmitting circuit T/R-40-16 is capable of emitting a series of ultrasonic signals at a frequency of 40 kHz. This circuit operates at a voltage of 9V, with an operating current of 25 mA, and can control distances of up to 8 meters.
The T/R-40-16 ultrasonic transmitting circuit utilizes discrete components to generate high-frequency ultrasonic signals. The circuit is designed to operate efficiently at a supply voltage of 9 volts, drawing a current of 25 milliamperes during operation. The primary function of this circuit is to emit ultrasonic waves at a frequency of 40 kHz, which is commonly used in various applications such as distance measurement, object detection, and proximity sensing.
The circuit typically consists of a signal generator, which may include a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller, to produce the desired frequency output. The generated signal is then amplified using a suitable transistor or operational amplifier to ensure sufficient power for transmission. The output stage is connected to an ultrasonic transducer, which converts the electrical signal into ultrasonic sound waves.
The effective control distance of the circuit is up to 8 meters, making it suitable for applications where short-range ultrasonic communication or sensing is required. The design may also include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to stabilize the circuit and filter out noise, ensuring a clean output signal.
In summary, the T/R-40-16 ultrasonic transmitting circuit is a compact and efficient solution for generating ultrasonic signals, with its straightforward design allowing for easy integration into various electronic systems.Discrete components ultrasonic transmitting circuit T / R-40-16 can emit a series of ultrasonic signal of 40kHz. This circuit voltage of 9V, operating current of 25mA, control distance of up to 8m.
The T/R-40-16 ultrasonic transmitting circuit utilizes discrete components to generate high-frequency ultrasonic signals. The circuit is designed to operate efficiently at a supply voltage of 9 volts, drawing a current of 25 milliamperes during operation. The primary function of this circuit is to emit ultrasonic waves at a frequency of 40 kHz, which is commonly used in various applications such as distance measurement, object detection, and proximity sensing.
The circuit typically consists of a signal generator, which may include a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller, to produce the desired frequency output. The generated signal is then amplified using a suitable transistor or operational amplifier to ensure sufficient power for transmission. The output stage is connected to an ultrasonic transducer, which converts the electrical signal into ultrasonic sound waves.
The effective control distance of the circuit is up to 8 meters, making it suitable for applications where short-range ultrasonic communication or sensing is required. The design may also include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to stabilize the circuit and filter out noise, ensuring a clean output signal.
In summary, the T/R-40-16 ultrasonic transmitting circuit is a compact and efficient solution for generating ultrasonic signals, with its straightforward design allowing for easy integration into various electronic systems.Discrete components ultrasonic transmitting circuit T / R-40-16 can emit a series of ultrasonic signal of 40kHz. This circuit voltage of 9V, operating current of 25mA, control distance of up to 8m.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713