diy laser power gauge
For some time, a method to measure laser power has been sought without incurring significant expenses on a power meter. Initially, constructing such a device may seem unfeasible.
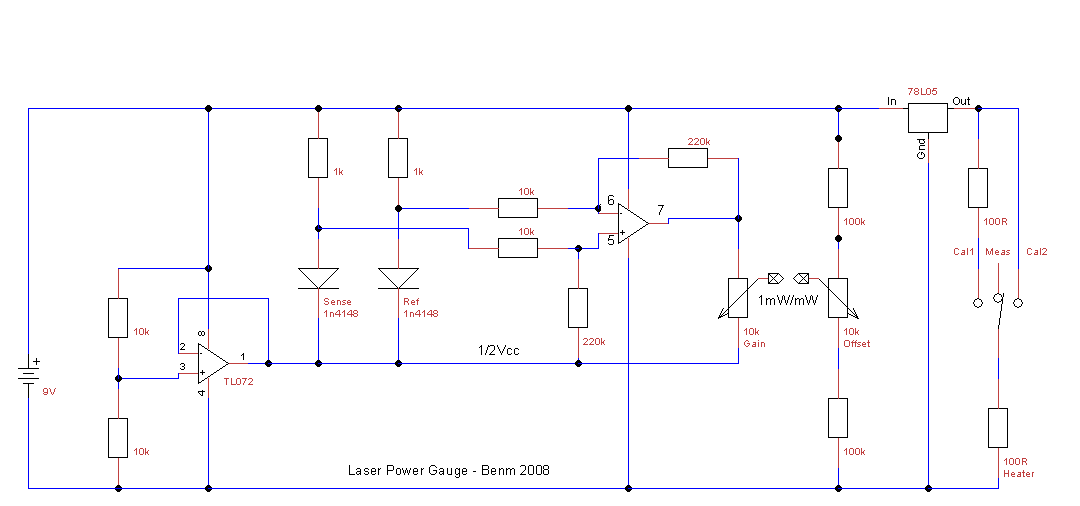
To create a cost-effective laser power measurement system, one approach involves utilizing a photodiode in conjunction with an operational amplifier (op-amp) to convert the light energy from the laser into an electrical signal. The photodiode should be selected based on its spectral sensitivity to the specific wavelength of the laser being measured.
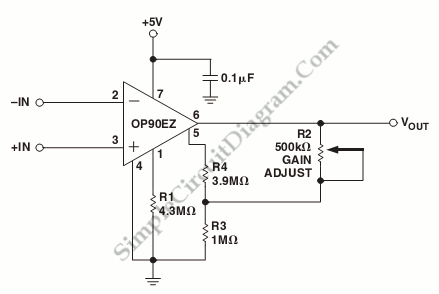
The circuit can be designed as follows: The photodiode is placed in a reverse bias configuration to enhance its response speed. When the laser beam strikes the photodiode, it generates a current proportional to the intensity of the laser light. This current is then fed into an op-amp configured as a transimpedance amplifier, which converts the current into a voltage output. The gain of the op-amp circuit can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback resistor values, allowing for calibration based on the specific laser power range.
To further enhance measurement accuracy, a low-pass filter can be implemented at the output of the op-amp to reduce noise and provide a stable voltage reading. Additionally, a microcontroller can be integrated into the circuit to digitize the output voltage and provide a user-friendly interface for displaying the measured power levels. This setup allows for real-time monitoring and can be tailored to various laser types and power levels.
In summary, this circuit design provides a practical and economical solution for measuring laser power without the need for expensive commercial power meters, utilizing readily available electronic components to achieve reliable results.For some time i wanted some way to measure laser power, without spending a fortune on a power meter. First off, it is not possible to build something.. 🔗 External reference
To create a cost-effective laser power measurement system, one approach involves utilizing a photodiode in conjunction with an operational amplifier (op-amp) to convert the light energy from the laser into an electrical signal. The photodiode should be selected based on its spectral sensitivity to the specific wavelength of the laser being measured.
The circuit can be designed as follows: The photodiode is placed in a reverse bias configuration to enhance its response speed. When the laser beam strikes the photodiode, it generates a current proportional to the intensity of the laser light. This current is then fed into an op-amp configured as a transimpedance amplifier, which converts the current into a voltage output. The gain of the op-amp circuit can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback resistor values, allowing for calibration based on the specific laser power range.
To further enhance measurement accuracy, a low-pass filter can be implemented at the output of the op-amp to reduce noise and provide a stable voltage reading. Additionally, a microcontroller can be integrated into the circuit to digitize the output voltage and provide a user-friendly interface for displaying the measured power levels. This setup allows for real-time monitoring and can be tailored to various laser types and power levels.
In summary, this circuit design provides a practical and economical solution for measuring laser power without the need for expensive commercial power meters, utilizing readily available electronic components to achieve reliable results.For some time i wanted some way to measure laser power, without spending a fortune on a power meter. First off, it is not possible to build something.. 🔗 External reference